
Sub-irrigated planters vs drip-irrigated pots Illustration
Sub-irrigated planters deliver water directly to the root zone, reducing water waste and promoting healthier plant growth compared to drip-irrigated pots. This method minimizes evaporation and runoff, ensuring consistent moisture levels ideal for container gardening. Drip-irrigated pots, while effective, require more frequent monitoring to prevent overwatering or drying out of soil surfaces.
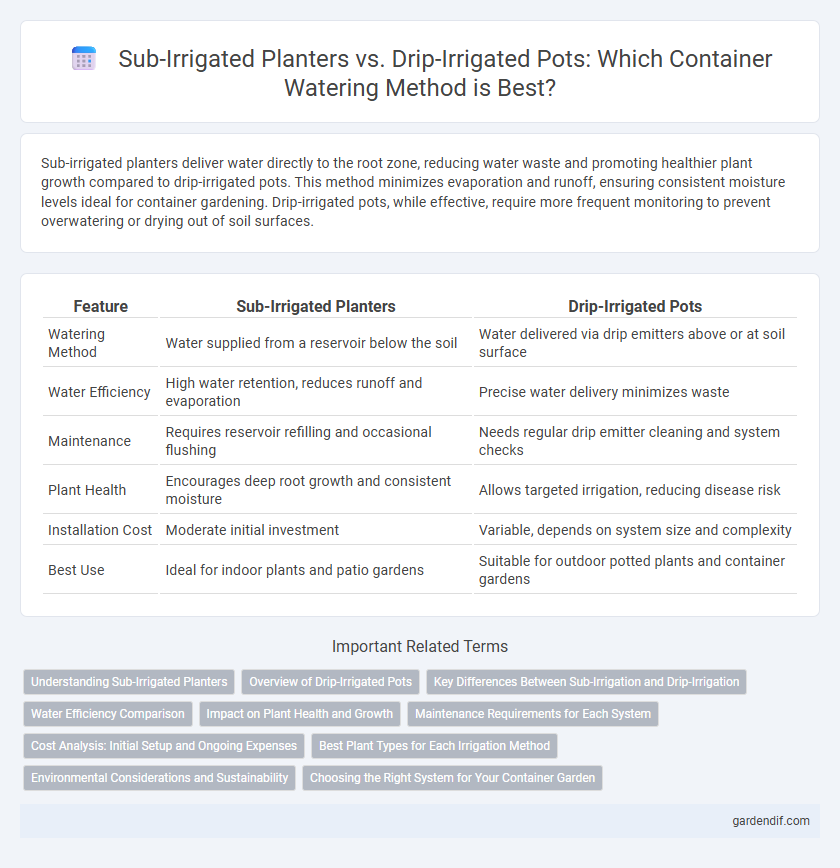
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sub-Irrigated Planters | Drip-Irrigated Pots |
|---|---|---|
| Watering Method | Water supplied from a reservoir below the soil | Water delivered via drip emitters above or at soil surface |
| Water Efficiency | High water retention, reduces runoff and evaporation | Precise water delivery minimizes waste |
| Maintenance | Requires reservoir refilling and occasional flushing | Needs regular drip emitter cleaning and system checks |
| Plant Health | Encourages deep root growth and consistent moisture | Allows targeted irrigation, reducing disease risk |
| Installation Cost | Moderate initial investment | Variable, depends on system size and complexity |
| Best Use | Ideal for indoor plants and patio gardens | Suitable for outdoor potted plants and container gardens |
Understanding Sub-Irrigated Planters
Sub-irrigated planters utilize a reservoir at the base, allowing plants to draw water upward through capillary action, promoting efficient water use and reducing evaporation compared to drip-irrigated pots. This self-watering mechanism ensures roots receive consistent moisture, minimizing overwatering risks and enhancing plant health in container gardening. Understanding the water distribution dynamics in sub-irrigated planters is critical for optimizing soil aeration and nutrient uptake while reducing maintenance frequency.
Overview of Drip-Irrigated Pots
Drip-irrigated pots provide precise water delivery directly to the root zone, minimizing water waste and promoting efficient nutrient uptake in container gardening. These pots often feature built-in emitters or can be connected to automated drip irrigation systems, allowing for consistent moisture levels without overwatering. Their design supports healthy root development and reduces the risk of fungal diseases by maintaining optimal soil aeration.
Key Differences Between Sub-Irrigation and Drip-Irrigation
Sub-irrigated planters deliver water directly to the root zone through a reservoir system, enhancing water efficiency and reducing surface evaporation, while drip-irrigated pots supply water at the soil surface, targeting individual plants with precise water amounts. Sub-irrigation promotes consistent moisture levels, minimizing water stress and encouraging deeper root growth, whereas drip irrigation allows flexible watering schedules suitable for variable plant needs. The self-watering nature of sub-irrigated planters often reduces maintenance compared to drip systems that require regular adjustment and monitoring to prevent clogging and ensure uniform distribution.
Water Efficiency Comparison
Sub-irrigated planters significantly enhance water efficiency by delivering moisture directly to plant roots through a reservoir, reducing surface evaporation and runoff by up to 50% compared to drip-irrigated pots. Drip-irrigated pots rely on above-soil water application, which can lead to uneven moisture distribution and higher water loss, particularly in windy or hot conditions. Studies indicate sub-irrigation systems can save up to 30% more water annually while maintaining optimal plant growth, making them superior for sustainable container gardening.
Impact on Plant Health and Growth
Sub-irrigated planters provide consistent moisture from below, reducing water stress and promoting deeper root growth, which enhances overall plant health. Drip-irrigated pots deliver water directly to the soil surface, allowing precise control but may lead to uneven moisture distribution and surface root development. Plants in sub-irrigated systems often exhibit increased nutrient uptake and reduced risk of overwatering compared to drip irrigation, resulting in more vigorous and resilient growth.
Maintenance Requirements for Each System
Sub-irrigated planters require less frequent watering and reduce the risk of overwatering by supplying water directly to the root zone through a reservoir system, minimizing maintenance efforts. Drip-irrigated pots demand regular monitoring of emitter functionality and occasional flushing to prevent clogs, ensuring consistent water delivery. Both systems benefit from periodic inspections, but sub-irrigated planters generally offer lower maintenance due to their self-regulating water distribution.
Cost Analysis: Initial Setup and Ongoing Expenses
Sub-irrigated planters typically involve a higher initial setup cost due to their complex reservoir systems, but they reduce ongoing water expenses by minimizing evaporation and runoff. Drip-irrigated pots generally have lower upfront costs and greater flexibility, though their continual use of pumps and emitters can increase water and energy bills over time. Evaluating long-term expenses reveals sub-irrigated planters may offer better cost efficiency for water conservation despite the initial investment.
Best Plant Types for Each Irrigation Method
Sub-irrigated planters best support moisture-loving plants such as ferns, peace lilies, and herbs like basil, which thrive with consistent soil hydration from below. Drip-irrigated pots suit drought-tolerant plants, including succulents, cacti, and Mediterranean herbs like rosemary, that require controlled water delivery to prevent root rot. Selecting the appropriate irrigation method enhances growth efficiency by matching water needs to plant species' natural habitats.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Sub-irrigated planters reduce water waste by allowing plants to draw moisture from a reservoir, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to drip-irrigated pots, which often lose water through surface evaporation. These planters promote water conservation and reduce the need for frequent watering, enhancing sustainability in container gardening. Their efficient use of resources contributes to lower environmental impact, making them a more eco-friendly option for sustainable plant care.
Choosing the Right System for Your Container Garden
Sub-irrigated planters provide water from the bottom, promoting consistent moisture and reducing water waste, ideal for plants requiring steady hydration. Drip-irrigated pots deliver water directly to the soil surface, offering precise control over irrigation frequency and volume, suitable for varied plant types and growing conditions. Selecting the right system depends on plant water needs, container size, and maintenance preferences to optimize growth and conserve water efficiently.
Sub-irrigated planters vs drip-irrigated pots Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com