
Culinary herbs vs Medicinal herbs Illustration
Culinary herbs are primarily used to enhance the flavor and aroma of food, including common varieties like basil, thyme, and rosemary known for their savory and fresh notes. Medicinal herbs, such as echinacea, chamomile, and ginseng, are valued for their therapeutic properties and are often utilized in teas, tinctures, or supplements to support health and wellness. While some herbs serve both culinary and medicinal purposes, their primary distinction lies in their intended use for either enhancing cuisine or promoting healing.
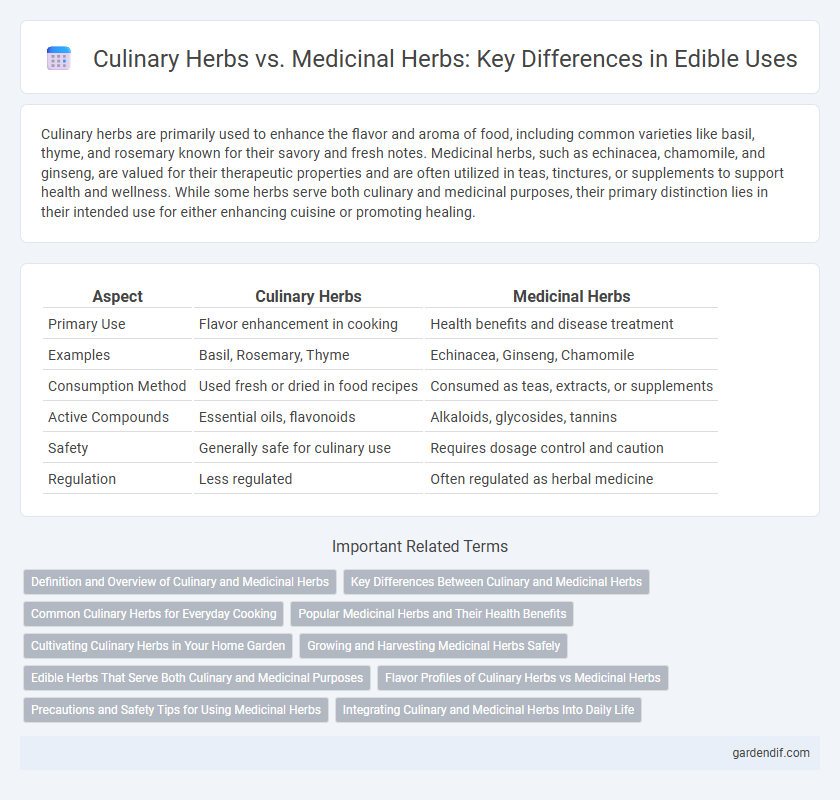
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Culinary Herbs | Medicinal Herbs |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Flavor enhancement in cooking | Health benefits and disease treatment |
| Examples | Basil, Rosemary, Thyme | Echinacea, Ginseng, Chamomile |
| Consumption Method | Used fresh or dried in food recipes | Consumed as teas, extracts, or supplements |
| Active Compounds | Essential oils, flavonoids | Alkaloids, glycosides, tannins |
| Safety | Generally safe for culinary use | Requires dosage control and caution |
| Regulation | Less regulated | Often regulated as herbal medicine |
Definition and Overview of Culinary and Medicinal Herbs
Culinary herbs are plants primarily used to enhance the flavor, aroma, and appearance of food, including common varieties like basil, thyme, and rosemary. Medicinal herbs are plants employed for their therapeutic properties to prevent or treat ailments, such as echinacea, ginseng, and chamomile. Both categories often overlap, but culinary herbs focus on taste and culinary applications, while medicinal herbs emphasize health benefits and healing properties.
Key Differences Between Culinary and Medicinal Herbs
Culinary herbs primarily enhance flavor and aroma in food, such as basil, thyme, and rosemary, while medicinal herbs like echinacea, ginseng, and chamomile are used for therapeutic benefits. The active compounds in medicinal herbs target specific health issues, including inflammation, immune support, and digestion, whereas culinary herbs generally offer mild health benefits and antioxidant properties. Understanding these key differences aids in appropriate usage, ensuring culinary herbs improve taste without adverse effects and medicinal herbs deliver intended health outcomes.
Common Culinary Herbs for Everyday Cooking
Common culinary herbs such as basil, thyme, rosemary, and parsley are indispensable in everyday cooking due to their aromatic flavors and nutritional benefits. These herbs enhance dishes with essential oils rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to both taste and health. Unlike medicinal herbs primarily used for health treatments, culinary herbs are integrated regularly into meals for seasoning and garnishing, making them staples in kitchens worldwide.
Popular Medicinal Herbs and Their Health Benefits
Popular medicinal herbs such as echinacea, ginseng, and turmeric are prized for their health benefits, including immune system support, enhanced energy levels, and powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Unlike culinary herbs primarily used for flavoring, these medicinal herbs are often consumed in teas, tinctures, or supplements to promote wellness and manage specific health conditions. Their bioactive compounds, like curcumin in turmeric and ginsenosides in ginseng, provide significant therapeutic effects recognized in traditional and modern herbal medicine.
Cultivating Culinary Herbs in Your Home Garden
Cultivating culinary herbs in your home garden enhances flavor and freshness for everyday cooking, promoting convenience and sustainability. Common culinary herbs such as basil, rosemary, thyme, and parsley thrive in well-drained soil and require consistent sunlight for optimal growth. Incorporating organic fertilizers and regular pruning supports healthy plants, increasing yields and prolonging harvest periods while minimizing pest infestations.
Growing and Harvesting Medicinal Herbs Safely
Medicinal herbs require careful growing conditions to preserve their therapeutic properties, including well-drained soil and appropriate sunlight exposure. Harvesting should be done at peak potency, often during flowering stages, using clean tools to prevent contamination. Proper drying and storage methods are crucial to maintain the efficacy and safety of medicinal herbs for consumption.
Edible Herbs That Serve Both Culinary and Medicinal Purposes
Edible herbs such as basil, thyme, and rosemary are prized for their dual role in enhancing flavor and offering medicinal benefits like antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These culinary and medicinal herbs contain essential oils and bioactive compounds that support digestion, boost immunity, and reduce stress. Integrating herbs like oregano, sage, and mint into daily meals not only elevates taste but also promotes overall health and well-being.
Flavor Profiles of Culinary Herbs vs Medicinal Herbs
Culinary herbs like basil, thyme, and rosemary feature vibrant, aromatic flavor profiles designed to enhance dishes with fresh, savory, or citrusy notes. Medicinal herbs such as echinacea, ginseng, and chamomile often have more bitter, earthy, or floral flavors that support therapeutic properties rather than culinary appeal. The flavor intensity and complexity of culinary herbs prioritize palatability, whereas medicinal herbs emphasize bioactive compounds linked to health benefits.
Precautions and Safety Tips for Using Medicinal Herbs
Medicinal herbs require careful consideration due to their potent bioactive compounds, which can cause adverse reactions or interact with medications. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals before use, adhere to recommended dosages, and avoid self-medicating especially during pregnancy or with chronic conditions. Proper identification and sourcing from reputable suppliers reduce risks of contamination or misidentification, ensuring safe and effective use.
Integrating Culinary and Medicinal Herbs Into Daily Life
Integrating culinary and medicinal herbs into daily life enhances both flavor and health by using common herbs like basil, rosemary, and thyme for seasoning meals while harnessing their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Culinary herbs such as oregano and sage offer essential nutrients and natural remedies for digestion and immune support, making them versatile additions to everyday cooking and wellness routines. Regular use of these herbs promotes holistic health by combining culinary enjoyment with therapeutic benefits in soups, teas, and salads.
Culinary herbs vs Medicinal herbs Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com