
Dry seed storage vs Wet seed storage Illustration
Dry seed storage maintains seed viability longer by reducing moisture content, which prevents fungal growth and metabolic activity that can lead to deterioration. In contrast, wet seed storage increases the risk of seed rot and fungal infections due to higher humidity levels, resulting in reduced germination rates. Proper drying before storage is essential for preserving seed quality and ensuring successful crop establishment.
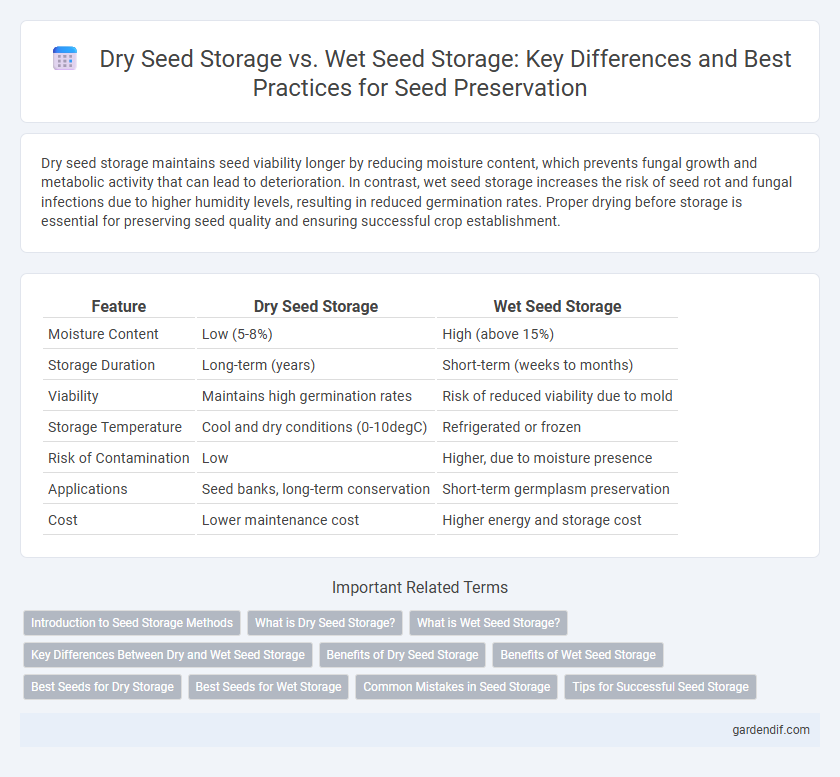
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dry Seed Storage | Wet Seed Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | Low (5-8%) | High (above 15%) |
| Storage Duration | Long-term (years) | Short-term (weeks to months) |
| Viability | Maintains high germination rates | Risk of reduced viability due to mold |
| Storage Temperature | Cool and dry conditions (0-10degC) | Refrigerated or frozen |
| Risk of Contamination | Low | Higher, due to moisture presence |
| Applications | Seed banks, long-term conservation | Short-term germplasm preservation |
| Cost | Lower maintenance cost | Higher energy and storage cost |
Introduction to Seed Storage Methods
Dry seed storage preserves seed viability by reducing moisture content to optimal levels, typically below 8%, which inhibits fungal growth and metabolic activity. Wet seed storage, involving seeds stored with higher moisture, is less common due to increased risks of mold development and reduced lifespan. Proper temperature control in dry seed storage environments, usually around 0-5degC, further extends seed longevity and genetic stability for future planting.
What is Dry Seed Storage?
Dry seed storage involves maintaining seeds in low moisture conditions, typically below 8-10% water content, to preserve viability and prevent fungal growth. It ensures long-term seed longevity by reducing metabolic activity and minimizing deterioration. This method is commonly used in seed banks and conservation facilities for effective germplasm preservation.
What is Wet Seed Storage?
Wet seed storage involves preserving seeds in a high-moisture environment to maintain viability for specific plant species requiring hydration for germination. This method is often used for short-term storage of recalcitrant seeds that cannot withstand drying or freezing without losing viability. Proper wet seed storage requires controlled temperature and humidity to prevent fungal growth and seed deterioration.
Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Seed Storage
Dry seed storage maintains seed viability by keeping moisture content low, typically below 12%, which reduces metabolic activity and prevents fungal growth. Wet seed storage involves storing seeds in a hydrated state, often submerged in water or moist conditions, which can accelerate germination but increases susceptibility to mold and decay. The key differences lie in moisture levels, storage duration--dry seeds last longer--and preservation methods tailored to seed type and intended use.
Benefits of Dry Seed Storage
Dry seed storage significantly enhances seed longevity by reducing moisture content, which minimizes metabolic activity and prevents fungal growth, thus preserving viability over extended periods. This method allows for stable, long-term genetic conservation, crucial for agricultural biodiversity and seed banks. Maintaining seeds in low-humidity, cool environments ensures optimal germination rates and reduces the risk of spoilage compared to wet seed storage.
Benefits of Wet Seed Storage
Wet seed storage maintains seed viability by preserving moisture content crucial for metabolic processes, enhancing germination rates compared to dry storage. This method reduces the risk of seed coat cracking and preserves enzyme activity, which supports faster and more uniform seedling emergence. Furthermore, wet storage mitigates oxidative stress, protecting seeds from deterioration during extended storage periods.
Best Seeds for Dry Storage
Seeds such as wheat, barley, and sunflower are best suited for dry seed storage due to their low moisture content, which helps maintain viability and prevents fungal growth. Dry storage conditions with temperatures below 10degC and humidity levels under 40% are ideal for preserving seed longevity. This method ensures that orthodox seeds retain their germination capacity for several years compared to wet storage techniques.
Best Seeds for Wet Storage
Best seeds for wet storage include rice, oats, and certain legumes like chickpeas, which tolerate higher moisture levels without germination or spoilage. Wet seed storage requires controlled temperature and oxygen levels to prevent fungal growth and maintain seed viability over time. Selecting seeds with naturally higher moisture resilience ensures optimal preservation and successful germination after storage.
Common Mistakes in Seed Storage
Common mistakes in dry seed storage include storing seeds at improper humidity levels, which can cause mold growth or loss of seed viability due to desiccation. In wet seed storage, high moisture content often leads to fungal infections and rapid seed deterioration, reducing germination rates. Proper control of temperature and moisture is critical to prevent microbial contamination and maintain seed longevity in both storage methods.
Tips for Successful Seed Storage
Dry seed storage requires maintaining moisture content below 8% and storing seeds in airtight, cool environments around 4degC to maximize longevity and viability. In contrast, wet seed storage involves keeping seeds hydrated but demands strict temperature control and sterilization to prevent microbial growth. Using moisture-proof containers and regularly monitoring seed condition are essential tips for successful seed storage regardless of the method.
Dry seed storage vs Wet seed storage Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com