
Cutting propagation vs Seed propagation Illustration
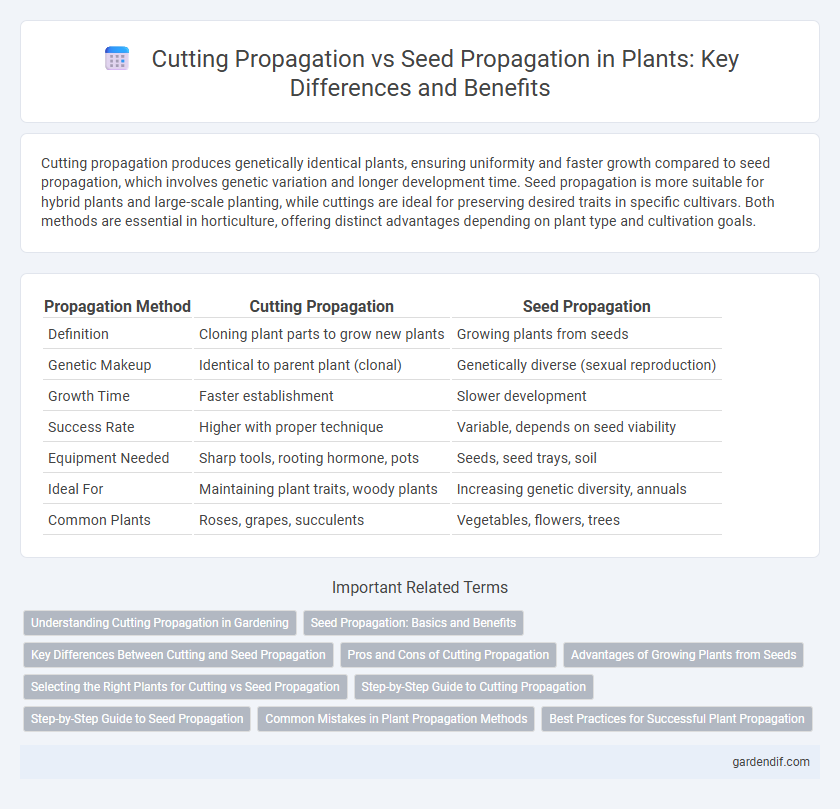
Cutting propagation produces genetically identical plants, ensuring uniformity and faster growth compared to seed propagation, which involves genetic variation and longer development time. Seed propagation is more suitable for hybrid plants and large-scale planting, while cuttings are ideal for preserving desired traits in specific cultivars. Both methods are essential in horticulture, offering distinct advantages depending on plant type and cultivation goals.
Table of Comparison
| Propagation Method | Cutting Propagation | Seed Propagation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloning plant parts to grow new plants | Growing plants from seeds |
| Genetic Makeup | Identical to parent plant (clonal) | Genetically diverse (sexual reproduction) |
| Growth Time | Faster establishment | Slower development |
| Success Rate | Higher with proper technique | Variable, depends on seed viability |
| Equipment Needed | Sharp tools, rooting hormone, pots | Seeds, seed trays, soil |
| Ideal For | Maintaining plant traits, woody plants | Increasing genetic diversity, annuals |
| Common Plants | Roses, grapes, succulents | Vegetables, flowers, trees |
Understanding Cutting Propagation in Gardening
Cutting propagation involves using a part of a parent plant, such as a stem, leaf, or root, to grow a new plant genetically identical to the original. This method allows for faster maturity compared to seed propagation, which grows plants from seeds and can exhibit genetic variability. Gardeners often prefer cutting propagation for maintaining desirable traits and ensuring uniformity in plants like roses, succulents, and herbs.
Seed Propagation: Basics and Benefits
Seed propagation involves growing plants from seeds, offering genetic diversity that enhances resilience to pests and environmental changes. This method is cost-effective and allows for large-scale plant production with minimal initial resources. Seed propagation supports the development of stronger root systems, leading to healthier and more robust plants compared to cuttings.
Key Differences Between Cutting and Seed Propagation
Cutting propagation involves taking a portion of a parent plant, such as a stem or leaf, to produce a genetically identical offspring, ensuring true-to-type characteristics. Seed propagation allows for genetic variation and diversity but typically requires longer time for germination and growth to maturity. Key differences include the speed of propagation, genetic uniformity, and the method's suitability depending on plant species and desired outcomes.
Pros and Cons of Cutting Propagation
Cutting propagation allows for faster plant replication and ensures genetic consistency, producing clones identical to the parent plant. However, it often requires careful maintenance of humidity and temperature to prevent rot and disease, making it more labor-intensive. This method may also limit genetic diversity, reducing the plant population's adaptability to environmental changes.
Advantages of Growing Plants from Seeds
Growing plants from seeds offers genetic diversity, enhancing resilience to diseases and environmental changes. Seed propagation is cost-effective and allows for large-scale cultivation, making it ideal for agricultural production. Furthermore, plants grown from seeds often develop stronger root systems and better overall vigor, ensuring healthier growth and higher yields.
Selecting the Right Plants for Cutting vs Seed Propagation
Selecting the right plants for cutting propagation involves choosing species with strong, flexible stems such as coleus, pothos, and hibiscus, which root easily from cuttings, ensuring faster growth and genetic consistency. Seed propagation is ideal for plants like tomatoes, peppers, and beans that benefit from genetic diversity and resilient root systems, promoting adaptability and longevity. Understanding plant types and propagation goals is crucial for optimizing growth efficiency and successful cultivation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Cutting Propagation
Cutting propagation involves selecting a healthy stem, making a clean cut just below a node, and removing lower leaves to expose the rooting area. The cutting is then dipped in rooting hormone and planted in a well-draining medium to encourage root development. Maintaining consistent moisture and warmth accelerates root growth, enabling successful plant multiplication without genetic variation found in seed propagation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Seed Propagation
Seed propagation involves selecting high-quality seeds, soaking them in water for 12-24 hours to soften the seed coat, and sowing them in a sterile, well-draining seed-starting mix. Maintain consistent moisture and warmth around 70-75degF (21-24degC), using a humidity dome or plastic cover to encourage germination within 7-21 days, depending on the plant species. Once seedlings develop true leaves, gradually acclimate them to outdoor conditions before transplanting into larger containers or garden beds.
Common Mistakes in Plant Propagation Methods
Cutting propagation often faces common mistakes such as improper cutting size, inadequate humidity control, and failure to use rooting hormones to stimulate root development. Seed propagation errors include using old or non-viable seeds, incorrect planting depth, and insufficient moisture, which hinder germination rates. Both methods benefit from sterile tools and well-prepared growing media to minimize disease and maximize successful plant establishment.
Best Practices for Successful Plant Propagation
Cutting propagation offers faster plant establishment and genetic consistency, making it ideal for preserving desirable traits, while seed propagation promotes genetic diversity and is suited for species with viable seeds. Best practices for cutting propagation include selecting healthy parent plants, using sterilized tools to prevent disease, and maintaining high humidity for root development. For seed propagation, proper seed stratification or scarification, optimal soil moisture, and temperature conditions are critical to maximize germination rates and produce vigorous seedlings.
Cutting propagation vs Seed propagation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com