
Misting vs soaking Illustration
Misting provides a gentle spray that helps increase humidity and lightly moisten plant leaves without saturating the soil, perfect for delicate plants or seedlings. Soaking delivers deep, thorough watering that penetrates the soil, ensuring roots receive adequate moisture and preventing drought stress. Understanding when to mist versus soak depends on the plant's species, growth stage, and environmental conditions.
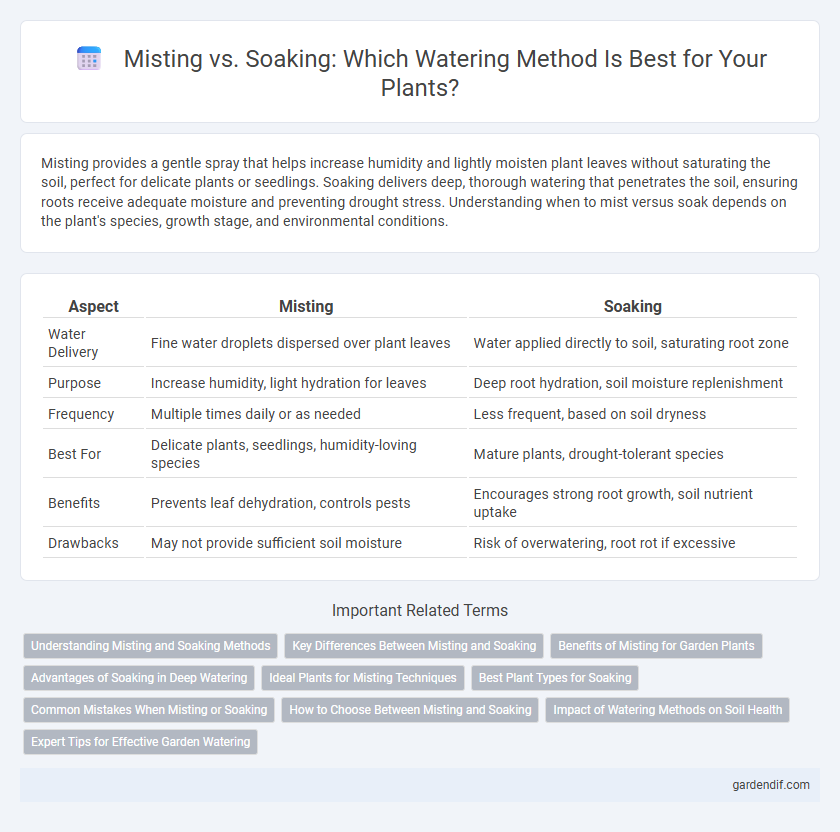
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Misting | Soaking |
|---|---|---|
| Water Delivery | Fine water droplets dispersed over plant leaves | Water applied directly to soil, saturating root zone |
| Purpose | Increase humidity, light hydration for leaves | Deep root hydration, soil moisture replenishment |
| Frequency | Multiple times daily or as needed | Less frequent, based on soil dryness |
| Best For | Delicate plants, seedlings, humidity-loving species | Mature plants, drought-tolerant species |
| Benefits | Prevents leaf dehydration, controls pests | Encourages strong root growth, soil nutrient uptake |
| Drawbacks | May not provide sufficient soil moisture | Risk of overwatering, root rot if excessive |
Understanding Misting and Soaking Methods
Misting involves applying a fine spray of water to maintain surface moisture and support delicate plants without saturating the soil, enhancing humidity. Soaking delivers deep, thorough watering that penetrates the root zone, ideal for drought-tolerant plants requiring substantial hydration. Understanding these methods helps optimize water usage and promotes healthier plant growth by matching watering techniques to specific plant needs.
Key Differences Between Misting and Soaking
Misting delivers a fine spray of water that lightly moistens plant leaves and soil surface, promoting humidity and reducing water waste, while soaking thoroughly saturates the soil to ensure deep root hydration and nutrient absorption. Misting is ideal for delicate plants or seedlings requiring gentle moisture without waterlogging, whereas soaking supports established plants needing consistent, deep watering to prevent root stress. The key differences lie in water volume, application method, and impact on plant health, with misting focusing on surface hydration and soaking targeting root zone moisture.
Benefits of Misting for Garden Plants
Misting garden plants helps maintain optimal humidity levels, reducing the risk of leaf dehydration and promoting healthier foliage. This method conserves water by delivering fine droplets directly to the plant surface, minimizing runoff and soil erosion. Misting also supports pest control by washing away dust and deterring insects without over-saturating the soil, which benefits overall plant growth.
Advantages of Soaking in Deep Watering
Soaking in deep watering ensures that moisture penetrates deeply into the soil, promoting robust root growth and improving plant drought resistance. This method reduces water runoff and evaporation compared to misting, delivering more efficient hydration to plants. Deep watering also minimizes the frequency of irrigation by maintaining soil moisture for longer periods, supporting healthier plant development.
Ideal Plants for Misting Techniques
Misting is ideal for plants that thrive in high humidity environments, such as ferns, orchids, and air plants, as it provides gentle moisture without waterlogging the soil. This technique suits plants with delicate leaves that can absorb water through their foliage, enhancing hydration and preventing dryness. Avoid misting succulents and cacti, which prefer deep watering to maintain healthy root systems and prevent rot.
Best Plant Types for Soaking
Succulent plants and cacti thrive best with soaking because their thick, water-storing tissues benefit from deep, infrequent watering that reaches the roots. Plants with extensive root systems like shrubs and trees also prefer soaking to ensure water penetrates deeply into the soil. Soaking suits plants in arid environments or those prone to root rot if watered superficially, promoting strong root growth and overall health.
Common Mistakes When Misting or Soaking
Overwatering by soaking can lead to root rot and suffocation due to poor soil aeration, while misting too frequently may cause fungal diseases and inadequate hydration. Many gardeners mistakenly assume misting replaces deep watering, resulting in shallow root growth and stressed plants. Proper watering requires balancing frequency and volume based on plant type, soil conditions, and environmental factors to avoid common hydration errors.
How to Choose Between Misting and Soaking
Choosing between misting and soaking depends on the plant's water requirements and soil drainage. Misting suits delicate plants and seedlings that need humidity without waterlogging, while soaking benefits drought-tolerant species needing deep hydration. Assess leaf texture, root depth, and environmental conditions to determine optimal watering methods for healthy growth.
Impact of Watering Methods on Soil Health
Misting maintains surface moisture without oversaturating soil, promoting optimal aeration and preventing root rot by avoiding waterlogged conditions common with soaking. Soaking deeply saturates the soil, which can lead to reduced oxygen availability for roots and increased risk of soil compaction, negatively affecting microbial activity and nutrient uptake. Choosing misting helps preserve soil structure and microbial balance, enhancing long-term soil health compared to frequent soaking.
Expert Tips for Effective Garden Watering
Misting is ideal for delicate seedlings and humidity-loving plants, providing gentle moisture without overwhelming their roots, while soaking deeply irrigates the soil, encouraging robust root growth essential for mature plants. Experts recommend misting in the early morning or late afternoon to minimize evaporation and using soaking methods infrequently but thoroughly to promote deep water penetration and healthy root development. Combining both techniques based on plant type and growth stage maximizes hydration efficiency and supports vibrant garden health.
Misting vs soaking Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com