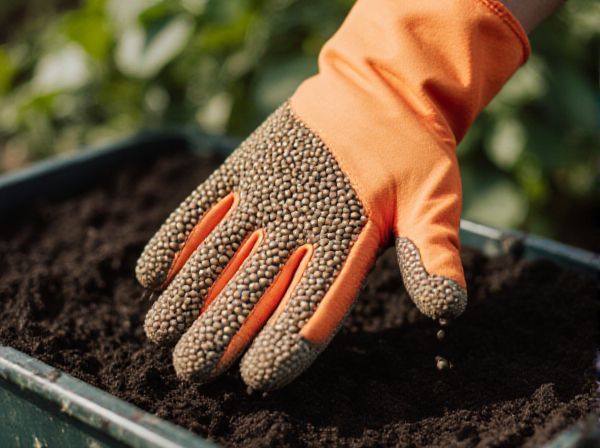

Pelleted seed vs Raw seed Illustration
Pelleted seeds offer enhanced precision in planting and improved germination rates compared to raw seeds due to their uniform size and shape, which facilitates better seed-to-soil contact. Raw seeds maintain their natural state, often resulting in variable seed spacing and potentially inconsistent emergence, but they require less processing and remain more cost-effective. Choosing between pelleted and raw seeds depends on the specific crop requirements, planting equipment, and desired growth uniformity.
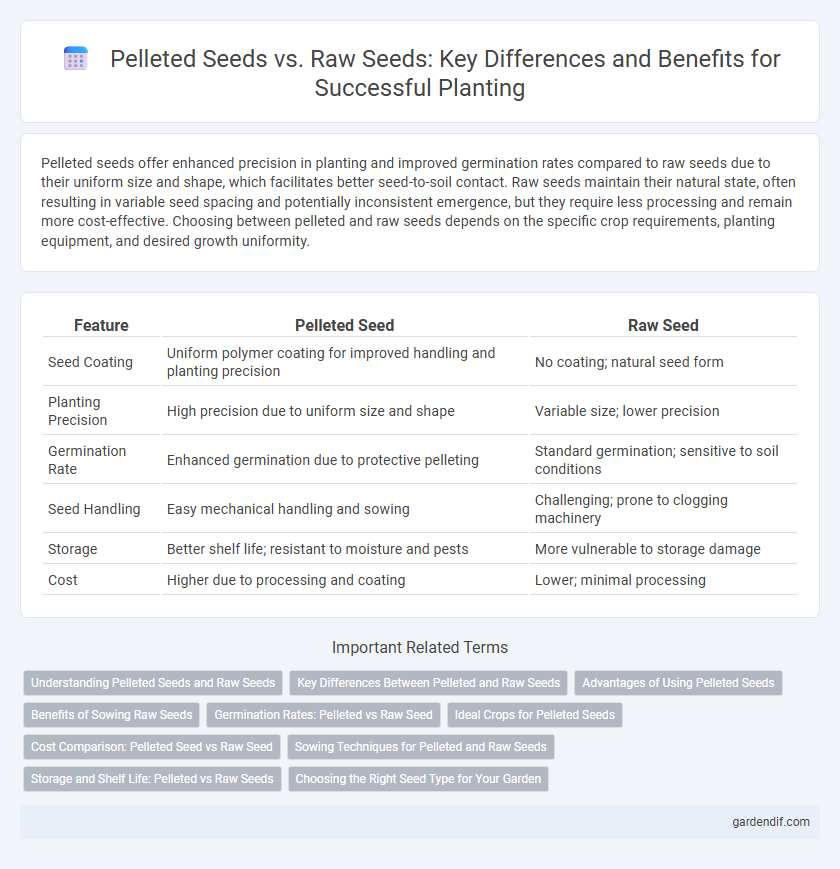
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pelleted Seed | Raw Seed |
|---|---|---|
| Seed Coating | Uniform polymer coating for improved handling and planting precision | No coating; natural seed form |
| Planting Precision | High precision due to uniform size and shape | Variable size; lower precision |
| Germination Rate | Enhanced germination due to protective pelleting | Standard germination; sensitive to soil conditions |
| Seed Handling | Easy mechanical handling and sowing | Challenging; prone to clogging machinery |
| Storage | Better shelf life; resistant to moisture and pests | More vulnerable to storage damage |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and coating | Lower; minimal processing |
Understanding Pelleted Seeds and Raw Seeds
Pelleted seeds are encased in a coating of inert material that enhances handling, planting precision, and protection from pests or diseases, making them ideal for crops requiring uniform spacing and germination. Raw seeds, in contrast, are untreated and maintain their natural form, often preferred by organic farmers for their untreated purity and potential for faster germination in suitable conditions. Understanding the differences between pelleted and raw seeds helps optimize planting strategies according to crop type, soil conditions, and desired yield outcomes.
Key Differences Between Pelleted and Raw Seeds
Pelleted seeds are coated with inert materials to improve seed size, shape, and handling, while raw seeds remain in their natural form, often irregular and varying in size. Pelleting enhances precision in sowing, promotes uniform germination, and protects seeds from pests and diseases by incorporating fungicides or insecticides. Raw seeds may be more cost-effective but can lead to uneven planting depth and germination rates compared to pelleted seeds.
Advantages of Using Pelleted Seeds
Pelleted seeds offer enhanced precision in planting by providing uniform size and shape, which facilitates accurate sowing and reduces seed wastage. The coating improves seed handling, protects against pests and diseases, and enhances germination rates through moisture retention and controlled release of nutrients. This technology ensures higher crop establishment and consistent seedling vigor compared to raw seeds.
Benefits of Sowing Raw Seeds
Sowing raw seeds promotes natural germination by allowing direct soil contact, enhancing moisture absorption and root penetration for healthier plant development. Raw seeds maintain genetic diversity and vigor, supporting ecosystem resilience and adaptability. This practice reduces costs and processing time, making it an eco-friendly and cost-effective choice for sustainable agriculture.
Germination Rates: Pelleted vs Raw Seed
Pelleted seeds exhibit improved germination rates compared to raw seeds due to their uniform shape and size, which facilitate better soil contact and moisture absorption. The coating on pelleted seeds also protects the embryo from environmental stressors, enhancing seedling vigor. Studies show pelleted seeds can increase germination success by up to 20% relative to untreated raw seeds.
Ideal Crops for Pelleted Seeds
Pelleted seeds are ideal for small, hard-to-handle seeds such as lettuce, carrot, and petunia due to their uniform size and shape, which facilitates precise planting and better germination rates. These seeds benefit crops requiring accurate spacing and depth control, including herbs like basil and flowers like snapdragons. In contrast, raw seeds are often preferred for larger seeds that do not require pelleting for handling or planting accuracy.
Cost Comparison: Pelleted Seed vs Raw Seed
Pelleted seed typically incurs higher upfront costs due to the additional processing and coating materials used to enhance seed handling and planting precision. Raw seed, lacking this treatment, is generally less expensive per unit but may result in increased planting inefficiencies and higher labor costs. Evaluating overall expenses requires considering both the initial purchase price and potential savings in planting accuracy and crop yield associated with pelleted seed.
Sowing Techniques for Pelleted and Raw Seeds
Pelleted seeds offer precise spacing and uniform depth during sowing, promoting consistent germination compared to raw seeds, which require careful manual handling to avoid uneven planting. Specialized sowing equipment designed for pelleted seeds enhances efficiency, while raw seeds often need traditional broadcasting or hand sowing methods that may reduce planting accuracy. Optimal sowing techniques for pelleted seeds include mechanical planters calibrated for size and weight, whereas raw seeds benefit from soil preparation that minimizes seed loss and ensures adequate soil contact.
Storage and Shelf Life: Pelleted vs Raw Seeds
Pelleted seeds offer enhanced storage stability by protecting the seed embryo from moisture and physical damage, extending shelf life significantly compared to raw seeds. Raw seeds are more susceptible to environmental factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and pests, often resulting in reduced viability over time. Proper storage conditions, including controlled temperature and humidity, further influence the shelf life disparity between pelleted and raw seeds, with pelleted seeds generally maintaining higher germination rates during prolonged storage.
Choosing the Right Seed Type for Your Garden
Pelleted seeds offer easier handling, precise spacing, and improved germination rates compared to raw seeds, making them ideal for gardeners seeking uniform plant growth. Raw seeds preserve natural seed coats but may require more careful sowing and longer germination times, suitable for experienced gardeners focusing on organic cultivation. Selecting pelleted seeds enhances planting efficiency and consistency, while raw seeds provide a cost-effective option with traditional planting methods.
Pelleted seed vs Raw seed Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com