
Heirloom seeds vs GMO seeds Illustration
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by offering open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, maintaining unique flavors and resilience. GMO seeds are genetically engineered for traits like pest resistance and higher yields, often leading to uniform crops but reduced biodiversity. Choosing heirloom seeds supports sustainable agriculture and seed sovereignty, while GMO seeds emphasize efficiency and large-scale production.
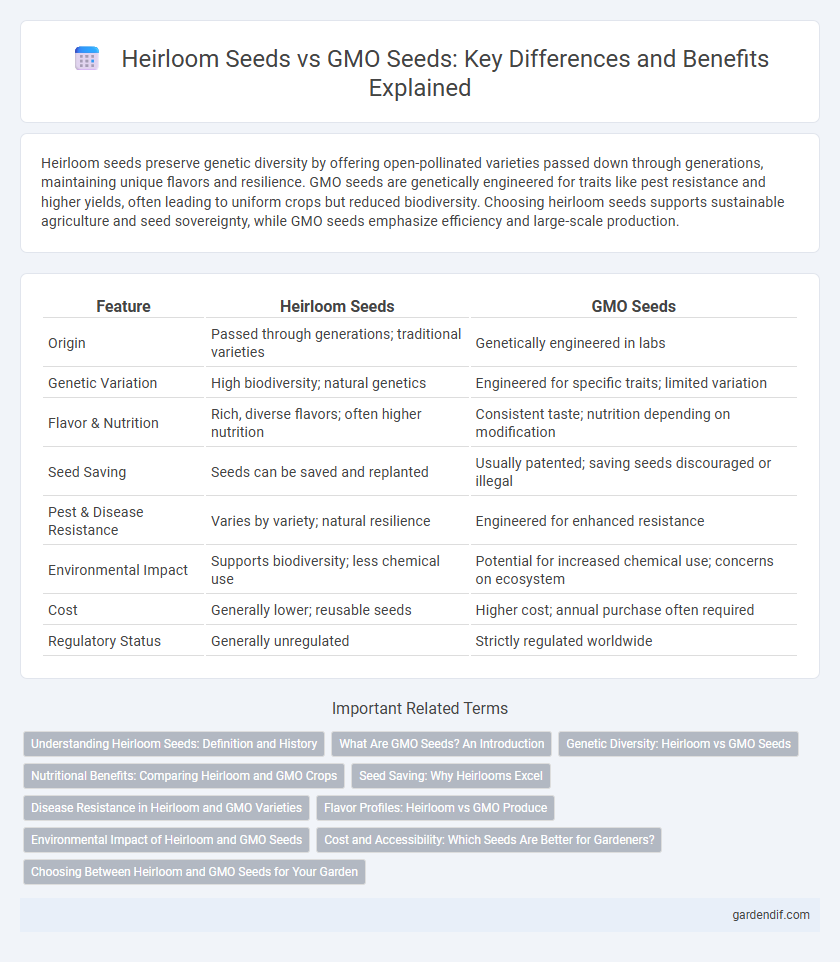
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom Seeds | GMO Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Passed through generations; traditional varieties | Genetically engineered in labs |
| Genetic Variation | High biodiversity; natural genetics | Engineered for specific traits; limited variation |
| Flavor & Nutrition | Rich, diverse flavors; often higher nutrition | Consistent taste; nutrition depending on modification |
| Seed Saving | Seeds can be saved and replanted | Usually patented; saving seeds discouraged or illegal |
| Pest & Disease Resistance | Varies by variety; natural resilience | Engineered for enhanced resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Supports biodiversity; less chemical use | Potential for increased chemical use; concerns on ecosystem |
| Cost | Generally lower; reusable seeds | Higher cost; annual purchase often required |
| Regulatory Status | Generally unregulated | Strictly regulated worldwide |
Understanding Heirloom Seeds: Definition and History
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated seeds passed down through generations, valued for preserving genetic diversity and traditional flavors. Originating before the widespread use of industrial agriculture and genetic modification, these seeds maintain traits adapted to local climates and soils. Unlike GMO seeds engineered for uniformity and specific traits, heirloom seeds offer rich biodiversity and cultural heritage in agriculture.
What Are GMO Seeds? An Introduction
GMO seeds are genetically modified organisms engineered by altering their DNA to enhance traits such as pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, or increased yield. Unlike heirloom seeds, which are open-pollinated and preserved through traditional breeding methods, GMO seeds result from advanced biotechnology techniques like gene splicing. These modifications aim to improve agricultural efficiency and crop performance under various environmental conditions.
Genetic Diversity: Heirloom vs GMO Seeds
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity through open pollination and natural seed saving, allowing adaptation to local environments and resilience against pests and diseases. GMO seeds offer specific genetic modifications targeting traits like pest resistance or herbicide tolerance but often reduce genetic variability within crops. Maintaining heirloom seed varieties supports agricultural biodiversity crucial for ecosystem stability and long-term food security.
Nutritional Benefits: Comparing Heirloom and GMO Crops
Heirloom seeds produce crops with higher antioxidant levels and richer nutrient profiles compared to many GMO seeds, which often prioritize traits like pest resistance or herbicide tolerance over nutrition. Studies reveal that heirloom varieties contain greater vitamin content and secondary metabolites beneficial for human health. Nutritional differences arise from genetic diversity in heirloom crops, enhancing micronutrients like vitamins A, C, and E, while GMO seeds typically focus on yield and resistance traits.
Seed Saving: Why Heirlooms Excel
Heirloom seeds excel in seed saving due to their open-pollinated nature, allowing gardeners to collect and replant seeds while preserving genetic traits and biodiversity. Unlike GMO seeds, which are often patented and genetically modified for specific traits, heirlooms provide true-to-type plants year after year without legal restrictions. This trait ensures sustainable gardening practices and supports local ecosystems by maintaining seed diversity and resilience.
Disease Resistance in Heirloom and GMO Varieties
Heirloom seeds offer natural disease resistance developed through generations of selective breeding, often tailored to local environmental conditions. GMO seeds incorporate specific genes engineered for enhanced resistance to particular diseases, providing more targeted protection against pathogens. While heirloom varieties contribute to biodiversity and resilience, GMO seeds deliver consistent, scientifically optimized disease resistance traits.
Flavor Profiles: Heirloom vs GMO Produce
Heirloom seeds produce fruits and vegetables with rich, complex flavor profiles that reflect their traditional cultivation methods and genetic diversity. In contrast, GMO seeds are often engineered for traits like pest resistance and higher yields, which can lead to a more uniform but sometimes less intense flavor. Studies highlight that heirloom produce tends to offer superior taste experiences compared to the often milder flavors found in GMO-grown crops.
Environmental Impact of Heirloom and GMO Seeds
Heirloom seeds promote biodiversity by preserving a wide variety of plant genetics, which enhances ecosystem resilience and supports sustainable agriculture. In contrast, GMO seeds can lead to reduced genetic diversity due to monoculture practices and raise concerns about potential long-term environmental effects, such as gene transfer to wild plants. The use of heirloom seeds generally results in lower chemical inputs, minimizing soil and water pollution compared to some GMO crops engineered for herbicide tolerance.
Cost and Accessibility: Which Seeds Are Better for Gardeners?
Heirloom seeds are generally more affordable and accessible to home gardeners because they can be saved and replanted year after year without loss of genetic traits, lowering long-term costs. GMO seeds often come with higher initial prices and licensing fees, limiting accessibility to commercial growers and increasing overall investment for gardeners. The choice between heirloom and GMO seeds depends on budget constraints and the desire for seed-saving advantages versus potential yield improvements.
Choosing Between Heirloom and GMO Seeds for Your Garden
Selecting between heirloom and GMO seeds for your garden hinges on priorities such as genetic diversity, flavor, and environmental impact. Heirloom seeds offer unique, open-pollinated varieties with rich heritage and diverse traits, promoting biodiversity and traditional flavors. GMO seeds provide engineered resistance to pests and diseases, higher yield potential, and consistent crop performance, ideal for maximizing productivity in challenging growing conditions.
Heirloom seeds vs GMO seeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com