
Raised container bed vs ground-level container Illustration
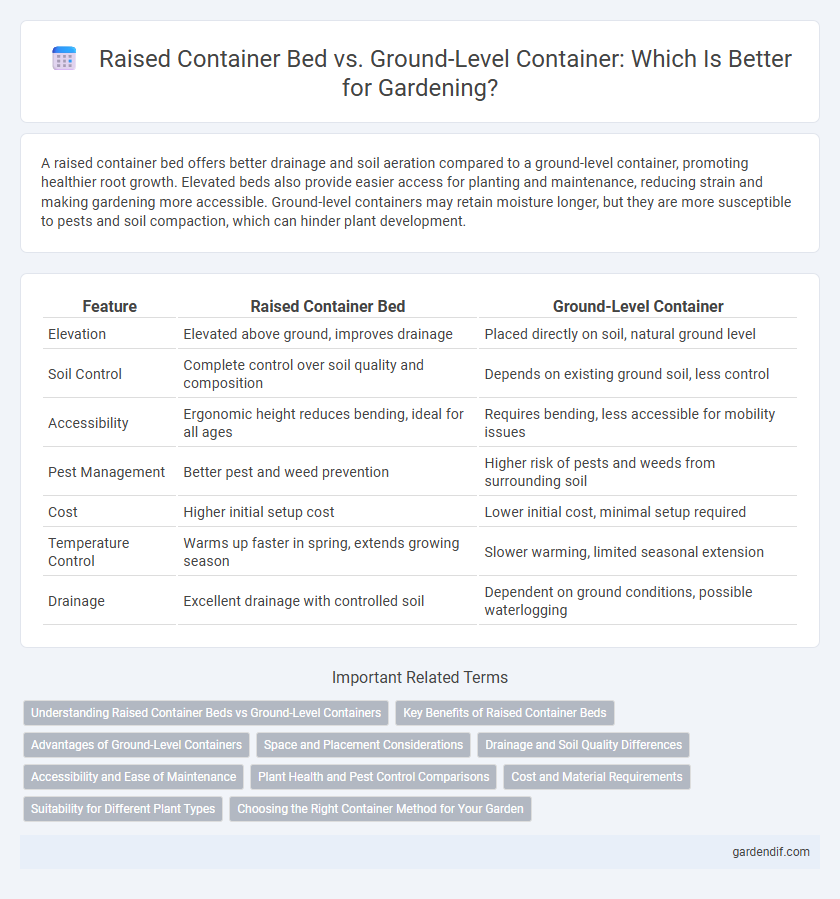
A raised container bed offers better drainage and soil aeration compared to a ground-level container, promoting healthier root growth. Elevated beds also provide easier access for planting and maintenance, reducing strain and making gardening more accessible. Ground-level containers may retain moisture longer, but they are more susceptible to pests and soil compaction, which can hinder plant development.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raised Container Bed | Ground-Level Container |
|---|---|---|
| Elevation | Elevated above ground, improves drainage | Placed directly on soil, natural ground level |
| Soil Control | Complete control over soil quality and composition | Depends on existing ground soil, less control |
| Accessibility | Ergonomic height reduces bending, ideal for all ages | Requires bending, less accessible for mobility issues |
| Pest Management | Better pest and weed prevention | Higher risk of pests and weeds from surrounding soil |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost | Lower initial cost, minimal setup required |
| Temperature Control | Warms up faster in spring, extends growing season | Slower warming, limited seasonal extension |
| Drainage | Excellent drainage with controlled soil | Dependent on ground conditions, possible waterlogging |
Understanding Raised Container Beds vs Ground-Level Containers
Raised container beds offer improved soil drainage, better root aeration, and easier access for planting and maintenance compared to ground-level containers, which often face challenges with soil compaction and limited aeration. Elevated beds provide enhanced control over soil quality and temperature, promoting healthier plant growth by reducing pest and weed intrusion common in ground-level options. Choosing between raised beds and ground-level containers depends on factors such as garden space, plant type, and desired soil management.
Key Benefits of Raised Container Beds
Raised container beds improve drainage and soil aeration, promoting healthier root growth and reducing the risk of waterlogging. Elevated soil temperatures in raised beds extend the growing season, allowing plants to thrive earlier in spring and later in fall. These beds also offer easier access for planting, weeding, and harvesting, minimizing back strain and making gardening more accessible.
Advantages of Ground-Level Containers
Ground-level containers offer superior heat retention due to direct soil contact, promoting earlier planting and faster root development compared to raised container beds. They provide better water accessibility by allowing natural moisture exchange between the soil and roots, reducing the frequency of irrigation. Additionally, ground-level containers support larger plant growth as roots can expand freely into the surrounding soil, enhancing overall plant health and yield.
Space and Placement Considerations
Raised container beds maximize vertical space, making them ideal for small yards or balconies, while ground-level containers require more horizontal area but allow easier access to soil nutrients and natural drainage. Placement flexibility for raised beds includes patios, decks, or uneven ground, whereas ground-level containers need flat, stable surfaces to prevent tipping and optimize plant growth. Choosing between the two depends on available space, sunlight exposure, and ease of maintenance in the garden layout.
Drainage and Soil Quality Differences
Raised container beds provide superior drainage due to elevated soil that prevents waterlogging, promoting healthier root systems compared to ground-level containers where drainage can be inconsistent. Soil quality in raised beds is easily controlled and enriched with organic matter, reducing compaction and improving aeration; ground-level containers often struggle with soil contamination and limited nutrient availability. Enhanced drainage and optimized soil conditions in raised beds significantly improve plant growth and reduce root diseases compared to traditional ground-level container setups.
Accessibility and Ease of Maintenance
Raised container beds offer enhanced accessibility by reducing the need to bend or kneel, benefiting individuals with mobility challenges or back issues. Ground-level containers require more frequent bending and can be harder to maintain, especially for extended gardening sessions. The elevated design of raised beds also facilitates easier soil management and pest control, improving overall garden maintenance efficiency.
Plant Health and Pest Control Comparisons
Raised container beds improve plant health by providing better soil drainage and root aeration compared to ground-level containers, reducing the risk of root rot and fungal diseases. Elevated designs limit exposure to soil-borne pests and facilitate easier pest management through physical barriers or traps. Ground-level containers may face increased pest intrusion from crawling insects and soil pathogens due to direct contact with the ground, affecting overall plant vitality.
Cost and Material Requirements
Raised container beds generally incur higher initial costs due to the need for durable framing materials such as cedar, composite wood, or metal, which provide structural support and longevity. Ground-level containers tend to be more cost-effective, requiring only a simple barrier or liner to contain soil, minimizing material expenses. Material requirements for raised beds include sturdy boards, screws, and often soil amendments, while ground-level setups primarily need quality soil and a weed barrier, reducing overall material investment.
Suitability for Different Plant Types
Raised container beds provide improved drainage and soil aeration, making them ideal for root vegetables like carrots and potatoes that require loose, well-drained soil. Ground-level containers retain moisture better, benefiting plants such as leafy greens and herbs that thrive in consistent soil hydration. The choice between raised and ground-level containers depends on plant root depth, moisture needs, and susceptibility to soil-borne diseases.
Choosing the Right Container Method for Your Garden
Raised container beds offer superior soil drainage and root aeration compared to ground-level containers, promoting healthier plant growth and reducing soil compaction. Ground-level containers retain more moisture, making them ideal for plants that require consistent hydration and are typically easier to access for maintenance. Selecting the right container method depends on plant type, soil conditions, and garden space, with raised beds enhancing root development while ground-level containers suit water-loving and shade-tolerant species.
Raised container bed vs ground-level container Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com