
Heirloom varieties vs Hybrid varieties Illustration
Heirloom plant varieties preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional traits passed down through generations, often valued for their unique flavors and adaptability to local conditions. Hybrid varieties are bred by crossing different parent plants to enhance specific characteristics such as increased yield, disease resistance, and uniformity. Choosing heirloom or hybrid plants depends on gardening goals, whether prioritizing genetic heritage or maximizing performance and resilience.
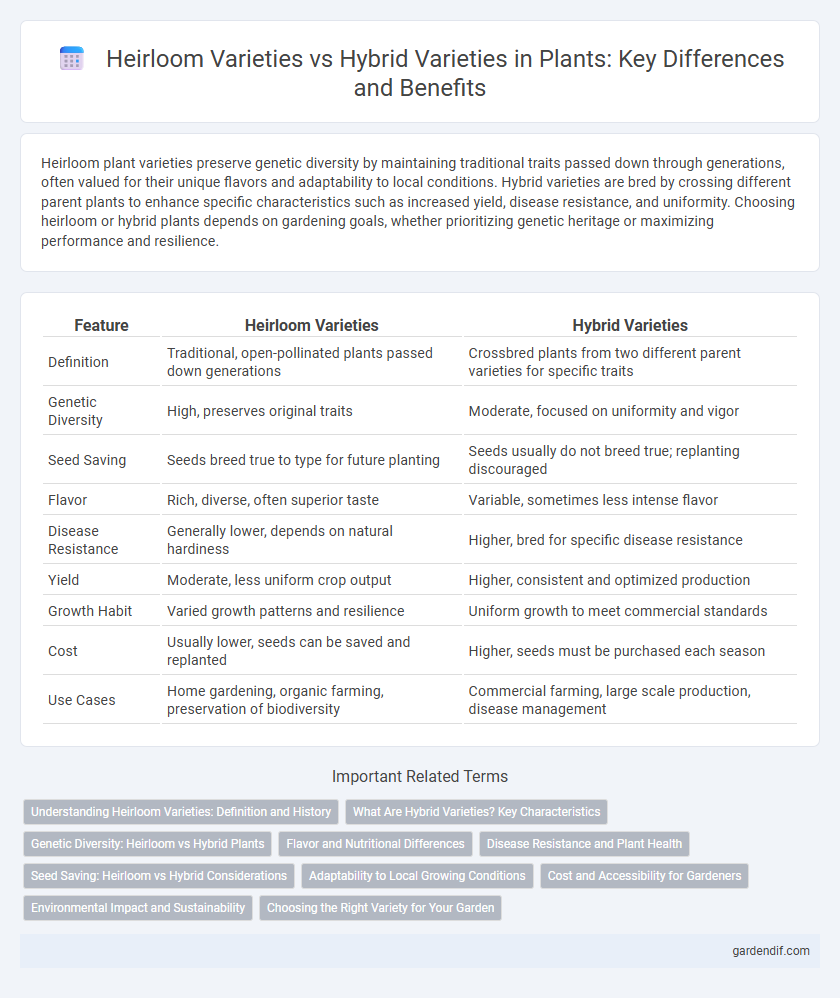
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom Varieties | Hybrid Varieties |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional, open-pollinated plants passed down generations | Crossbred plants from two different parent varieties for specific traits |
| Genetic Diversity | High, preserves original traits | Moderate, focused on uniformity and vigor |
| Seed Saving | Seeds breed true to type for future planting | Seeds usually do not breed true; replanting discouraged |
| Flavor | Rich, diverse, often superior taste | Variable, sometimes less intense flavor |
| Disease Resistance | Generally lower, depends on natural hardiness | Higher, bred for specific disease resistance |
| Yield | Moderate, less uniform crop output | Higher, consistent and optimized production |
| Growth Habit | Varied growth patterns and resilience | Uniform growth to meet commercial standards |
| Cost | Usually lower, seeds can be saved and replanted | Higher, seeds must be purchased each season |
| Use Cases | Home gardening, organic farming, preservation of biodiversity | Commercial farming, large scale production, disease management |
Understanding Heirloom Varieties: Definition and History
Heirloom varieties are traditional plant cultivars that have been passed down through generations, often grown for their unique flavors, colors, and adaptability to specific regions. These varieties are open-pollinated, allowing them to reproduce true to type, preserving genetic diversity and cultural heritage. The history of heirloom plants dates back centuries, with many originating before the widespread use of modern hybridization techniques in agriculture.
What Are Hybrid Varieties? Key Characteristics
Hybrid varieties are plants produced by crossbreeding two genetically distinct parent plants to combine desirable traits such as disease resistance, higher yields, and uniform growth. These varieties often exhibit hybrid vigor, resulting in enhanced performance under specific environmental conditions. Hybrid seeds typically do not produce true-to-type offspring, requiring new seeds each season for consistent crop quality.
Genetic Diversity: Heirloom vs Hybrid Plants
Heirloom varieties maintain high genetic diversity by preserving traditional plant traits passed through generations, which enhances resilience to pests and environmental changes. Hybrid plants result from controlled crossbreeding between specific parent lines, often producing uniform and high-yield crops but with reduced genetic variation. This limited genetic diversity in hybrids can increase vulnerability to diseases and reduce adaptability over time compared to heirloom varieties.
Flavor and Nutritional Differences
Heirloom plant varieties typically offer richer, more complex flavors and higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals compared to hybrid varieties. Hybrid plants are often bred for yield, disease resistance, and uniform appearance but may sacrifice some flavor intensity and nutritional content. Studies show heirloom tomatoes, for instance, contain greater lycopene and vitamin C concentrations than their hybrid counterparts.
Disease Resistance and Plant Health
Heirloom plant varieties often exhibit diverse genetic traits but may lack strong resistance to modern diseases compared to hybrid varieties, which are selectively bred for enhanced disease resistance and overall plant health. Hybrid plants typically demonstrate improved vigor and reduced susceptibility to pathogens due to targeted crossbreeding, resulting in higher yields and longevity. Prioritizing hybrid varieties can significantly reduce the need for chemical treatments, promoting sustainable gardening and agricultural practices.
Seed Saving: Heirloom vs Hybrid Considerations
Heirloom varieties offer reliable seed saving potential due to their open-pollinated nature, ensuring genetic traits remain stable across generations. Hybrid varieties, created by crossing two distinct parent plants, often produce sterile seeds or offspring with unpredictable traits, complicating seed saving efforts. Gardeners prioritizing sustainable seed saving typically prefer heirloom seeds for their consistency and heritage preservation.
Adaptability to Local Growing Conditions
Heirloom varieties exhibit superior adaptability to local growing conditions due to their long history of cultivation in specific regions, resulting in enhanced resilience to local pests, diseases, and climate variations. Hybrid varieties often prioritize traits like higher yield or uniformity but may lack the genetic diversity necessary for optimal performance in diverse or challenging environments. Selecting heirloom seeds can improve garden sustainability and reduce the need for chemical interventions by leveraging natural adaptability.
Cost and Accessibility for Gardeners
Heirloom varieties often come with a lower initial seed cost but may require more care and specific growing conditions, making them less accessible for beginner gardeners. Hybrid varieties usually have higher seed prices but offer greater disease resistance and uniformity, reducing long-term maintenance costs and increasing accessibility. Gardeners prioritizing budget might choose heirlooms for affordability, while those seeking convenience and reliability often opt for hybrids despite the higher upfront investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heirloom varieties promote biodiversity by preserving genetic diversity and adapting naturally to local environments, reducing the need for chemical inputs and enhancing soil health. Hybrid varieties often require higher resource inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to increased environmental strain and potential soil degradation. Sustainable agriculture benefits from integrating heirloom plants to support resilient ecosystems and long-term food security.
Choosing the Right Variety for Your Garden
Heirloom varieties offer rich genetic diversity and unique flavors, making them ideal for gardeners seeking traditional, open-pollinated plants with stable traits. Hybrid varieties provide higher yields, disease resistance, and uniformity, suited for gardeners prioritizing productivity and resilience. Selecting the right variety depends on balancing preferences for flavor, adaptability, and ease of cultivation in your specific garden environment.
Heirloom varieties vs Hybrid varieties Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com