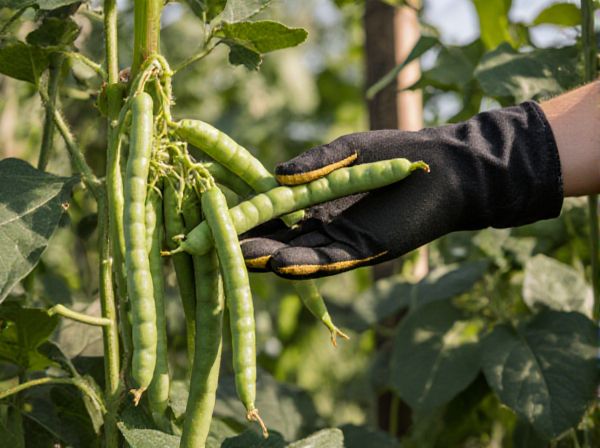

Pole beans vs Bush beans Illustration
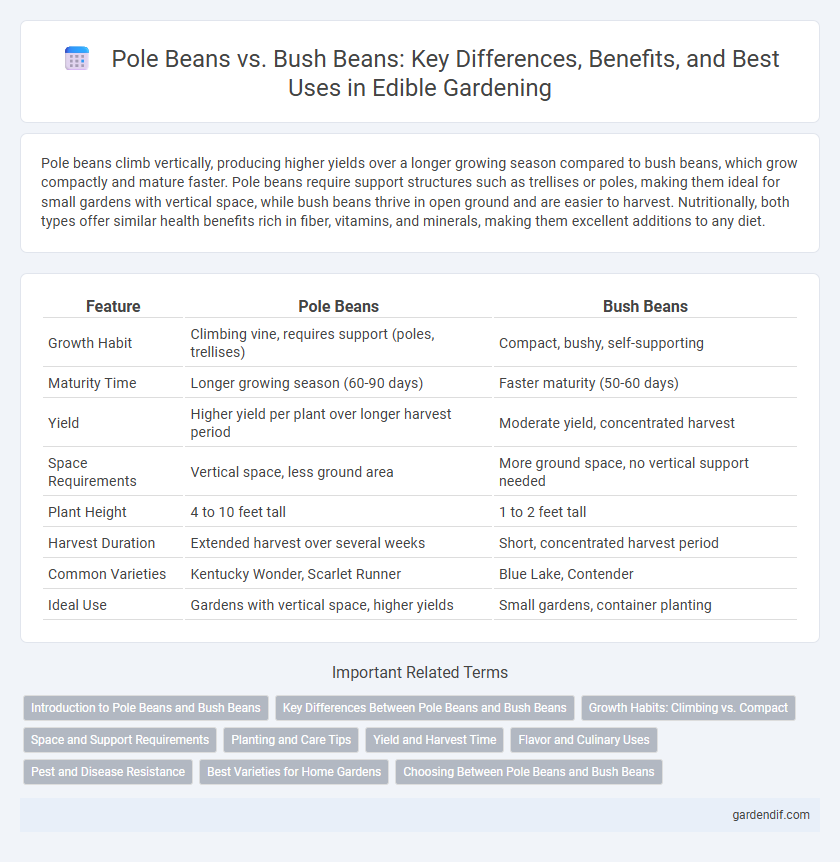
Pole beans climb vertically, producing higher yields over a longer growing season compared to bush beans, which grow compactly and mature faster. Pole beans require support structures such as trellises or poles, making them ideal for small gardens with vertical space, while bush beans thrive in open ground and are easier to harvest. Nutritionally, both types offer similar health benefits rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them excellent additions to any diet.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pole Beans | Bush Beans |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Habit | Climbing vine, requires support (poles, trellises) | Compact, bushy, self-supporting |
| Maturity Time | Longer growing season (60-90 days) | Faster maturity (50-60 days) |
| Yield | Higher yield per plant over longer harvest period | Moderate yield, concentrated harvest |
| Space Requirements | Vertical space, less ground area | More ground space, no vertical support needed |
| Plant Height | 4 to 10 feet tall | 1 to 2 feet tall |
| Harvest Duration | Extended harvest over several weeks | Short, concentrated harvest period |
| Common Varieties | Kentucky Wonder, Scarlet Runner | Blue Lake, Contender |
| Ideal Use | Gardens with vertical space, higher yields | Small gardens, container planting |
Introduction to Pole Beans and Bush Beans
Pole beans grow as climbing vines requiring vertical support, producing higher yields over a longer growing season, and often preferred for home gardens with limited space. Bush beans are compact, self-supporting plants that mature faster, typically yielding a single, concentrated harvest ideal for quick production and smaller gardens. Both types belong to the same species, Phaseolus vulgaris, but their growth habits and harvesting timelines influence cultivation choices.
Key Differences Between Pole Beans and Bush Beans
Pole beans grow as climbing vines that require support structures and have a longer harvesting period, while bush beans grow compactly without support and mature faster, typically within 50-60 days. Pole beans tend to produce higher yields over an extended season, making them ideal for continuous harvesting, whereas bush beans provide a concentrated harvest in a shorter time frame. Nutritionally, both types are similar, but their growth habits and space requirements are the primary factors influencing choice for home gardeners and commercial growers.
Growth Habits: Climbing vs. Compact
Pole beans exhibit a climbing growth habit, requiring trellises or poles to support their vertical development, which maximizes garden space and increases air circulation. Bush beans grow compactly with a self-supporting, bushy structure, making them ideal for smaller gardens or container planting due to their shorter, more manageable height. The distinct growth habits influence harvest methods and yield timing, with pole beans offering continuous production and bush beans producing all at once.
Space and Support Requirements
Pole beans require vertical support such as trellises or poles, making them ideal for small gardens where maximizing vertical space is essential. Bush beans grow compactly without the need for support, taking up more horizontal space but allowing for easier maintenance and harvesting. Choosing between pole and bush beans depends on the available garden space and whether vertical structures can be installed.
Planting and Care Tips
Pole beans require sturdy support such as trellises or poles for vertical growth, maximizing garden space and improving air circulation, while bush beans grow compactly without support, making them ideal for smaller areas. Plant pole beans after the last frost when soil temperatures reach around 65degF, spacing seeds 3-4 inches apart, and provide consistent watering to maintain moist but not waterlogged soil. Bush beans prefer slightly cooler soil around 60degF, with seeds spaced 2-3 inches apart, and benefit from well-drained soil with regular watering and mulching to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Yield and Harvest Time
Pole beans typically produce higher yields compared to bush beans due to their vining growth habit, allowing multiple harvests over an extended period. Bush beans mature faster, often ready for harvest in 50 to 60 days, while pole beans can take 60 to 90 days but continue producing pods throughout the growing season. Yield efficiency depends on available space, with pole beans maximizing vertical gardening areas for prolonged, prolific harvests.
Flavor and Culinary Uses
Pole beans offer a richer, more robust flavor compared to bush beans, making them ideal for hearty dishes like stews and casseroles. Bush beans have a milder taste and tender texture, often preferred in fresh salads and quick sautes. Culinary use of pole beans typically involves longer cooking times to enhance their earthiness, while bush beans excel when cooked briefly to retain their crispness and sweetness.
Pest and Disease Resistance
Pole beans exhibit higher pest resistance, particularly against bean beetles and aphids, due to their vigorous growth and dense foliage. Bush beans, while faster to mature, are more susceptible to common diseases like powdery mildew and bacterial blight, often requiring vigilant monitoring. Integrated pest management strategies are essential for both types to minimize crop losses and maintain healthy yields.
Best Varieties for Home Gardens
Pole beans, such as Blue Lake and Kentucky Wonder, offer high yields and vertical growth, making them ideal for limited spaces in home gardens. Bush beans like Provider and Contender mature faster and require less support, providing a convenient option for beginners. Choosing varieties resistant to common diseases like rust and mosaic virus enhances productivity and reduces maintenance in edible home gardens.
Choosing Between Pole Beans and Bush Beans
Pole beans require sturdy support structures and typically produce higher yields over a longer growing season, making them ideal for gardeners with vertical space and time to nurture climbing plants. Bush beans grow more compactly without support, mature faster, and are better suited for small gardens or shorter growing seasons. Selecting between pole and bush beans depends on garden space, desired harvest duration, and planting preferences.
Pole beans vs Bush beans Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com