
Drought-tolerant vs moisture-loving Illustration
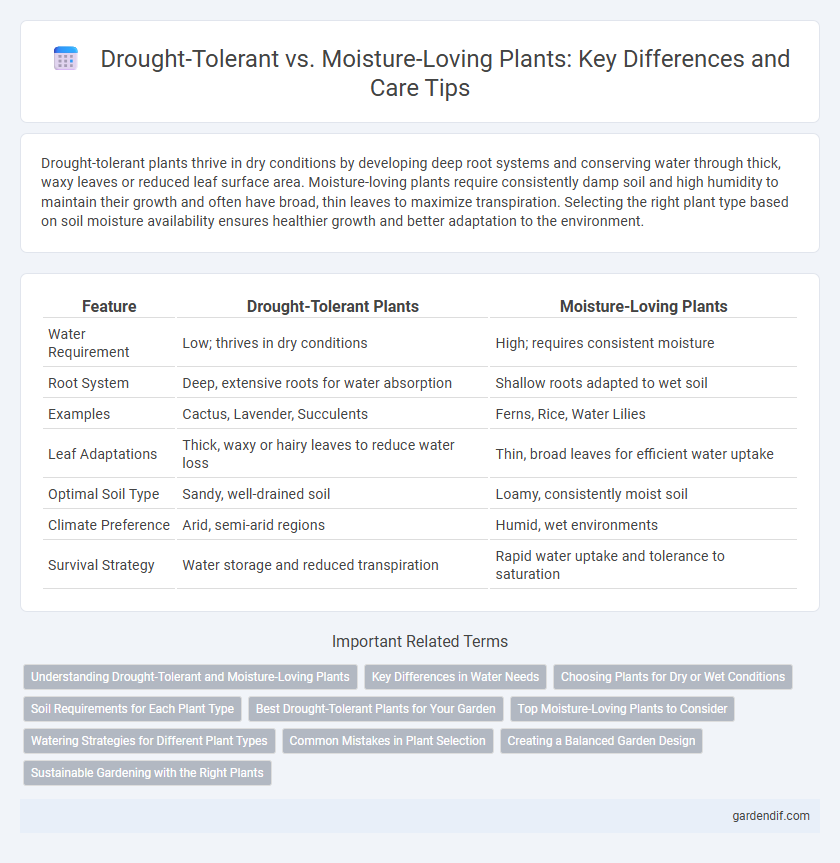
Drought-tolerant plants thrive in dry conditions by developing deep root systems and conserving water through thick, waxy leaves or reduced leaf surface area. Moisture-loving plants require consistently damp soil and high humidity to maintain their growth and often have broad, thin leaves to maximize transpiration. Selecting the right plant type based on soil moisture availability ensures healthier growth and better adaptation to the environment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drought-Tolerant Plants | Moisture-Loving Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Water Requirement | Low; thrives in dry conditions | High; requires consistent moisture |
| Root System | Deep, extensive roots for water absorption | Shallow roots adapted to wet soil |
| Examples | Cactus, Lavender, Succulents | Ferns, Rice, Water Lilies |
| Leaf Adaptations | Thick, waxy or hairy leaves to reduce water loss | Thin, broad leaves for efficient water uptake |
| Optimal Soil Type | Sandy, well-drained soil | Loamy, consistently moist soil |
| Climate Preference | Arid, semi-arid regions | Humid, wet environments |
| Survival Strategy | Water storage and reduced transpiration | Rapid water uptake and tolerance to saturation |
Understanding Drought-Tolerant and Moisture-Loving Plants
Drought-tolerant plants, such as succulents and cacti, possess specialized adaptations like deep root systems and water-storing tissues that enable survival in arid environments. Moisture-loving plants, including ferns and tropical species, require consistently damp soil and high humidity to thrive, relying on shallow roots and delicate leaf structures for efficient water absorption. Understanding these distinct physiological traits allows gardeners and ecologists to select appropriate species for varying climates and optimize plant care strategies.
Key Differences in Water Needs
Drought-tolerant plants have adapted to survive with minimal water, featuring deep root systems and reduced leaf surface to conserve moisture, making them ideal for arid environments. In contrast, moisture-loving plants require consistent and abundant water supply, thriving in environments with high humidity and wet soil conditions. Understanding these key differences is crucial for selecting plants based on regional water availability and irrigation capacities.
Choosing Plants for Dry or Wet Conditions
Drought-tolerant plants such as succulents, lavender, and agave thrive in dry conditions by efficiently storing water and reducing transpiration, making them ideal for arid climates and xeriscaping. Moisture-loving plants like ferns, willows, and cattails require consistently wet or swampy environments to flourish, relying on abundant water availability for nutrient uptake and growth. Selecting plants based on their water needs ensures sustainable landscaping, conserves resources, and promotes plant health in either dry or wet settings.
Soil Requirements for Each Plant Type
Drought-tolerant plants thrive in well-drained, sandy, or rocky soils with low water retention, minimizing root rot risks. Moisture-loving plants require consistently moist, nutrient-rich, loamy soils that retain water to support their higher hydration needs. Proper soil composition directly influences plant health, growth rates, and overall drought resistance or moisture adaptation.
Best Drought-Tolerant Plants for Your Garden
Best drought-tolerant plants for your garden include succulents like Agave and Sedum, which store water efficiently in their leaves. Native grasses such as Blue Grama and Buffalo Grass require minimal irrigation and thrive in dry conditions. Xeriscape shrubs like Lavender and Russian Sage offer vibrant blooms while conserving water and reducing maintenance.
Top Moisture-Loving Plants to Consider
Top moisture-loving plants include ferns, hostas, and marsh marigolds, which thrive in consistently damp or wet soils and provide lush, vibrant foliage. These plants require regular watering and high humidity to maintain their health and prevent wilting or leaf scorch. Ideal for rain gardens and shaded wetlands, moisture-loving plants enhance soil stability and support diverse ecosystems in moisture-rich environments.
Watering Strategies for Different Plant Types
Drought-tolerant plants, such as succulents and cacti, require infrequent deep watering to encourage strong root development and conserve water. Moisture-loving plants, including ferns and tropical species, thrive with consistent, frequent watering that maintains evenly moist soil conditions. Tailoring watering strategies to the plant's water needs optimizes growth, reduces stress, and prevents root rot or dehydration.
Common Mistakes in Plant Selection
Choosing drought-tolerant plants for consistently moist environments often leads to poor growth and increased susceptibility to disease. Moisture-loving species planted in dry or low-humidity areas typically suffer from dehydration and root rot. Ignoring the specific water requirements of plants during selection results in higher maintenance costs and reduced garden longevity.
Creating a Balanced Garden Design
Incorporating drought-tolerant plants such as succulents and lavender alongside moisture-loving species like ferns and hostas creates a balanced garden design that maximizes water efficiency. Utilizing native plants adapted to local climate conditions ensures resilience and reduces maintenance while enhancing biodiversity. Strategic placement of these contrasting plant types fosters microclimates, improving overall garden health and visual appeal.
Sustainable Gardening with the Right Plants
Drought-tolerant plants such as succulents, lavender, and native grasses conserve water and thrive in arid conditions, making them ideal for sustainable gardening in dry climates. Moisture-loving plants like ferns, hostas, and rice require consistent hydration and are best suited for areas with abundant rainfall or irrigation systems. Selecting plants based on their water needs reduces resource consumption, supports ecosystem resilience, and promotes long-term garden sustainability.
Drought-tolerant vs moisture-loving Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com