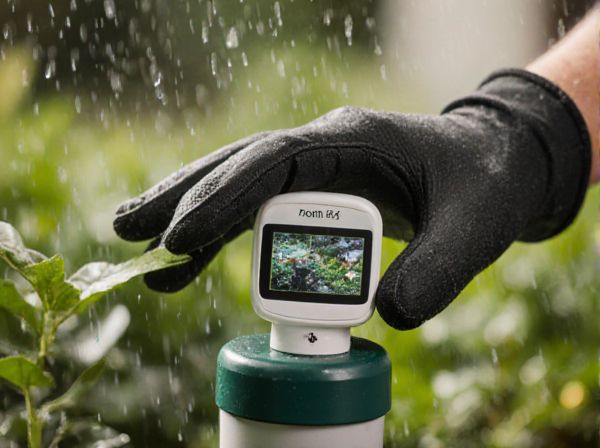

Rain gauge monitoring vs Soil moisture sensor monitoring Illustration
Rain gauge monitoring measures the amount of rainfall to estimate water availability, helping to adjust irrigation schedules based on precipitation data. Soil moisture sensor monitoring detects the actual moisture levels within the soil, providing precise information on when and how much to water for optimal plant health. Combining both methods enhances watering efficiency by balancing external weather inputs with real-time soil conditions.
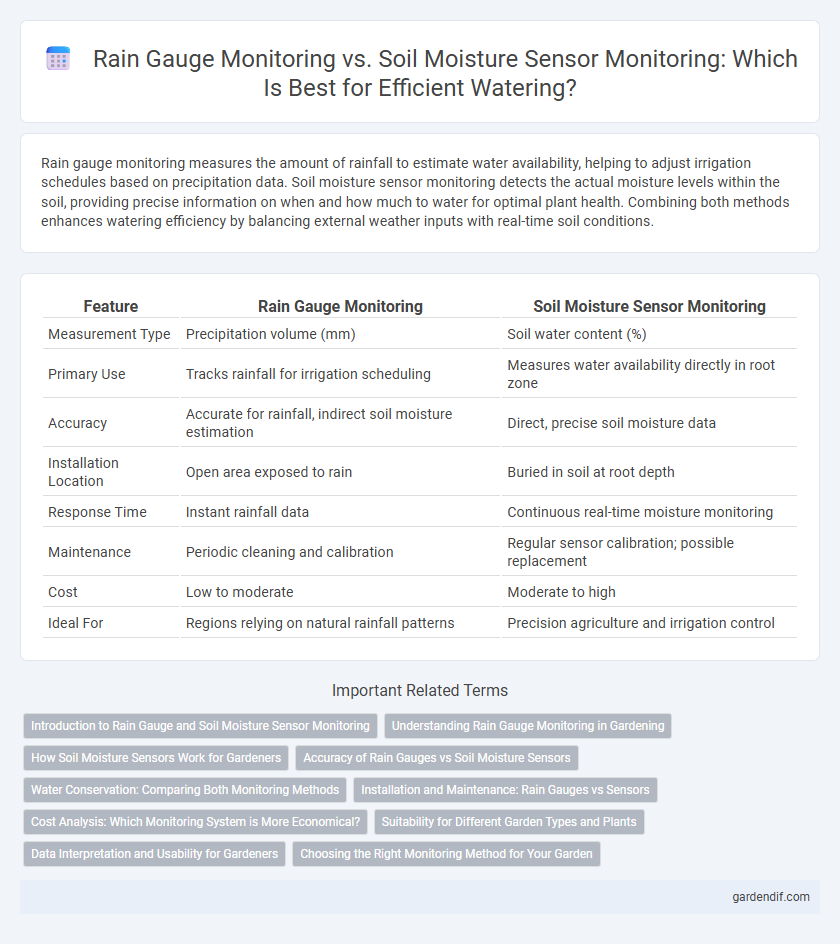
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rain Gauge Monitoring | Soil Moisture Sensor Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Precipitation volume (mm) | Soil water content (%) |
| Primary Use | Tracks rainfall for irrigation scheduling | Measures water availability directly in root zone |
| Accuracy | Accurate for rainfall, indirect soil moisture estimation | Direct, precise soil moisture data |
| Installation Location | Open area exposed to rain | Buried in soil at root depth |
| Response Time | Instant rainfall data | Continuous real-time moisture monitoring |
| Maintenance | Periodic cleaning and calibration | Regular sensor calibration; possible replacement |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Ideal For | Regions relying on natural rainfall patterns | Precision agriculture and irrigation control |
Introduction to Rain Gauge and Soil Moisture Sensor Monitoring
Rain gauge monitoring measures the amount of rainfall collected over a specific period, providing precise data on precipitation levels essential for efficient irrigation scheduling. Soil moisture sensor monitoring directly assesses the water content within the soil, delivering real-time information critical for maintaining optimal soil hydration and preventing overwatering. Both technologies enhance water management by enabling data-driven decisions tailored to crop and environmental conditions.
Understanding Rain Gauge Monitoring in Gardening
Rain gauge monitoring in gardening measures the precise amount of rainfall, allowing gardeners to adjust irrigation schedules based on actual precipitation data. Unlike soil moisture sensors that detect water content directly in the soil, rain gauges capture external water input to prevent overwatering and conserve water resources. Accurate rain gauge data supports efficient water management by aligning watering activities with natural rainfall patterns.
How Soil Moisture Sensors Work for Gardeners
Soil moisture sensors measure the volumetric water content directly in the root zone by detecting the dielectric constant of the soil, providing precise data on moisture levels where plants absorb water. Unlike rain gauges that track precipitation, these sensors enable gardeners to optimize irrigation schedules based on real-time soil moisture, preventing overwatering and promoting healthy root growth. This technology improves water efficiency and supports sustainable gardening practices by ensuring plants receive the exact amount of water needed.
Accuracy of Rain Gauges vs Soil Moisture Sensors
Rain gauge monitoring provides precise measurement of precipitation levels, capturing the exact volume of rainfall over a specific period. Soil moisture sensors deliver real-time data on water content in the soil, offering localized accuracy that accounts for soil heterogeneity and root zone conditions. While rain gauges measure external water input, soil moisture sensors directly assess the water available to plants, making them more accurate for irrigation management decisions.
Water Conservation: Comparing Both Monitoring Methods
Rain gauge monitoring measures rainfall amounts to determine irrigation needs, optimizing water use by preventing overwatering based on actual precipitation data. Soil moisture sensor monitoring provides real-time data on soil water content, allowing precise irrigation tailored to the plants' immediate needs and minimizing water waste. Combining both methods enhances water conservation by integrating environmental input with direct soil conditions, resulting in more efficient and sustainable watering practices.
Installation and Maintenance: Rain Gauges vs Sensors
Rain gauge installation involves placing a simple, weather-resistant device in an open area to accurately collect precipitation data with minimal setup effort. Soil moisture sensors require strategic placement at varying root depths and often need calibration for soil type, along with more frequent maintenance to ensure sensor accuracy and longevity. Maintenance for rain gauges primarily consists of occasional cleaning to prevent debris buildup, whereas soil moisture sensors demand regular inspection and recalibration to maintain precise moisture readings and avoid sensor damage.
Cost Analysis: Which Monitoring System is More Economical?
Rain gauge monitoring systems typically involve lower upfront costs, averaging around $20 to $50 for basic models, making them more affordable for widespread use. Soil moisture sensors, although initially more expensive, ranging from $50 to $150, provide precise data that can optimize irrigation schedules, potentially reducing water consumption and long-term costs. Cost efficiency depends on specific agricultural needs, where rain gauge systems suit budget-conscious users and soil moisture sensors benefit operations emphasizing water use optimization and crop yield improvements.
Suitability for Different Garden Types and Plants
Rain gauge monitoring is ideal for large gardens and lawns where measuring overall rainfall provides sufficient data for watering needs, especially for drought-tolerant plants. Soil moisture sensors are more suited for container gardens, raised beds, and plant-specific irrigation, offering precise moisture levels critical for sensitive or high-value plants like vegetables and herbs. Combining both tools allows gardeners to optimize water use by addressing both atmospheric input and soil conditions across diverse garden types.
Data Interpretation and Usability for Gardeners
Rain gauge monitoring provides precise measurement of precipitation levels, offering gardeners clear data on the amount of natural water their garden receives, which helps in adjusting supplemental watering schedules. Soil moisture sensor monitoring delivers real-time information about the actual water content in the soil, allowing for targeted irrigation specific to plant needs and minimizing water waste. Combining these data sources enhances usability by enabling gardeners to interpret weather conditions alongside soil hydration, resulting in more efficient and effective garden watering management.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Method for Your Garden
Rain gauge monitoring provides accurate data on rainfall amounts, helping gardeners understand natural water input and adjust supplemental watering schedules accordingly. Soil moisture sensor monitoring delivers real-time information on the water content within the soil, enabling precise irrigation tailored to the specific needs of plants. Selecting the right method depends on garden size, plant types, and local climate, with soil moisture sensors ideal for targeted watering and rain gauges better for tracking overall water availability.
Rain gauge monitoring vs Soil moisture sensor monitoring Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com