
Large containers vs small containers Illustration
Large containers offer significant storage capacity ideal for bulk shipments, reducing transportation costs per unit and enhancing efficiency in logistics operations. Small containers provide greater flexibility for handling diverse cargo types, better suited for urban deliveries and smaller-scale distribution needs. Selecting the appropriate container size optimizes space utilization and aligns with specific shipping requirements to improve overall supply chain performance.
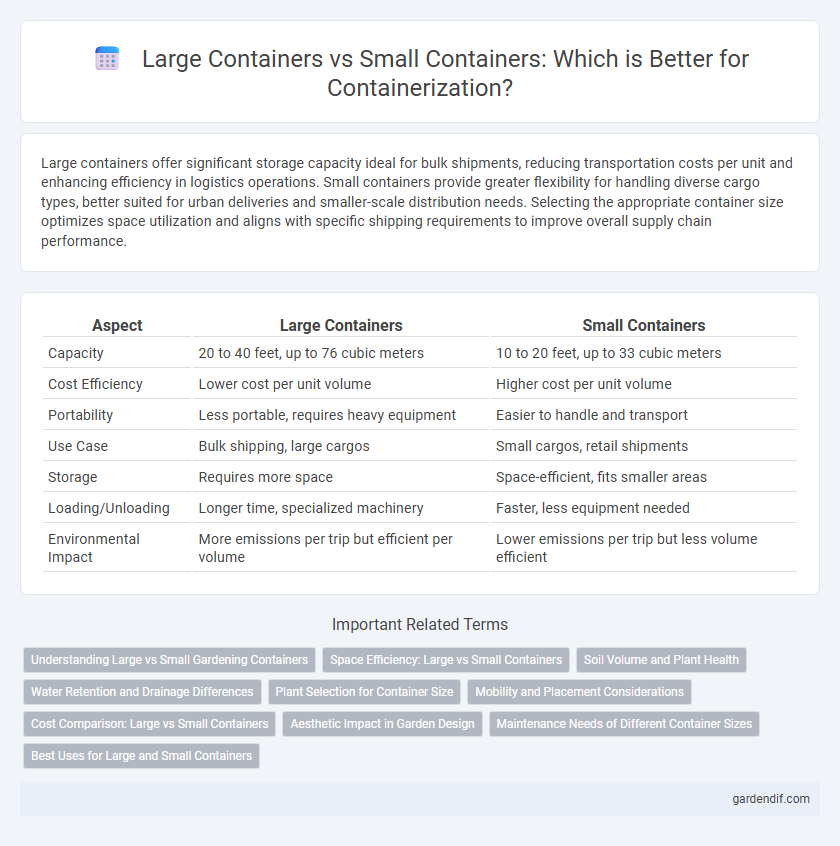
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Large Containers | Small Containers |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | 20 to 40 feet, up to 76 cubic meters | 10 to 20 feet, up to 33 cubic meters |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost per unit volume | Higher cost per unit volume |
| Portability | Less portable, requires heavy equipment | Easier to handle and transport |
| Use Case | Bulk shipping, large cargos | Small cargos, retail shipments |
| Storage | Requires more space | Space-efficient, fits smaller areas |
| Loading/Unloading | Longer time, specialized machinery | Faster, less equipment needed |
| Environmental Impact | More emissions per trip but efficient per volume | Lower emissions per trip but less volume efficient |
Understanding Large vs Small Gardening Containers
Large gardening containers provide ample space for root growth, ensuring better nutrient absorption and plant stability, which is essential for plants with extensive root systems or higher water needs. Small containers are ideal for compact spaces and plants with shallow roots, offering better control over soil moisture but requiring more frequent watering and attention. Choosing the right container size impacts plant health, growth rate, and maintenance requirements, making it crucial for successful gardening outcomes.
Space Efficiency: Large vs Small Containers
Large containers maximize space efficiency by reducing the frequency of loading and unloading, leading to optimized cargo capacity and lower transportation costs. Small containers offer flexibility for partial loads and easier handling in constrained spaces, but often incur higher per-unit shipping expenses. Choosing between large and small containers depends on balancing volume requirements, operational logistics, and cost-effectiveness in supply chain management.
Soil Volume and Plant Health
Large containers provide increased soil volume, promoting extensive root growth and improving nutrient absorption, which significantly enhances plant health. Small containers restrict root expansion, often leading to water stress and nutrient deficiencies that can stunt growth and reduce overall plant vitality. Optimizing soil volume by selecting appropriately sized containers supports robust root systems and sustained plant development.
Water Retention and Drainage Differences
Large containers typically retain more water due to their greater soil volume, reducing the frequency of irrigation and providing consistent moisture for plant roots. Small containers drain more quickly, promoting faster drying of the soil which helps prevent waterlogging but may require more frequent watering. Effective container gardening balances water retention and drainage based on container size to optimize plant health and growth.
Plant Selection for Container Size
Plant selection for container size is crucial, as large containers support deep-rooted species like shrubs and small trees, promoting healthy growth and stability. Small containers are best suited for compact plants such as succulents and herbs, which require less soil volume and limited root space. Matching plant size and root system to container capacity ensures optimal water retention, nutrient availability, and overall plant health.
Mobility and Placement Considerations
Large containers offer reduced mobility due to their heavier weight and bulk, making transportation and repositioning more challenging compared to small containers, which can be easily moved by forklifts or cranes. Placement of large containers requires ample space and stable ground conditions to support their size and weight, while small containers provide greater flexibility in placement, fitting into tighter spaces and allowing for modular stacking. The choice between large and small containers significantly impacts operational efficiency based on site accessibility and handling equipment availability.
Cost Comparison: Large vs Small Containers
Large containers offer economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit of storage and transportation compared to small containers. Small containers, while more flexible and easier to handle, typically incur higher costs per cubic foot due to less efficient space utilization and increased handling fees. Choosing between large and small containers depends on budget constraints, shipment volume, and specific logistical requirements.
Aesthetic Impact in Garden Design
Large containers create bold focal points that anchor garden spaces and highlight structural plants, enhancing visual impact through scale and presence. Small containers offer versatility for grouping and layering, contributing intricate details and color contrasts that enrich garden texture without overwhelming the surrounding greenery. Incorporating both container sizes strategically balances the overall aesthetic, promoting harmony between statement pieces and delicate accents in garden design.
Maintenance Needs of Different Container Sizes
Large containers require more frequent inspections and structural maintenance due to increased exposure to environmental stress and potential damage during handling. Small containers, while easier to manage, often need more regular cleaning and sealing to ensure contents remain secure and uncontaminated. Maintenance protocols should be tailored to container size, with large units focusing on corrosion control and structural integrity, and small units emphasizing hygiene and seal preservation.
Best Uses for Large and Small Containers
Large containers excel in storing bulk materials, transporting heavy machinery, and supporting industrial-scale shipping due to their capacity and durability. Small containers are ideal for organizing personal items, facilitating efficient inventory management, and enabling easy transport of compact goods. Selecting the right container size enhances operational efficiency and reduces transportation costs across logistics and storage applications.
Large containers vs small containers Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com