
Self-watering pots vs Manual watering Illustration
Self-watering pots maintain consistent soil moisture by using a built-in reservoir that supplies water as needed, reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering. Manual watering requires regular attention and careful monitoring to avoid stress on plants caused by inconsistent watering schedules. Choosing self-watering pots enhances convenience and promotes healthier plant growth by providing a steady water supply.
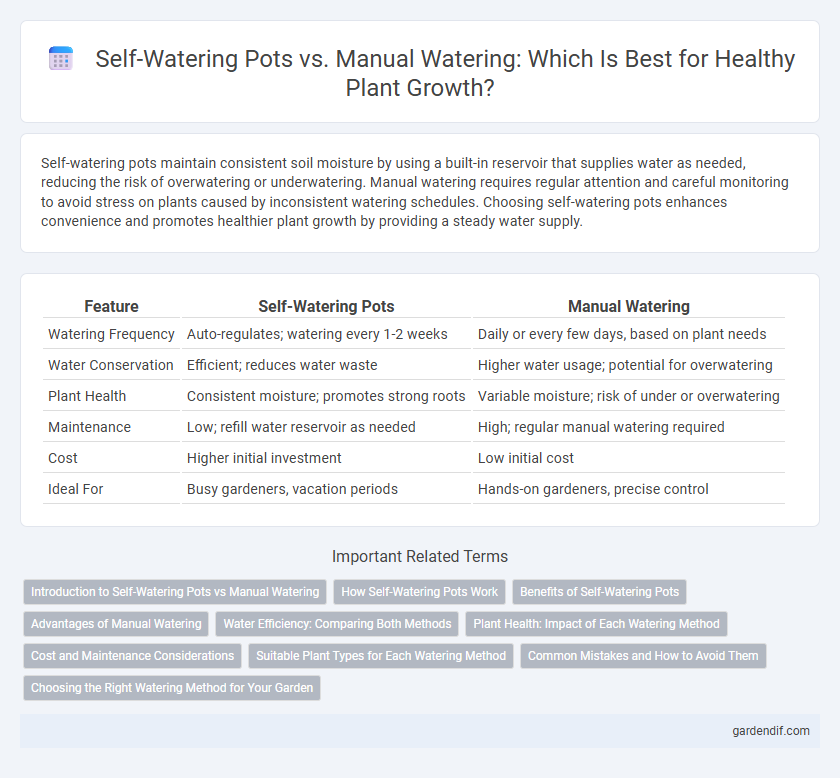
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Watering Pots | Manual Watering |
|---|---|---|
| Watering Frequency | Auto-regulates; watering every 1-2 weeks | Daily or every few days, based on plant needs |
| Water Conservation | Efficient; reduces water waste | Higher water usage; potential for overwatering |
| Plant Health | Consistent moisture; promotes strong roots | Variable moisture; risk of under or overwatering |
| Maintenance | Low; refill water reservoir as needed | High; regular manual watering required |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Low initial cost |
| Ideal For | Busy gardeners, vacation periods | Hands-on gardeners, precise control |
Introduction to Self-Watering Pots vs Manual Watering
Self-watering pots feature a built-in reservoir that provides consistent moisture to plants, reducing the frequency of manual watering and preventing over- or under-watering. Manual watering requires regular attention to soil dryness and can lead to uneven water distribution, especially for busy gardeners. Self-watering systems optimize water usage and promote healthier root development by maintaining a balanced moisture level.
How Self-Watering Pots Work
Self-watering pots operate through a built-in reservoir that supplies water directly to plant roots via capillary action, ensuring consistent moisture levels. This system minimizes water waste and reduces the frequency of watering compared to manual methods. By promoting efficient water uptake, self-watering pots support healthier plant growth and reduce the risk of over- or underwatering.
Benefits of Self-Watering Pots
Self-watering pots provide consistent moisture levels by automatically delivering water to plant roots, reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering. These pots conserve water efficiently, promoting healthier plant growth and minimizing maintenance efforts for gardeners. Ideal for busy individuals or those new to gardening, they ensure plants receive optimal hydration without frequent manual watering.
Advantages of Manual Watering
Manual watering offers precise control over the amount and timing of water each plant receives, reducing the risk of overwatering and root rot. It allows gardeners to inspect soil moisture and plant health regularly, ensuring timely adjustments for optimal growth. This method also encourages a hands-on approach, fostering a deeper connection with the plants and enabling immediate responses to environmental changes.
Water Efficiency: Comparing Both Methods
Self-watering pots optimize water efficiency by supplying consistent moisture directly to plant roots through a reservoir system, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to manual watering. Manual watering often leads to uneven soil moisture levels and increased water waste, especially when done excessively or irregularly. Studies show self-watering containers can reduce water usage by up to 50% while maintaining healthy plant growth, making them ideal for conserving water in gardening.
Plant Health: Impact of Each Watering Method
Self-watering pots provide consistent moisture levels that reduce the risk of overwatering or underwatering, promoting healthier root development and stronger plants. Manual watering can lead to irregular moisture patterns, potentially causing stress through either drought or waterlogging. Maintaining optimal hydration with self-watering systems supports nutrient uptake and improves overall plant resilience compared to traditional manual watering.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Self-watering pots often have a higher upfront cost compared to manual watering methods but reduce long-term expenses by minimizing water waste and plant stress. Maintenance for self-watering systems involves periodic cleaning and monitoring for clogs, while manual watering requires consistent attention and labor to ensure adequate hydration. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment with ongoing maintenance efforts and convenience.
Suitable Plant Types for Each Watering Method
Self-watering pots are ideal for moisture-loving plants such as ferns, peace lilies, and tropical houseplants that require consistent hydration without waterlogging. Manual watering suits plants with specific watering needs like succulents, cacti, and herbs, which benefit from controlled moisture levels and occasional dry periods. Choosing the appropriate watering method depends on the plant species' tolerance for soil moisture fluctuations and root oxygen availability.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Self-watering pots often face issues like root rot or algae growth due to overwatering, which can be avoided by monitoring water levels and ensuring proper drainage. Manual watering frequently leads to inconsistent moisture, resulting in underwatering or overwatering; using moisture meters and establishing a regular schedule helps maintain optimal soil hydration. Understanding each method's watering frequency and soil needs prevents common mistakes and supports healthy plant growth.
Choosing the Right Watering Method for Your Garden
Self-watering pots provide consistent moisture through a built-in reservoir, reducing the risk of over- or underwatering and saving time for busy gardeners. Manual watering allows precise control over water amounts, making it ideal for plants with specific hydration needs or during varying weather conditions. Selecting the right method depends on plant species, garden size, and the gardener's daily availability to ensure optimal growth and water efficiency.
Self-watering pots vs Manual watering Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com