
Vertical Gardening vs Traditional Row Planting Illustration
Vertical gardening maximizes limited space by growing plants upward, improving air circulation and reducing pest issues compared to traditional row planting. This method enhances yield per square foot and eases harvesting, especially for climbing crops like beans and cucumbers. Traditional row planting suits larger areas and root vegetables, providing straightforward soil management but often requires more ground space and labor.
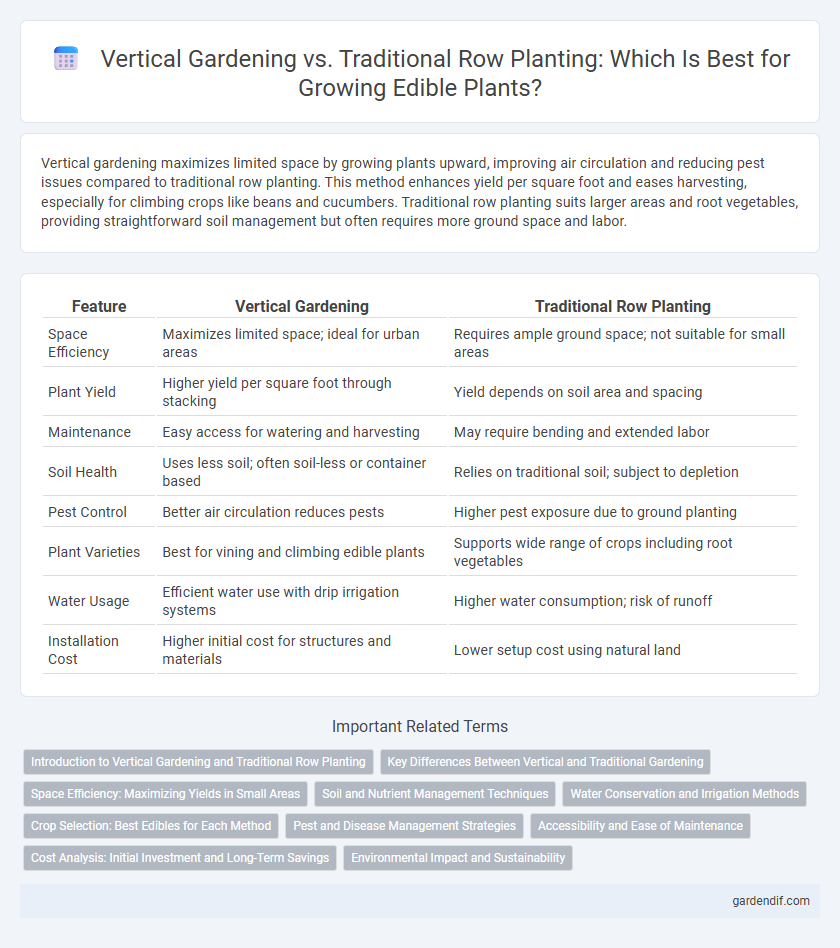
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vertical Gardening | Traditional Row Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes limited space; ideal for urban areas | Requires ample ground space; not suitable for small areas |
| Plant Yield | Higher yield per square foot through stacking | Yield depends on soil area and spacing |
| Maintenance | Easy access for watering and harvesting | May require bending and extended labor |
| Soil Health | Uses less soil; often soil-less or container based | Relies on traditional soil; subject to depletion |
| Pest Control | Better air circulation reduces pests | Higher pest exposure due to ground planting |
| Plant Varieties | Best for vining and climbing edible plants | Supports wide range of crops including root vegetables |
| Water Usage | Efficient water use with drip irrigation systems | Higher water consumption; risk of runoff |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost for structures and materials | Lower setup cost using natural land |
Introduction to Vertical Gardening and Traditional Row Planting
Vertical gardening maximizes limited space by growing plants upward using structures like trellises, towers, or stacked containers, enhancing air circulation and reducing pest issues. Traditional row planting involves sowing crops in horizontal rows spaced evenly on the ground, optimizing sunlight exposure and facilitating mechanical cultivation. Both methods influence yield potential, maintenance requirements, and suitability depending on available area and crop type.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Traditional Gardening
Vertical gardening maximizes space by growing plants upward on structures, making it ideal for small areas, while traditional row planting requires extensive horizontal ground space. Vertical gardens enhance air circulation and reduce pest issues, contrasting with traditional rows that may face soil-borne diseases and limited airflow. Crop accessibility and maintenance also differ; vertical systems offer easier harvesting and pruning at eye level compared to bending and kneeling in traditional row planting.
Space Efficiency: Maximizing Yields in Small Areas
Vertical gardening maximizes space efficiency by utilizing vertical surfaces to grow crops, allowing for higher yields in limited areas compared to traditional row planting, which requires expansive horizontal plots. This method enables urban gardeners and small-scale farmers to optimize square footage by stacking plants vertically, thereby increasing production per square foot. Innovative structures such as trellises, wall-mounted containers, and hydroponic towers enhance plant growth density, making vertical gardening ideal for maximizing yields in confined spaces.
Soil and Nutrient Management Techniques
Vertical gardening optimizes soil usage by allowing plants to grow in stacked layers, reducing soil compaction and enhancing nutrient cycling through improved aeration and drainage systems. Traditional row planting often requires extensive soil tilling and amendments to maintain fertility, leading to potential nutrient runoff and soil degradation. Both methods benefit from organic compost and targeted fertilization, but vertical gardening's soil pockets enable more precise nutrient delivery and water retention, promoting healthier plant growth with efficient resource use.
Water Conservation and Irrigation Methods
Vertical gardening significantly reduces water usage by enabling targeted drip irrigation systems that minimize evaporation and runoff, unlike traditional row planting which often relies on extensive overhead watering. The concentrated planting area in vertical gardens allows for efficient water capture and reuse, promoting sustainable irrigation practices. Traditional row planting requires larger volumes of water spread over wider soil surfaces, leading to higher water loss and decreased irrigation efficiency.
Crop Selection: Best Edibles for Each Method
Vertical gardening excels with vining crops such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and pole beans, which thrive on trellises and maximize space efficiency. Traditional row planting favors root vegetables like carrots, potatoes, and beets, benefiting from loose soil and ample room for tuber development. Leafy greens including lettuce and spinach perform well in both methods but often yield higher quality in traditional rows due to better soil aeration.
Pest and Disease Management Strategies
Vertical gardening reduces pest and disease incidence by improving air circulation and minimizing soil contact, which limits fungal growth and soil-borne pathogens compared to traditional row planting. It facilitates easier monitoring and targeted pest management through elevated plant structures, enabling early detection and localized treatment with organic or chemical controls. Traditional row planting often requires broader pesticide applications due to denser foliage and ground-level planting, increasing the risk of pathogen spread and pest infestation.
Accessibility and Ease of Maintenance
Vertical gardening significantly improves accessibility by elevating plants to eye level, reducing the need for bending and kneeling, which benefits individuals with limited mobility. Traditional row planting often requires more physical effort for planting, weeding, and harvesting due to ground-level access. Maintenance for vertical gardens is streamlined through controlled spaces that minimize weed growth and simplify watering systems, making them ideal for urban and small-space environments.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Vertical gardening requires a higher initial investment due to the need for specialized structures and vertical supports, but it optimizes space, reducing land costs and maximizing yield per square foot. Traditional row planting has lower upfront costs but often demands more land, higher water usage, and increased labor for maintenance, leading to greater recurring expenses. Over time, vertical gardening offers long-term savings through efficient resource use, reduced pest exposure, and improved crop productivity, making it a cost-effective solution for urban and small-space gardening.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vertical gardening significantly reduces soil erosion and conserves water by using less land and enabling efficient irrigation systems, making it more sustainable compared to traditional row planting. Traditional row planting often involves larger land use and higher water consumption, contributing to soil degradation and resource depletion. Implementing vertical gardening in urban and limited spaces promotes biodiversity and reduces the carbon footprint associated with food production.
Vertical Gardening vs Traditional Row Planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com