
Rain gauge vs Soil probe Illustration
Rain gauges measure the amount of precipitation falling on a given area, providing data on rainfall volume to guide watering schedules and prevent overwatering. Soil probes assess moisture levels directly within the soil, offering precise insights into root zone hydration for optimal irrigation decisions. Combining both tools enhances water management by aligning irrigation with actual rainfall and soil moisture conditions.
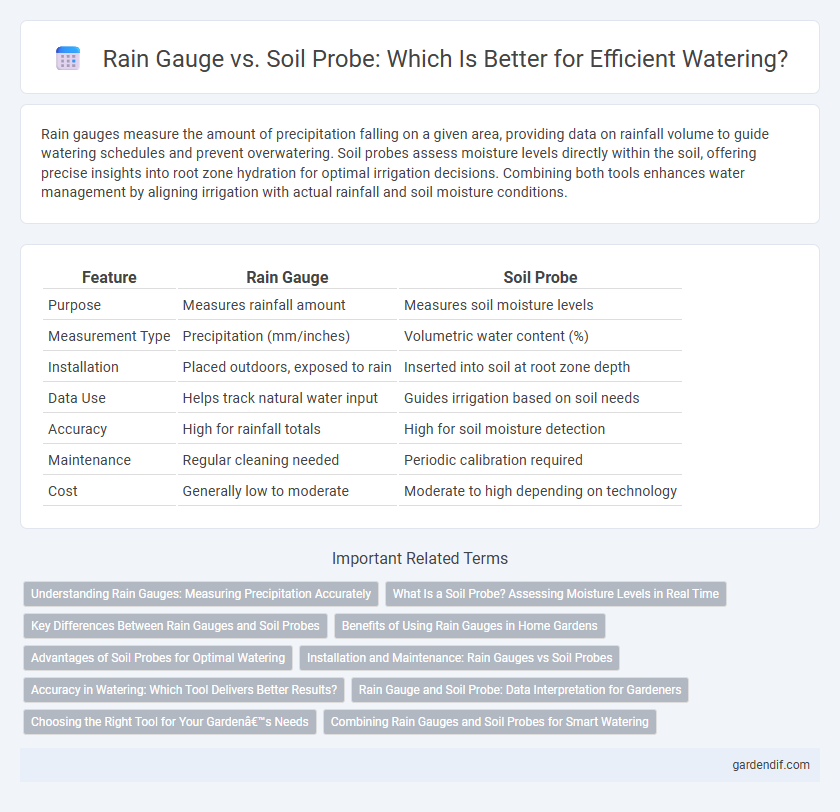
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rain Gauge | Soil Probe |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures rainfall amount | Measures soil moisture levels |
| Measurement Type | Precipitation (mm/inches) | Volumetric water content (%) |
| Installation | Placed outdoors, exposed to rain | Inserted into soil at root zone depth |
| Data Use | Helps track natural water input | Guides irrigation based on soil needs |
| Accuracy | High for rainfall totals | High for soil moisture detection |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning needed | Periodic calibration required |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Moderate to high depending on technology |
Understanding Rain Gauges: Measuring Precipitation Accurately
Rain gauges precisely measure precipitation by collecting and quantifying rainfall over a specific period, providing essential data for irrigation scheduling and water management. Unlike soil probes that assess moisture content directly in the soil, rain gauges offer accurate measurement of rainfall input, aiding in understanding natural water availability. Accurate precipitation data from rain gauges helps optimize watering practices, prevent over-irrigation, and promote sustainable water use in agriculture and gardening.
What Is a Soil Probe? Assessing Moisture Levels in Real Time
A soil probe is a tool used to measure soil moisture levels directly by inserting it into the ground, providing real-time, accurate data on soil hydration. Unlike rain gauges, which measure the amount of rainfall collected, soil probes assess the actual water content in the root zone, helping gardeners and farmers make informed watering decisions. This precise moisture monitoring prevents overwatering and underwatering, promoting healthier plant growth and efficient water use.
Key Differences Between Rain Gauges and Soil Probes
Rain gauges measure the amount of precipitation that falls in a specific area, providing data on rainfall rates and aiding in irrigation planning based on weather conditions. Soil probes directly assess soil moisture levels at various depths, delivering precise information on water availability for plant roots and helping prevent over- or under-watering. Key differences include rain gauges monitoring atmospheric water input while soil probes evaluate actual soil moisture, making them complementary tools for effective water management in agriculture and gardening.
Benefits of Using Rain Gauges in Home Gardens
Rain gauges provide precise measurement of precipitation, helping gardeners make informed irrigation decisions and prevent overwatering. Unlike soil probes that only measure moisture at a specific soil depth, rain gauges track the actual amount of rainfall collected, ensuring efficient water use according to weather conditions. Using rain gauges in home gardens reduces water waste and promotes healthier plant growth by aligning watering schedules with natural rainfall patterns.
Advantages of Soil Probes for Optimal Watering
Soil probes provide precise moisture readings directly from the root zone, enabling targeted watering that conserves water and promotes healthier plant growth. Unlike rain gauges, which only measure rainfall, soil probes assess real-time soil moisture levels, ensuring irrigation occurs only when necessary. This accuracy helps prevent overwatering and underwatering, optimizing water use efficiency in agricultural and gardening practices.
Installation and Maintenance: Rain Gauges vs Soil Probes
Rain gauges require straightforward installation, typically placed in open areas free from obstructions to accurately measure precipitation with periodic cleaning to prevent debris buildup. Soil probes demand more complex installation, involving insertion at multiple soil depths to monitor moisture levels effectively, followed by occasional calibration and sensor maintenance to ensure precise readings. Both tools benefit from routine inspection, but soil probes generally require more technical upkeep due to their in-ground placement and sensitivity to soil conditions.
Accuracy in Watering: Which Tool Delivers Better Results?
Rain gauges measure actual rainfall, providing precise data on water input from precipitation, which is crucial for adjusting irrigation schedules accurately. Soil probes assess soil moisture levels directly, offering localized insights into water availability at root depth, enabling targeted watering decisions. Combining both tools enhances watering accuracy by correlating rainfall data with soil moisture status for optimal irrigation management.
Rain Gauge and Soil Probe: Data Interpretation for Gardeners
Rain gauges measure the amount of rainfall, providing crucial data to help gardeners determine if irrigation is necessary after natural precipitation. Soil probes offer direct insights into soil moisture levels at various depths, allowing precise adjustments for watering schedules based on real-time soil conditions. Combining rain gauge and soil probe data enables gardeners to optimize water use efficiently, promoting healthier plants and conserving resources.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Garden’s Needs
Selecting the right watering tool depends on garden requirements and environmental conditions. A rain gauge accurately measures rainfall, helping determine if supplemental watering is necessary, while a soil probe assesses moisture levels directly in the root zone, ensuring precise irrigation. Combining both tools improves water efficiency and supports healthier plant growth by preventing overwatering or underwatering.
Combining Rain Gauges and Soil Probes for Smart Watering
Combining rain gauges and soil probes enhances smart watering systems by providing accurate data on both precipitation levels and soil moisture content, enabling precise irrigation decisions. Rain gauges measure rainfall to prevent overwatering, while soil probes monitor real-time soil moisture, avoiding water stress or wastage. This integrated approach optimizes water usage, promotes plant health, and reduces environmental impact.
Rain gauge vs Soil probe Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com