
Leaf Cuttings vs Stem Cuttings Illustration
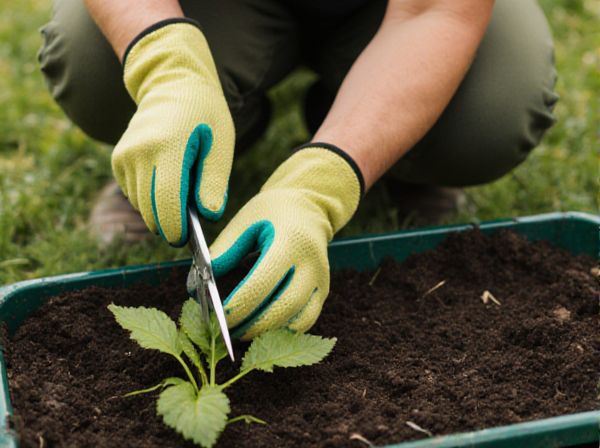
Leaf cuttings involve propagating plants using a single leaf or a leaf section, making them ideal for species like succulents and begonias that readily develop roots and new shoots from leaf tissue. Stem cuttings use a portion of the stem, often with nodes, to produce new plants, which is effective for a wider range of plants such as roses, coleus, and many shrubs due to the presence of meristematic cells promoting root growth. Choosing between leaf and stem cuttings depends on the plant species and desired propagation speed, as stem cuttings generally root faster and produce more vigorous plants.
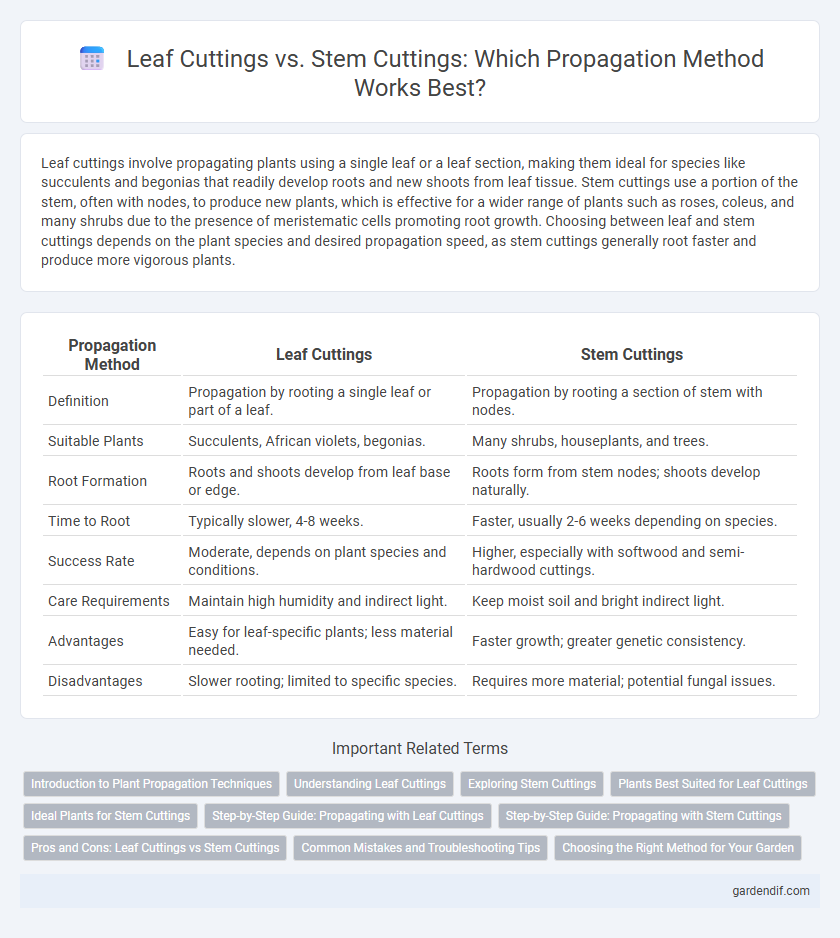
Table of Comparison
| Propagation Method | Leaf Cuttings | Stem Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Propagation by rooting a single leaf or part of a leaf. | Propagation by rooting a section of stem with nodes. |
| Suitable Plants | Succulents, African violets, begonias. | Many shrubs, houseplants, and trees. |
| Root Formation | Roots and shoots develop from leaf base or edge. | Roots form from stem nodes; shoots develop naturally. |
| Time to Root | Typically slower, 4-8 weeks. | Faster, usually 2-6 weeks depending on species. |
| Success Rate | Moderate, depends on plant species and conditions. | Higher, especially with softwood and semi-hardwood cuttings. |
| Care Requirements | Maintain high humidity and indirect light. | Keep moist soil and bright indirect light. |
| Advantages | Easy for leaf-specific plants; less material needed. | Faster growth; greater genetic consistency. |
| Disadvantages | Slower rooting; limited to specific species. | Requires more material; potential fungal issues. |
Introduction to Plant Propagation Techniques
Leaf cuttings involve using a single leaf or leaf section to grow a new plant, making them ideal for species like African violets and begonias. Stem cuttings consist of cutting a portion of the stem with nodes to propagate plants such as coleus and rosemary, promoting root development along the nodes. Both techniques serve as fundamental propagation methods, enabling gardeners to clone plants efficiently and maintain genetic consistency.
Understanding Leaf Cuttings
Leaf cuttings involve using an entire leaf, or a portion of it, to propagate new plants by encouraging roots and shoots to develop from the leaf tissue. This method is particularly effective for succulent species and plants like African violets, where a single leaf can generate a complete new plant. Understanding the cellular regeneration and nutrient distribution in leaf cuttings is crucial for successful propagation and growth optimization.
Exploring Stem Cuttings
Stem cuttings involve taking a section of a plant's stem, typically 4 to 6 inches long, equipped with nodes and leaves to encourage root development. This propagation method is highly effective for woody and soft-stemmed plants such as roses, coleus, and hydrangeas due to the stem's ability to produce roots and new shoots. Proper preparation includes removing lower leaves, applying rooting hormone, and placing cuttings in a well-draining medium to optimize root formation and increase propagation success rates.
Plants Best Suited for Leaf Cuttings
Leaf cuttings are best suited for succulent plants such as African violets, begonias, and snake plants, which have fleshy leaves capable of generating roots and shoots independently. These plants efficiently propagate through leaf cuttings due to their ability to store water and nutrients within leaf tissues, supporting root development. In contrast, woody or non-succulent plants generally require stem cuttings for successful propagation.
Ideal Plants for Stem Cuttings
Ideal plants for stem cuttings include many woody shrubs, soft-stemmed perennials, and certain houseplants like pothos and coleus, which root quickly and reliably. Woody plants such as hibiscus, rosemary, and camellia respond well to semi-hardwood cuttings taken during the growing season. Herbaceous plants like geraniums and fuchsia also propagate effectively from soft stem cuttings, making them preferred choices for stem-based propagation methods.
Step-by-Step Guide: Propagating with Leaf Cuttings
To propagate using leaf cuttings, start by selecting a healthy, mature leaf and gently detach it from the parent plant without causing damage. Prepare a sterile, well-draining potting mix and place the leaf flat or slightly inserted with its cut edge in the soil, maintaining consistent moisture and indirect light. Over several weeks, roots and new shoots will develop from the leaf base, signaling successful propagation before transplanting into individual pots.
Step-by-Step Guide: Propagating with Stem Cuttings
Propagating with stem cuttings involves selecting a healthy, semi-hardwood stem approximately 6-8 inches long, cutting just below a node to maximize root development. Remove the lower leaves to prevent rot, dip the cut end in rooting hormone to stimulate root growth, and plant it in well-draining propagation medium such as a mix of peat and perlite. Maintain consistent moisture and high humidity around the cutting, providing indirect light until roots establish, which typically occurs within 2-4 weeks.
Pros and Cons: Leaf Cuttings vs Stem Cuttings
Leaf cuttings offer a simple, low-cost propagation method ideal for plants like succulents and begonias, promoting faster root development with minimal damage to the parent plant. However, they often result in slower overall growth and limited plant development compared to stem cuttings. Stem cuttings enable propagation of a wider variety of species with higher success rates in producing mature plants but require more care to prevent disease and higher resource investment.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting Tips
Leaf cuttings often suffer from overwatering, leading to rot, while stem cuttings may fail due to insufficient humidity causing dehydration. Ensuring proper drainage and maintaining consistent moisture levels are crucial for both methods to promote root development. Using a sterile cutting tool and placing cuttings in a warm, well-lit environment without direct sunlight helps prevent fungal infections and enhances propagation success.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden
Leaf cuttings work best for plants like succulents and African violets, where new growth arises from a single leaf, ensuring faster root development and minimal space. Stem cuttings are ideal for woody or herbaceous plants such as roses and coleus, promoting robust plant structure through nodes that generate roots and shoots. Selecting the appropriate propagation method depends on plant species, growth habits, and desired propagation speed for a thriving garden.
Leaf Cuttings vs Stem Cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com