
Seasonal Sun Angle vs Year-round Light Illustration
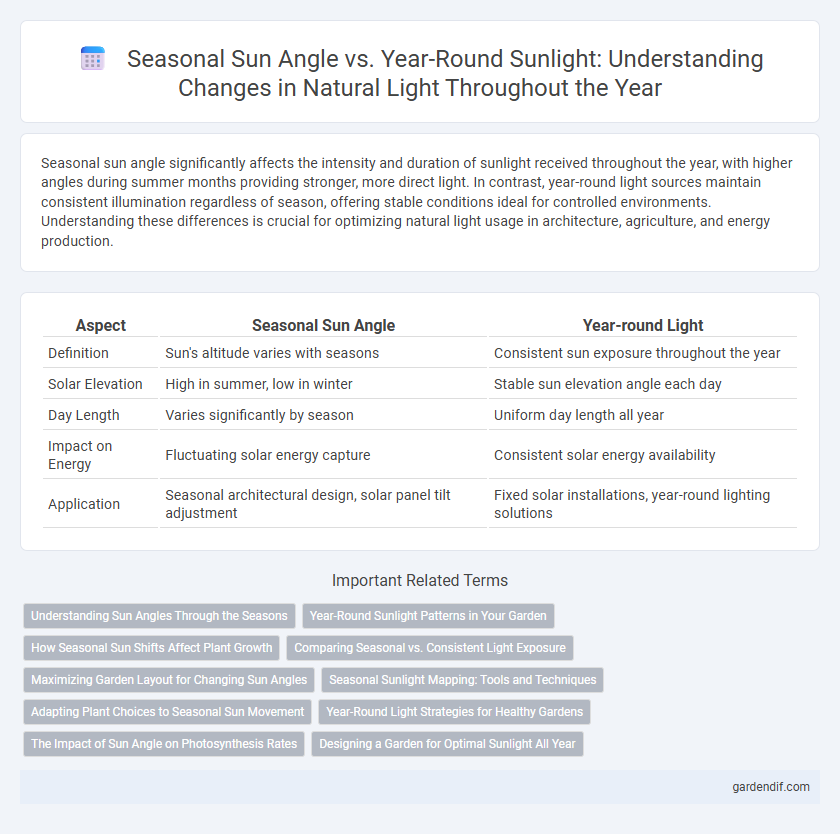
Seasonal sun angle significantly affects the intensity and duration of sunlight received throughout the year, with higher angles during summer months providing stronger, more direct light. In contrast, year-round light sources maintain consistent illumination regardless of season, offering stable conditions ideal for controlled environments. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing natural light usage in architecture, agriculture, and energy production.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Seasonal Sun Angle | Year-round Light |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sun's altitude varies with seasons | Consistent sun exposure throughout the year |
| Solar Elevation | High in summer, low in winter | Stable sun elevation angle each day |
| Day Length | Varies significantly by season | Uniform day length all year |
| Impact on Energy | Fluctuating solar energy capture | Consistent solar energy availability |
| Application | Seasonal architectural design, solar panel tilt adjustment | Fixed solar installations, year-round lighting solutions |
Understanding Sun Angles Through the Seasons
Seasonal sun angle variations significantly impact the intensity and duration of sunlight received at different latitudes throughout the year. During summer solstice, the sun reaches its highest elevation, providing longer daylight hours and stronger solar radiation, while the winter solstice yields the lowest sun angle and reduced light exposure. Understanding these sun angles is crucial for optimizing solar panel placement, architectural design, and agricultural planning to maximize year-round sunlight efficiency.
Year-Round Sunlight Patterns in Your Garden
Year-round sunlight patterns in your garden depend on the sun's seasonal angles, which shift between higher paths in summer and lower trajectories in winter. Understanding these variations allows for strategic plant placement to maximize exposure to consistent light, particularly for sun-loving species. Incorporating north-south garden orientations and selecting adaptable plant varieties optimizes growth despite changing sun angles throughout the year.
How Seasonal Sun Shifts Affect Plant Growth
Seasonal sun angle variations significantly influence plant growth by altering light intensity and duration throughout the year, affecting photosynthesis rates. During summer, higher sun angles provide prolonged, direct sunlight vital for robust development, while lower winter angles result in reduced light, slowing growth and dormancy in many plants. Understanding these shifts helps optimize planting schedules and species selection to align with natural sunlight patterns for optimal agricultural yield.
Comparing Seasonal vs. Consistent Light Exposure
Seasonal sun angle causes significant variations in light intensity and duration throughout the year, impacting plant growth cycles and energy absorption. In contrast, year-round consistent light exposure, such as that in equatorial regions or controlled environments, promotes steady photosynthesis and predictable biological rhythms. Comparing these conditions reveals how fluctuating sunlight shapes ecological adaptations while consistent exposure supports stable metabolic processes.
Maximizing Garden Layout for Changing Sun Angles
Seasonal sun angle variations significantly impact garden layout planning to maximize light exposure throughout the year. Designing with adjustable plant positioning and incorporating sun-loving species in areas with high summer sun angles ensures optimal photosynthesis during peak growth periods. Year-round light optimization involves selecting shade-tolerant plants for lower winter sun angles to maintain garden vitality during shorter daylight hours.
Seasonal Sunlight Mapping: Tools and Techniques
Seasonal sunlight mapping employs geographic information systems (GIS) and solar pathfinders to analyze sun angle variations throughout the year, crucial for optimizing building orientation and landscape design. Tools like digital elevation models (DEMs) integrate topographical data with solar geometry, enabling precise predictions of shading and solar exposure across different seasons. Techniques such as time-lapse sun path tracking and 3D modeling enhance accuracy in assessing seasonal sunlight patterns for energy efficiency and agricultural applications.
Adapting Plant Choices to Seasonal Sun Movement
Seasonal sun angle dramatically affects light intensity and duration, influencing optimal plant growth cycles. Selecting shade-tolerant species for low-angle winter sun and sun-loving plants for high-angle summer light maximizes photosynthesis efficiency. Adjusting plant placement according to seasonal sunlight patterns enhances growth and conserves energy in garden design.
Year-Round Light Strategies for Healthy Gardens
Maximizing year-round light availability in gardens involves strategic plant placement and utilizing reflective surfaces to enhance sunlight exposure during low-angle winter months. Employing vertical gardening and selecting light-adapted species ensures consistent photosynthesis and healthy growth despite seasonal sun angle variations. Incorporating adjustable shading systems enables control over light intensity, promoting optimal conditions throughout the year.
The Impact of Sun Angle on Photosynthesis Rates
Higher sun angles during summer increase light intensity and duration, significantly boosting photosynthesis rates by enhancing chlorophyll absorption efficiency. In contrast, lower sun angles in winter reduce light penetration and photon flux, limiting photosynthetic activity and plant growth. Year-round variations in sun angle directly influence carbon fixation rates and energy production in photosynthetic organisms.
Designing a Garden for Optimal Sunlight All Year
Designing a garden for optimal sunlight requires understanding the seasonal sun angle, which varies significantly from winter to summer, affecting light exposure duration and intensity. Incorporating plants that tolerate low winter sun angles while maximizing growth during the higher summer sun positions ensures year-round vitality. Strategic placement of sun-loving species in areas receiving maximum southern exposure enhances photosynthesis and garden productivity throughout all seasons.
Seasonal Sun Angle vs Year-round Light Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com