
Root Cuttings vs Tip Cuttings Illustration
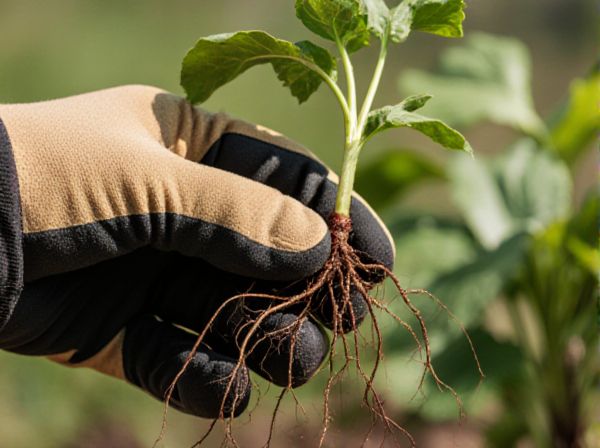
Root cuttings encourage the development of strong, established root systems, making them ideal for plants that root easily from underground stems. Tip cuttings promote rapid shoot growth by using the plant's tender terminal tips, which contain actively dividing cells for faster rooting. Choosing between root cuttings and tip cuttings depends on the species and desired growth speed, with root cuttings often producing more robust plants and tip cuttings enabling quicker propagation.
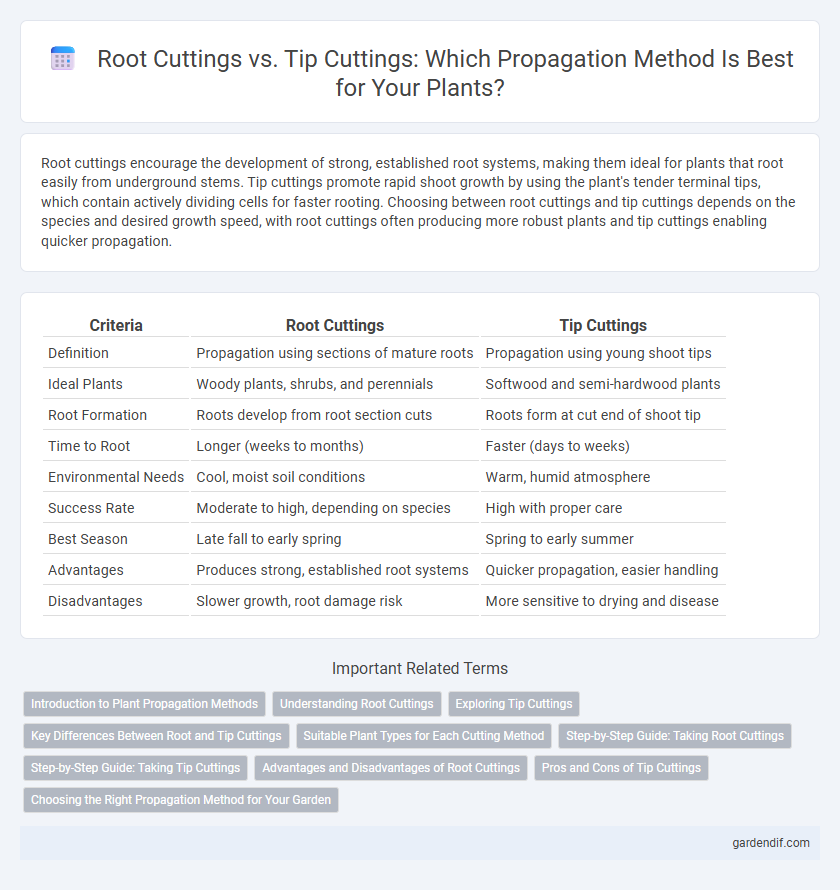
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Root Cuttings | Tip Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Propagation using sections of mature roots | Propagation using young shoot tips |
| Ideal Plants | Woody plants, shrubs, and perennials | Softwood and semi-hardwood plants |
| Root Formation | Roots develop from root section cuts | Roots form at cut end of shoot tip |
| Time to Root | Longer (weeks to months) | Faster (days to weeks) |
| Environmental Needs | Cool, moist soil conditions | Warm, humid atmosphere |
| Success Rate | Moderate to high, depending on species | High with proper care |
| Best Season | Late fall to early spring | Spring to early summer |
| Advantages | Produces strong, established root systems | Quicker propagation, easier handling |
| Disadvantages | Slower growth, root damage risk | More sensitive to drying and disease |
Introduction to Plant Propagation Methods
Root cuttings involve using a portion of the plant's root system to develop new plants, offering a reliable method for propagating hardy perennials and woody plants. Tip cuttings, taken from the actively growing tips of stems, allow faster rooting and are commonly used for soft-stemmed plants like herbs and shrubs. Both methods enhance genetic consistency and accelerate propagation cycles, tailored to specific plant types and growth habits.
Understanding Root Cuttings
Root cuttings involve using sections of a plant's root system to propagate new plants, ensuring genetic consistency and robust root development. This method is particularly effective for plants with strong, fleshy roots such as horseradish, blackberries, and currants. Root cuttings promote faster establishment compared to tip cuttings since the new plants already possess an established root structure.
Exploring Tip Cuttings
Tip cuttings involve taking the growing tips of plants, which often contain actively dividing meristematic tissues that promote faster root development compared to root cuttings. These cuttings typically include nodes with leaf buds, ensuring higher success rates and vigorous new growth suitable for many herbaceous and soft-wood plants. Optimizing tip cutting propagation entails precise cutting angles, appropriate hormone treatments like auxins, and maintaining humidity to enhance rooting efficiency.
Key Differences Between Root and Tip Cuttings
Root cuttings involve using sections of a plant's root system to propagate new plants, ensuring genetic consistency and often producing sturdier, more established root systems. Tip cuttings, taken from the growing tips of stems, encourage faster shoot development and branching but may require more care to prevent drying out or disease. Root cuttings typically take longer to sprout but result in vigorous root growth, while tip cuttings promote quicker above-ground growth and are ideal for rapid multiplication of herbaceous plants.
Suitable Plant Types for Each Cutting Method
Root cuttings work best with plants that have strong, woody root systems such as horseradish, raspberry, and fig, allowing new shoots to emerge directly from the roots. Tip cuttings are ideal for soft-stemmed plants like coleus, basil, and impatiens, where new growth can develop from the apical meristem at the shoot tips. Selecting the appropriate cutting method maximizes propagation success by aligning with the plant's natural growth patterns and tissue types.
Step-by-Step Guide: Taking Root Cuttings
To take root cuttings effectively, first select healthy, mature roots from a dormant or late-season plant, typically measuring 2-4 inches in length. Clean the roots and cut them into sections with at least one dormant bud per piece, then dip the cut ends in rooting hormone to encourage sprouting. Plant the cuttings horizontally in a well-draining medium, cover lightly with soil, and maintain consistent moisture and temperature around 65-75degF for optimal root development.
Step-by-Step Guide: Taking Tip Cuttings
Select healthy, non-flowering shoots approximately 4-6 inches long and cut just below a node to ensure rooting hormones are effective. Remove the lower leaves, leaving only a few at the top to minimize water loss and place the cutting in a well-draining propagation medium. Maintain high humidity and consistent moisture, while keeping the cuttings under indirect sunlight until roots develop, typically within 2-4 weeks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Root Cuttings
Root cuttings offer the advantage of producing genetically identical plants with strong root systems that establish quickly in soil, making them ideal for woody perennials and difficult-to-root species. However, they require careful handling to avoid damaging the root tissue, and the initial growth can be slower compared to tip cuttings, which benefit from active shoot meristems. Root cuttings have limited availability per parent plant and are less effective for plants that primarily propagate through soft, herbaceous stems.
Pros and Cons of Tip Cuttings
Tip cuttings offer rapid root development and higher success rates in many plant species due to their active growth tips, enabling quicker establishment compared to root cuttings. However, tip cuttings may be more susceptible to desiccation and require careful humidity control and proper handling to avoid damage, which can limit success in less controlled environments. Unlike root cuttings that produce plants genetically identical and often hardier, tip cuttings can sometimes result in less vigorous root systems, impacting early growth stability.
Choosing the Right Propagation Method for Your Garden
Root cuttings enable the cloning of mature plants with established root systems, ensuring strong and resilient new growth, while tip cuttings promote quicker development and branching from young, flexible stems. Selecting the ideal propagation method depends on the plant species, growth goals, and available resources, with root cuttings favored for woody plants and tip cuttings optimal for soft-stemmed herbaceous varieties. Understanding these distinctions supports improved success rates and healthier plant establishment in your garden.
Root Cuttings vs Tip Cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com