
Container tomatoes vs staked tomatoes Illustration
Container tomatoes offer flexibility and can thrive in small spaces, making them ideal for urban gardeners, while staked tomatoes typically yield larger harvests due to better support and air circulation. Container-grown tomatoes often require more frequent watering and nutrient monitoring, whereas staked tomatoes benefit from direct soil access and deeper root systems. Both methods demand proper sunlight and pruning techniques to maximize fruit production and plant health.
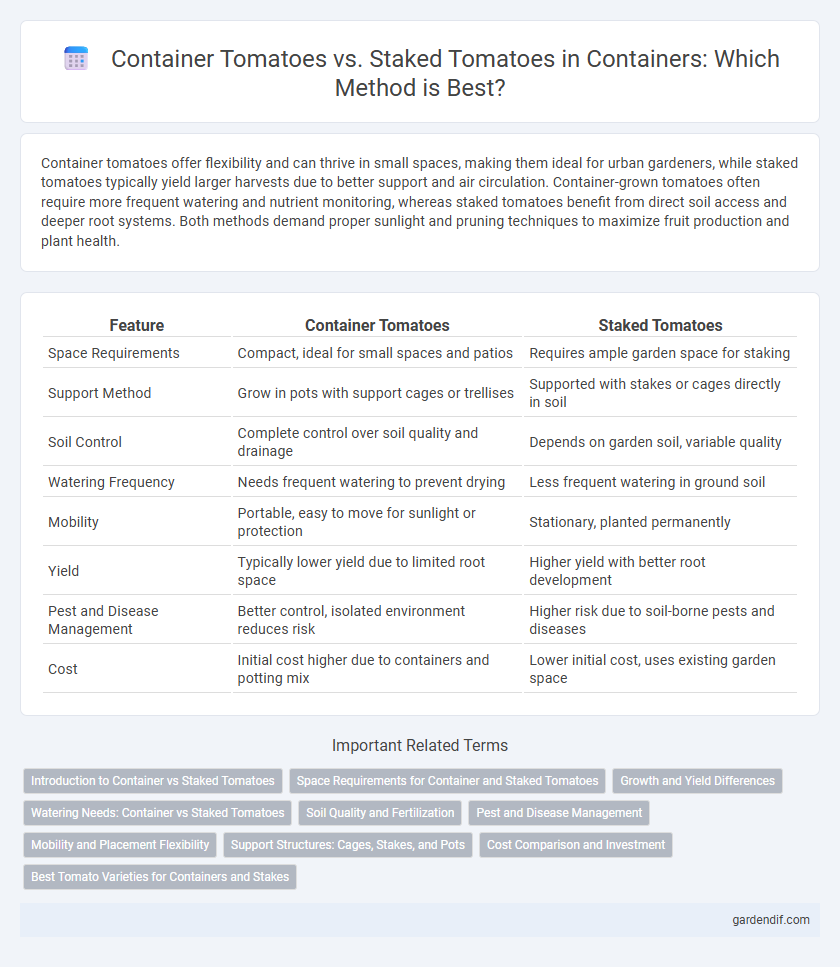
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Container Tomatoes | Staked Tomatoes |
|---|---|---|
| Space Requirements | Compact, ideal for small spaces and patios | Requires ample garden space for staking |
| Support Method | Grow in pots with support cages or trellises | Supported with stakes or cages directly in soil |
| Soil Control | Complete control over soil quality and drainage | Depends on garden soil, variable quality |
| Watering Frequency | Needs frequent watering to prevent drying | Less frequent watering in ground soil |
| Mobility | Portable, easy to move for sunlight or protection | Stationary, planted permanently |
| Yield | Typically lower yield due to limited root space | Higher yield with better root development |
| Pest and Disease Management | Better control, isolated environment reduces risk | Higher risk due to soil-borne pests and diseases |
| Cost | Initial cost higher due to containers and potting mix | Lower initial cost, uses existing garden space |
Introduction to Container vs Staked Tomatoes
Container tomatoes grow in pots or other confined spaces, offering flexibility and ease of management, ideal for urban gardeners or limited spaces. Staked tomatoes require support structures like stakes or cages to maintain upright growth, promoting better air circulation and reducing disease risks. Choosing between container and staked tomatoes depends on space availability, maintenance preference, and desired yield.
Space Requirements for Container and Staked Tomatoes
Container tomatoes require significantly less space, making them ideal for balconies, patios, or small urban gardens, typically needing about 5 gallons of soil per plant. Staked tomatoes demand more room as they grow vertically and spread out, often requiring 18 to 24 inches between plants to ensure proper airflow and sunlight exposure. Proper spacing for staked tomatoes prevents disease and promotes healthier fruit development, while container tomatoes benefit from controlled root growth in a confined area.
Growth and Yield Differences
Container tomatoes exhibit controlled root growth, which can limit plant size but improve fruit quality and pest management, while staked tomatoes develop extensive root systems supporting larger plants and higher yield potential. Growth in container tomatoes is more manageable with consistent watering and nutrient delivery, leading to uniform fruit development, whereas staked tomatoes rely on soil volume and natural nutrient uptake that can fluctuate. Yield differences favor staked tomatoes due to their ability to support greater biomass and fruit load, but container tomatoes offer efficient space use and reduced disease incidence.
Watering Needs: Container vs Staked Tomatoes
Container tomatoes require more frequent and consistent watering due to limited soil volume causing faster moisture evaporation, often needing daily watering in warm weather. Staked tomatoes benefit from deeper soil access, allowing roots to draw moisture from a larger area, reducing watering frequency to every 2-3 days. Proper irrigation techniques for container tomatoes include using drip irrigation or self-watering containers to maintain consistent moisture levels and prevent root stress.
Soil Quality and Fertilization
Container tomatoes require well-draining, nutrient-rich potting mix with balanced fertilization to support root development and fruit production, while staked tomatoes benefit from fertile, loamy soil enriched with compost and organic matter for sustained nutrient availability. Consistent monitoring of pH levels between 6.0 and 6.8 enhances nutrient uptake in both growing methods. Frequent, diluted applications of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium supplements optimize growth and yield depending on container size or garden bed conditions.
Pest and Disease Management
Container tomatoes benefit from improved pest and disease management due to controlled soil conditions, reducing exposure to soil-borne pathogens compared to staked tomatoes planted directly in the ground. The elevated position and restricted root zone in containers limit access for common pests like cutworms and soil nematodes, while staked tomatoes are more susceptible to foliar diseases from soil splash. Regular monitoring and targeted treatments are essential for both methods, but container cultivation offers a strategic advantage in minimizing pathogen reservoirs and pest habitats.
Mobility and Placement Flexibility
Container tomatoes offer superior mobility and placement flexibility compared to staked tomatoes, allowing growers to easily relocate plants to optimal light and temperature conditions. In contrast, staked tomatoes are fixed to a specific spot in the garden, limiting adjustments for environmental changes or space constraints. This mobility advantage of container tomatoes supports better pest management and seasonal adaptability.
Support Structures: Cages, Stakes, and Pots
Container tomatoes require sturdy pots that provide adequate drainage and space for root growth, while staked tomatoes depend heavily on vertical support structures like tall stakes or cages to keep vines upright and prevent breakage. Tomato cages are commonly used for container plants to contain sprawling branches, enhance air circulation, and promote even sunlight exposure, which improves fruit quality. Staked tomatoes benefit from tie-offs at multiple points along the main stem, ensuring stability and reducing the risk of wind damage or disease from soil contact.
Cost Comparison and Investment
Container tomatoes require a lower initial investment due to reduced structural materials and space needs compared to staked tomatoes, which demand stakes, ties, and more labor-intensive setup. Operational costs for container tomatoes often remain lower as they facilitate efficient water and nutrient management, reducing waste and input expenses. While staked tomatoes may yield higher production in larger areas, container tomatoes offer cost-effective scalability and flexibility, making them a strategic choice for budget-conscious growers.
Best Tomato Varieties for Containers and Stakes
Determinate tomato varieties like 'Bush Early Girl' and 'Patio Princess' are ideal for containers due to their compact growth habit and manageable size. Indeterminate tomatoes such as 'Sungold' and 'Brandywine' thrive when staked, providing higher yields through vertical support and better air circulation. Choosing disease-resistant cultivars like 'Celebrity' ensures healthy plants in both containers and stakes, maximizing flavor and productivity.
Container tomatoes vs staked tomatoes Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com