
Native seeds vs Invasive seeds Illustration
Native seeds are adapted to local climates and ecosystems, supporting biodiversity and soil health by promoting the growth of plants that co-evolved with native wildlife. Invasive seeds often lead to fast-spreading plants that outcompete native species, disrupting habitats and reducing biodiversity. Choosing native seeds enhances ecological balance and sustainability in landscaping and restoration projects.
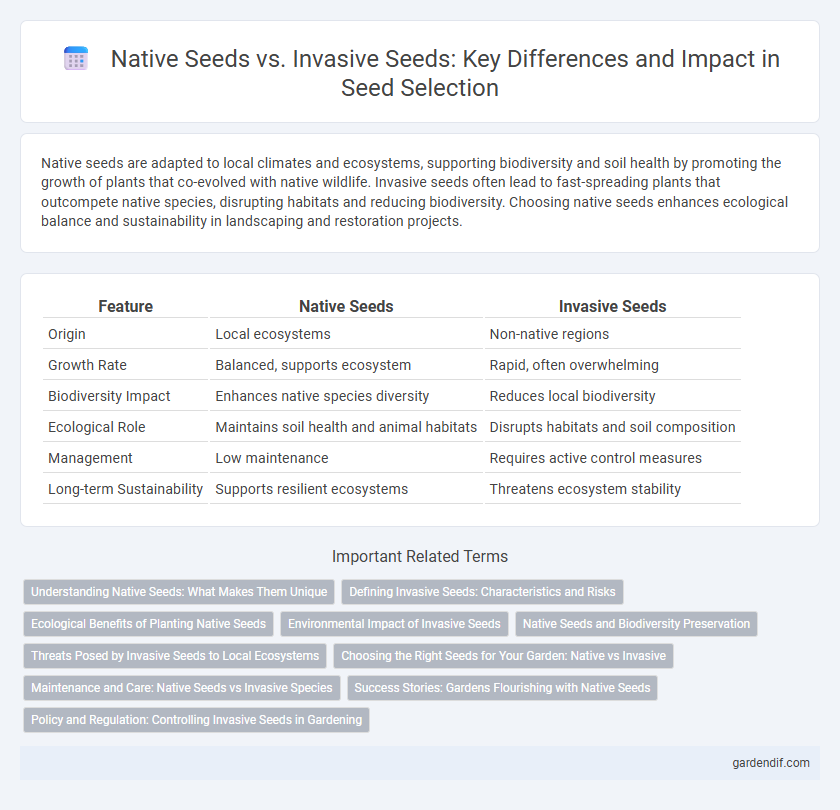
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Native Seeds | Invasive Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Local ecosystems | Non-native regions |
| Growth Rate | Balanced, supports ecosystem | Rapid, often overwhelming |
| Biodiversity Impact | Enhances native species diversity | Reduces local biodiversity |
| Ecological Role | Maintains soil health and animal habitats | Disrupts habitats and soil composition |
| Management | Low maintenance | Requires active control measures |
| Long-term Sustainability | Supports resilient ecosystems | Threatens ecosystem stability |
Understanding Native Seeds: What Makes Them Unique
Native seeds are genetically adapted to local environmental conditions, ensuring better survival rates and ecosystem compatibility. They support biodiversity by providing essential habitats and food sources for native wildlife. Unlike invasive seeds, native seeds contribute to soil health and ecosystem stability without disrupting existing plant communities.
Defining Invasive Seeds: Characteristics and Risks
Invasive seeds refer to those from plant species that rapidly spread beyond their native range, often outcompeting local flora and disrupting ecosystems. These seeds are typically characterized by high germination rates, vigorous growth, and adaptability to diverse environments, enabling them to dominate habitats. The risks associated with invasive seeds include loss of biodiversity, alteration of soil chemistry, and negative impacts on native plant populations and wildlife that depend on indigenous species.
Ecological Benefits of Planting Native Seeds
Planting native seeds supports local biodiversity by providing essential habitat and food sources for native wildlife, including pollinators and birds. Native plants are adapted to regional climate and soil conditions, which enhances soil health, reduces erosion, and promotes sustainable water use. Unlike invasive seeds, native seeds maintain ecosystem balance and prevent the spread of aggressive species that can disrupt native plant communities.
Environmental Impact of Invasive Seeds
Invasive seeds produce plant species that aggressively outcompete native vegetation, leading to reduced biodiversity and disrupted ecosystems. Their rapid growth and spread alter soil chemistry and water availability, causing long-term damage to habitats and native wildlife. Controlling invasive seeds is critical for preserving the balance of local environments and maintaining ecological resilience.
Native Seeds and Biodiversity Preservation
Native seeds play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity by supporting local ecosystems and maintaining genetic diversity unique to specific regions. Unlike invasive seeds, native seeds promote the growth of indigenous plants that provide habitat and food sources for native wildlife, contributing to ecological balance. Utilizing native seeds in restoration projects helps prevent the spread of invasive species and supports long-term ecosystem resilience.
Threats Posed by Invasive Seeds to Local Ecosystems
Invasive seeds disrupt local ecosystems by outcompeting native species for nutrients, water, and light, leading to reduced biodiversity and altered habitat structures. These seeds often produce plants that lack natural predators or diseases in the new environment, allowing unchecked proliferation and dominance. The resulting ecological imbalance can cause soil degradation, negatively impact pollinators, and diminish the resilience of native plant communities to environmental stressors.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Your Garden: Native vs Invasive
Choosing native seeds for your garden supports local ecosystems by providing habitat and food sources for indigenous wildlife, promoting biodiversity, and ensuring plants are well-adapted to regional climate and soil conditions. Invasive seeds, however, can outcompete native species, disrupt ecological balance, and lead to long-term environmental damage. Prioritizing native seeds enhances soil health, conserves water, and fosters a resilient, sustainable garden environment.
Maintenance and Care: Native Seeds vs Invasive Species
Native seeds require less maintenance and care as they are adapted to local climate, soil, and ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and soil health naturally. Invasive seeds often demand aggressive management, including frequent removal and chemical control, to prevent them from overwhelming native plant populations. Proper care of native plants reduces water usage and minimizes pest outbreaks, making them more sustainable and ecologically beneficial compared to invasive species.
Success Stories: Gardens Flourishing with Native Seeds
Gardens planted exclusively with native seeds have demonstrated remarkable resilience and biodiversity, thriving in their natural ecosystems without the need for excessive watering or chemical inputs. Successful restoration projects, such as those in California's coastal prairies and the Great Plains, showcase how native seed use supports pollinators, improves soil health, and sustains long-term plant communities. These success stories emphasize the ecological and economic benefits of prioritizing native seeds over invasive species, which often disrupt local habitats and reduce native biodiversity.
Policy and Regulation: Controlling Invasive Seeds in Gardening
Effective policy and regulation play a critical role in controlling invasive seeds in gardening by restricting the sale and distribution of non-native plant species known to disrupt local ecosystems. Government agencies often enforce quarantine measures and require certification for seed sources to prevent the introduction of invasive seeds. Strengthening these regulatory frameworks ensures that native seeds are prioritized, promoting biodiversity and protecting native habitats from ecological damage caused by invasive plants.
Native seeds vs Invasive seeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com