
Annual vs Perennial Illustration
Annual plants complete their life cycle within a single growing season, germinating, flowering, and dying all in one year. Perennial plants live for multiple years, often going dormant during unfavorable seasons and regrowing from their rootstock each year. Choosing between annuals and perennials depends on garden design, maintenance preferences, and desired long-term growth patterns.
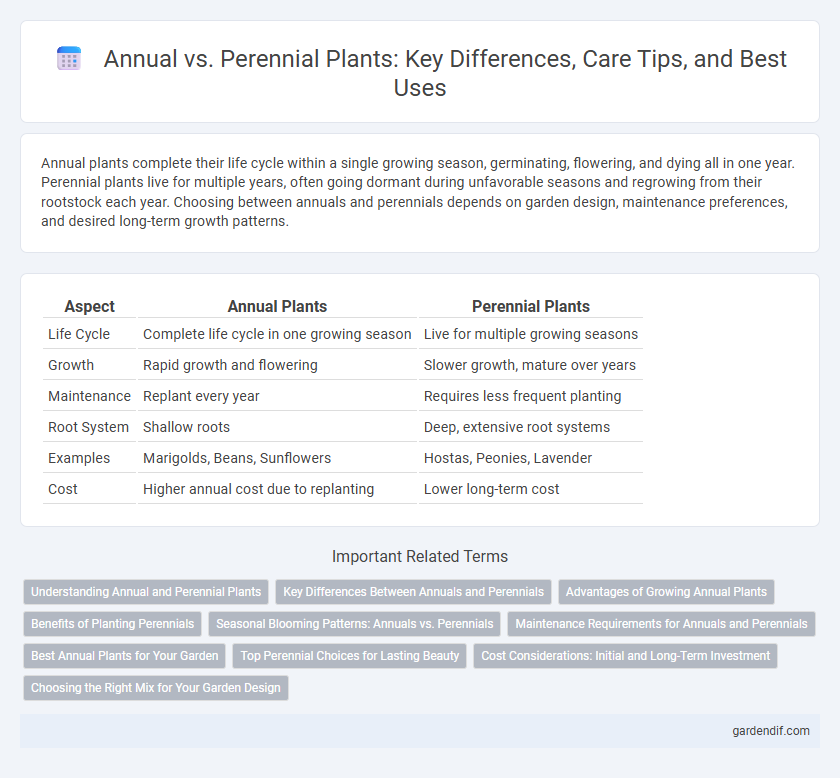
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Annual Plants | Perennial Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Life Cycle | Complete life cycle in one growing season | Live for multiple growing seasons |
| Growth | Rapid growth and flowering | Slower growth, mature over years |
| Maintenance | Replant every year | Requires less frequent planting |
| Root System | Shallow roots | Deep, extensive root systems |
| Examples | Marigolds, Beans, Sunflowers | Hostas, Peonies, Lavender |
| Cost | Higher annual cost due to replanting | Lower long-term cost |
Understanding Annual and Perennial Plants
Annual plants complete their life cycle within a single growing season, from germination to seed production, after which they die. Perennial plants live for multiple years, often going dormant in colder seasons and regrowing from the same root system each year. Understanding the differences in growth patterns and life span helps gardeners select appropriate plants for seasonal or long-term landscaping needs.
Key Differences Between Annuals and Perennials
Annual plants complete their life cycle, from germination to seed production, within one growing season, requiring replanting each year. Perennials live for multiple years, often entering dormancy during unfavorable seasons and regrowing annually from the same root system. The key differences lie in their lifespan, maintenance needs, and growth patterns, affecting garden planning and resource allocation.
Advantages of Growing Annual Plants
Annual plants complete their life cycle in one growing season, allowing gardeners to quickly refresh garden aesthetics with vibrant, diverse blooms each year. They often grow rapidly and produce abundant flowers or fruits, offering a high yield in a short time frame. Annuals also allow for flexibility in crop rotation, reducing soil depletion and minimizing pest and disease buildup.
Benefits of Planting Perennials
Planting perennials offers significant benefits including long-term soil stabilization and reduced erosion due to their deep and extensive root systems. These plants require less water and fewer nutrients over time, making them more sustainable and cost-effective compared to annuals. Perennials also provide continuous habitat and food sources for pollinators, promoting biodiversity year after year.
Seasonal Blooming Patterns: Annuals vs. Perennials
Annual plants complete their life cycle in one growing season, producing vibrant blooms that last intensively but briefly, often from spring to fall. Perennials bloom each season over multiple years, with flowering periods that may be shorter but recur annually, offering consistent seasonal color and structure. Understanding these blooming patterns helps gardeners plan for continuous garden interest by combining annuals' quick, bold displays with perennials' enduring presence.
Maintenance Requirements for Annuals and Perennials
Annual plants require replanting every growing season because they complete their life cycle in one year, which often demands more frequent soil preparation and fertilization. Perennials, by contrast, grow back year after year from established root systems, reducing overall maintenance tasks such as planting and soil amendment. While annuals may need more consistent watering and pest control during their short lifespan, perennials benefit from deeper root systems that enhance drought tolerance and minimize watering frequency.
Best Annual Plants for Your Garden
Best annual plants for your garden include marigolds, petunias, and zinnias, prized for their vibrant colors and continuous blooms throughout the growing season. Annuals complete their life cycle in one year, offering intense seasonal color and quick growth compared to perennials, which live multiple years but often bloom for shorter periods. Choosing annuals allows gardeners to easily change garden themes yearly and fill gaps in perennial beds with spectacular showy flowers.
Top Perennial Choices for Lasting Beauty
Top perennial choices like hostas, daylilies, and coneflowers offer lasting beauty with their ability to thrive year after year, reducing the need for replanting. Unlike annuals that complete their life cycle in one season, perennials invest energy in robust root systems, ensuring vigorous growth and continuous blooms. Selecting drought-tolerant perennials such as sedum and echinacea can enhance garden resilience while providing vibrant, long-lasting color.
Cost Considerations: Initial and Long-Term Investment
Annual plants typically require a lower initial investment due to their single-season lifecycle but incur higher long-term costs as they must be replanted each year. Perennials demand a higher upfront cost for durable root systems and longer establishment periods but reduce expenses over time by regrowing annually without the need for replanting. Evaluating cost considerations involves balancing the immediate budget constraints with potential savings on maintenance and replacement over multiple seasons.
Choosing the Right Mix for Your Garden Design
Selecting the right mix of annual and perennial plants enhances garden design by balancing vibrant seasonal color with long-term structure and stability. Annuals offer quick blooms and diverse color palettes, ideal for filling gaps and creating focal points during a single growing season. Perennials contribute durability and reduce maintenance by returning year after year, supporting soil health and attracting beneficial pollinators throughout multiple seasons.
Annual vs Perennial Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com