
Potting Soil vs Seed Starting Mix Illustration
Potting soil is formulated to provide nutrients and drainage for established plants, containing a blend of peat, compost, and sometimes perlite or vermiculite. Seed starting mix is lighter, sterile, and finely textured to support delicate seed germination without risk of disease or nutrient overload. Choosing the right medium ensures optimal root development and healthy propagation success.
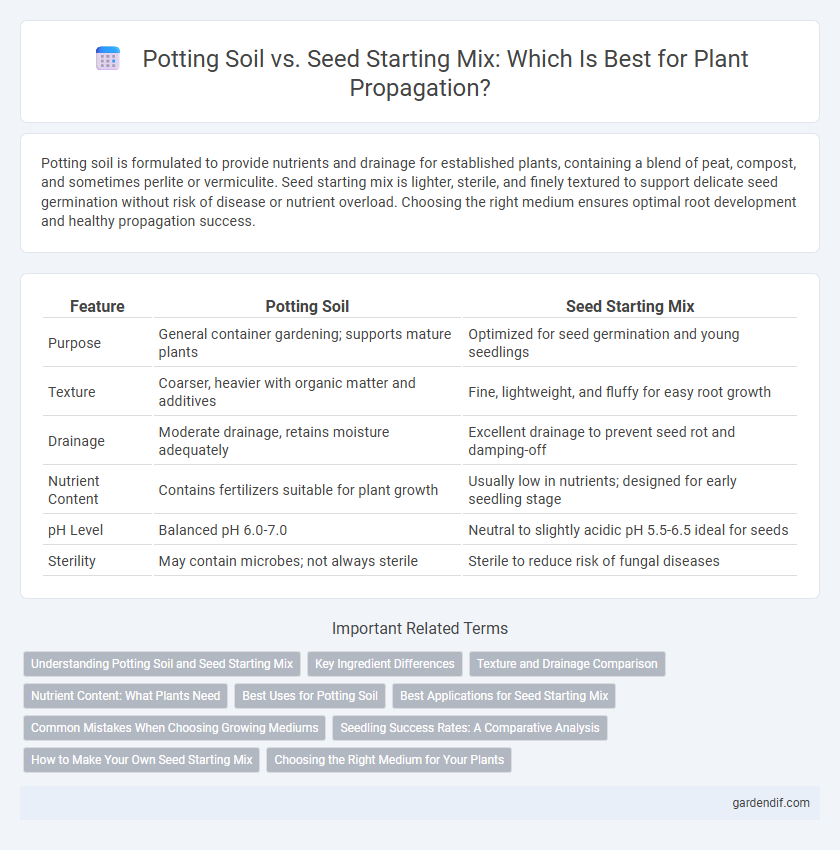
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Potting Soil | Seed Starting Mix |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | General container gardening; supports mature plants | Optimized for seed germination and young seedlings |
| Texture | Coarser, heavier with organic matter and additives | Fine, lightweight, and fluffy for easy root growth |
| Drainage | Moderate drainage, retains moisture adequately | Excellent drainage to prevent seed rot and damping-off |
| Nutrient Content | Contains fertilizers suitable for plant growth | Usually low in nutrients; designed for early seedling stage |
| pH Level | Balanced pH 6.0-7.0 | Neutral to slightly acidic pH 5.5-6.5 ideal for seeds |
| Sterility | May contain microbes; not always sterile | Sterile to reduce risk of fungal diseases |
Understanding Potting Soil and Seed Starting Mix
Potting soil is a versatile growing medium formulated with a blend of peat moss, composted bark, and perlite or vermiculite, designed to provide nutrients and retain moisture for mature plants in containers. Seed starting mix is a lightweight, fine-textured medium, typically free of added fertilizers, composed mainly of peat moss and vermiculite to promote optimal aeration and drainage for delicate seed germination. Understanding the differences in composition and purpose between potting soil and seed starting mix is essential for successful plant propagation and healthy seedling development.
Key Ingredient Differences
Potting soil typically contains a blend of peat moss, composted bark, and perlite or vermiculite, providing nutrients and good drainage for established plants. Seed starting mix is primarily composed of fine-textured peat moss or coconut coir with vermiculite, offering a lightweight, sterile medium optimized for moisture retention and delicate seedling roots. The absence of compost in seed starting mix prevents damping-off disease, ensuring optimal seed germination.
Texture and Drainage Comparison
Potting soil has a coarser texture with larger particles, providing excellent drainage and aeration suitable for established plants, while seed starting mix features a finer, lightweight texture designed to retain moisture and support delicate seedling roots. Seed starting mix typically contains less organic matter and no added fertilizers, promoting optimal germination without waterlogging, whereas potting soil's denser composition can hold more moisture but may reduce oxygen availability for young seedlings. Effective propagation depends on selecting seed starting mix for its superior drainage and gentle support during early growth stages, contrasting with potting soil's role in sustaining mature plants.
Nutrient Content: What Plants Need
Potting soil contains higher nutrient levels essential for sustained growth, making it ideal for transplanting established seedlings or container plants. Seed starting mix is designed with minimal nutrients to prevent burning delicate seedlings and promotes healthy root development during germination. Choosing the right medium based on nutrient content ensures optimal plant health and growth throughout propagation stages.
Best Uses for Potting Soil
Potting soil is best used for transplanting seedlings and growing mature plants in containers due to its rich organic matter and nutrient content that support longer-term growth. It provides improved drainage and aeration compared to garden soil, making it ideal for potted plants, houseplants, and container gardens. Potting soil's ability to retain moisture while preventing waterlogging helps maintain healthy root development during the propagation and growth stages.
Best Applications for Seed Starting Mix
Seed starting mix is specially formulated with fine particles and lightweight materials to promote optimal seed germination and young root development. Its sterile composition minimizes the risk of diseases and damping-off commonly encountered in early growth stages. Ideal applications include sowing delicate seeds, starting seedlings indoors, and nurturing transplants before moving them to heavier potting soil.
Common Mistakes When Choosing Growing Mediums
Choosing potting soil instead of seed starting mix can hinder germination due to its dense texture and higher nutrient content, which may damage delicate seedlings. Seed starting mix is finely textured and sterile, providing optimal aeration and moisture retention necessary for young seeds to sprout successfully. Avoid using garden soil or heavy potting mix for seed starting as it often contains pathogens and poor drainage, leading to damping-off disease and poor seedling development.
Seedling Success Rates: A Comparative Analysis
Seed starting mix is finely textured and formulated to provide optimal aeration, moisture retention, and nutrient availability, significantly increasing seedling success rates compared to potting soil. Potting soil's coarser composition and higher nutrient concentration can hinder delicate seed germination, often leading to lower emergence and growth consistency. Studies show seedlings in seed starting mix experience up to 30% higher germination rates and healthier root development, promoting stronger early-stage growth.
How to Make Your Own Seed Starting Mix
Creating your own seed starting mix involves combining finely textured materials such as peat moss or coconut coir with perlite or vermiculite to ensure optimal aeration and moisture retention. Incorporate a small amount of compost or worm castings to provide essential nutrients without overwhelming delicate seedlings. Adjust the mix ratio to approximately 2 parts peat moss or coir, 1 part perlite or vermiculite, and 0.5 parts compost for balanced drainage and fertility tailored to seed germination.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Plants
Potting soil contains a balanced mix of organic materials and nutrients ideal for established plants, while seed starting mix is lightweight, sterile, and designed to provide excellent drainage and aeration for fragile seeds and seedlings. Choosing the right medium depends on the plant stage: use seed starting mix for germination to prevent damping-off disease and potting soil for transplanting young plants to support robust root development. Selecting the appropriate growing medium ensures optimal moisture retention, nutrient availability, and root health for successful propagation.
Potting Soil vs Seed Starting Mix Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com