
Drip irrigation vs Sprinkler irrigation Illustration
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of tubes, minimizing water wastage and promoting efficient moisture absorption. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over a larger area by mimicking rainfall, making it suitable for lawns and crops requiring uniform coverage. Choosing between drip and sprinkler irrigation depends on factors like water availability, crop type, and soil conditions.
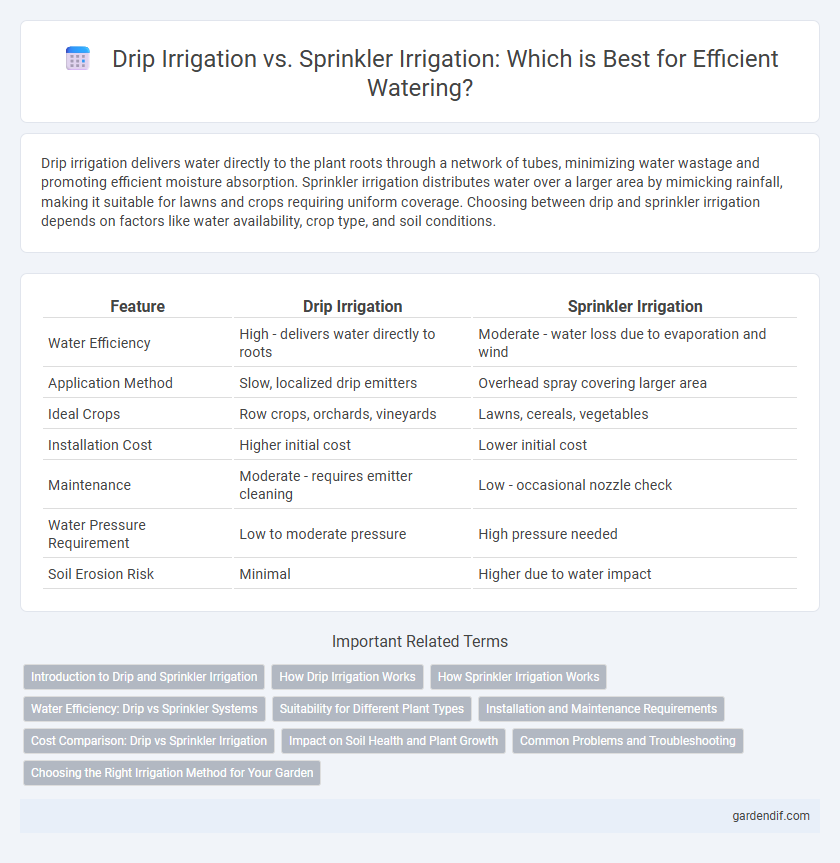
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High - delivers water directly to roots | Moderate - water loss due to evaporation and wind |
| Application Method | Slow, localized drip emitters | Overhead spray covering larger area |
| Ideal Crops | Row crops, orchards, vineyards | Lawns, cereals, vegetables |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Moderate - requires emitter cleaning | Low - occasional nozzle check |
| Water Pressure Requirement | Low to moderate pressure | High pressure needed |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Minimal | Higher due to water impact |
Introduction to Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots through a network of tubes and emitters, maximizing water efficiency and minimizing evaporation losses. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over the soil surface in the form of droplets, simulating natural rainfall and covering larger areas uniformly. Both systems address different agricultural needs, with drip irrigation preferred for water conservation and targeted application, while sprinkler systems offer versatility across various crop types and terrains.
How Drip Irrigation Works
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone through a network of tubes, valves, and emitters, minimizing evaporation and runoff. This method enables precise water application, promoting efficient moisture absorption and reducing water wastage compared to sprinkler systems that spray water over the entire soil surface. By maintaining consistent soil moisture levels, drip irrigation supports healthier plant growth and conserves water resources.
How Sprinkler Irrigation Works
Sprinkler irrigation distributes water through a system of pipes and sprays it into the air, mimicking natural rainfall to evenly hydrate crops. Sprinkler heads rotate or oscillate, covering large areas by projecting water droplets that penetrate the soil surface, promoting root absorption and reducing runoff. This method is efficient for various soil types and topographies, offering flexibility in water application rates and timing.
Water Efficiency: Drip vs Sprinkler Systems
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, resulting in water savings of up to 40% compared to sprinkler systems. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over a larger area but suffers from higher evaporation and wind drift losses, reducing overall water efficiency. Drip systems are especially advantageous in arid regions where water conservation is critical for sustainable agriculture.
Suitability for Different Plant Types
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone of individual plants, making it ideal for row crops, fruit trees, and vegetable gardens that require precise moisture control. Sprinkler irrigation spreads water over a larger area, suitable for lawns, turf, and plants that benefit from overhead watering, such as flowers and groundcovers. Choosing between these systems depends on plant species, root depth, and water sensitivity to ensure optimal growth and resource efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Drip irrigation systems require precise installation with emitters placed near plant roots, demanding careful layout and regular checks for clogging to maintain efficiency. Sprinkler irrigation installation is generally less complex, involving the setup of pipes and sprinkler heads, but requires periodic inspection to prevent nozzle blockages and ensure uniform water distribution. Maintenance for drip systems tends to be more labor-intensive due to the need for filtering and flushing, whereas sprinkler systems need routine adjustments and repairs for heads and valves.
Cost Comparison: Drip vs Sprinkler Irrigation
Drip irrigation systems generally have higher initial installation costs due to the need for specialized tubing and emitters but offer greater water efficiency and reduced labor expenses over time. Sprinkler irrigation tends to be less expensive upfront with simpler setup but can lead to higher water usage and maintenance costs. Evaluating long-term savings and water conservation benefits makes drip irrigation a more cost-effective choice for sustainable agricultural practices.
Impact on Soil Health and Plant Growth
Drip irrigation promotes healthier soil by delivering water directly to the root zone, reducing soil erosion and nutrient leaching while maintaining optimal moisture levels for plant growth. Sprinkler irrigation can lead to surface runoff and soil compaction, which negatively affect soil structure and root development. Consistent moisture from drip systems enhances plant growth by ensuring efficient water use and minimizing fungal diseases commonly associated with overhead watering.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
Drip irrigation often faces clogging issues due to mineral deposits and debris in emitters, requiring regular filter cleaning and system flushing to ensure consistent water flow. Sprinkler irrigation commonly encounters uniformity problems caused by wind drift, nozzle wear, or pressure fluctuations, which can be addressed by adjusting sprinkler placement and maintaining proper pressure settings. Both systems benefit from routine inspection and maintenance to prevent leaks, blockages, and coverage inefficiencies.
Choosing the Right Irrigation Method for Your Garden
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the soil at the root zone, reducing evaporation and promoting efficient water use for gardens with diverse plant types or limited water supply. Sprinkler irrigation mimics natural rainfall, providing broad coverage suitable for lawns and evenly spaced plants but can lead to water loss through evaporation and wind drift. Selecting the right irrigation method depends on plant species, soil type, water availability, and garden layout to optimize growth and conserve resources.
Drip irrigation vs Sprinkler irrigation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com