
Heirloom seeds vs Hybrid seeds Illustration
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by passing down traditional plant varieties that thrive in specific environments, offering unique flavors and adaptability. Hybrid seeds result from crossbreeding different plant strains to enhance traits such as yield, disease resistance, and uniformity, but their seeds often do not produce true-to-type offspring. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid seeds depends on the gardener's priorities for flavor, sustainability, and crop consistency.
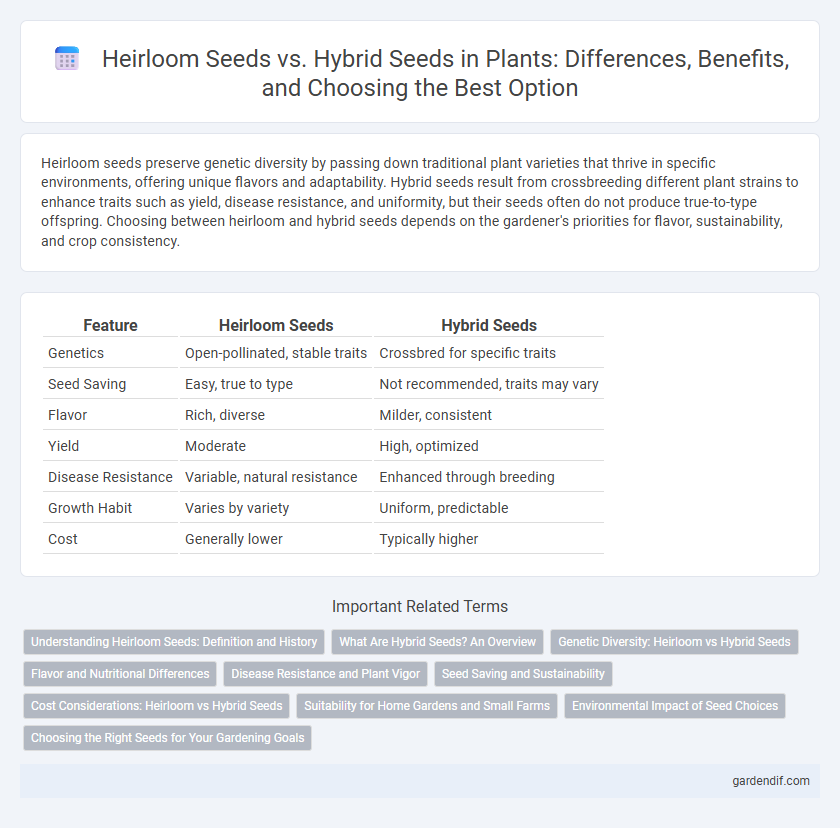
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Open-pollinated, stable traits | Crossbred for specific traits |
| Seed Saving | Easy, true to type | Not recommended, traits may vary |
| Flavor | Rich, diverse | Milder, consistent |
| Yield | Moderate | High, optimized |
| Disease Resistance | Variable, natural resistance | Enhanced through breeding |
| Growth Habit | Varies by variety | Uniform, predictable |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
Understanding Heirloom Seeds: Definition and History
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties of plants that have been preserved and passed down through generations for at least 50 years, often maintaining unique flavors, colors, and genetic traits. These seeds trace their origins to traditional farming practices and local culture, embodying a rich agricultural heritage that predates modern commercial hybrids. Understanding heirloom seeds involves recognizing their role in biodiversity preservation and their contribution to sustainable gardening by promoting genetic diversity and resilience.
What Are Hybrid Seeds? An Overview
Hybrid seeds result from the controlled cross-pollination between two genetically distinct parent plants, combining desirable traits such as disease resistance, higher yield, and uniform growth. These seeds produce plants that typically exhibit hybrid vigor, making them more robust but often sterile or unstable for seed saving. Hybrid seeds are widely used in commercial agriculture due to their predictable performance and improved productivity compared to heirloom varieties.
Genetic Diversity: Heirloom vs Hybrid Seeds
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining open-pollinated plant varieties that have adapted to specific local environments over generations, offering resilience against pests and diseases. In contrast, hybrid seeds result from controlled crossbreeding of two distinct parent plants, producing uniform traits but reducing genetic variability. This limited genetic diversity in hybrids can increase vulnerability to environmental changes and limit long-term sustainability compared to the diverse gene pool found in heirloom varieties.
Flavor and Nutritional Differences
Heirloom seeds often produce fruits and vegetables with richer, more complex flavors due to their open-pollinated, non-GMO genetic heritage, preserving traditional taste profiles. Hybrid seeds are bred for higher yields and disease resistance but may sacrifice some intensity in flavor and nutritional content compared to heirlooms. Nutritional analyses frequently show heirloom varieties contain higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to their appeal among health-conscious gardeners.
Disease Resistance and Plant Vigor
Heirloom seeds often exhibit weaker disease resistance compared to hybrid seeds, which are specifically bred for enhanced resistance to common pathogens and pests. Hybrid seeds typically demonstrate superior plant vigor, resulting in stronger growth, higher yields, and better adaptability to environmental stress. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid seeds depends on prioritizing genetic diversity and flavor preservation versus enhanced resilience and robust growth performance.
Seed Saving and Sustainability
Heirloom seeds promote sustainability by enabling gardeners to save seeds year after year, preserving genetic diversity and reducing reliance on commercial seed producers. Hybrid seeds often do not produce true-to-type offspring, making seed saving ineffective and requiring new purchases each season, which can increase costs and environmental impact. Choosing heirloom seeds supports resilient ecosystems and long-term agricultural sustainability through continuous seed saving practices.
Cost Considerations: Heirloom vs Hybrid Seeds
Heirloom seeds typically cost more upfront due to their preservation-focused cultivation and limited commercial production, while hybrid seeds are often cheaper because of large-scale industrial breeding and mass distribution. Long-term savings can occur with heirloom seeds since they produce plants that reliably reproduce true to type, eliminating the need for repurchasing seeds each season. Hybrid seeds may require annual purchase as they often do not produce viable seeds, impacting gardeners' overall cost efficiency.
Suitability for Home Gardens and Small Farms
Heirloom seeds are ideal for home gardens and small farms due to their strong adaptability to local conditions and superior flavor profiles, preserving genetic diversity and offering open-pollinated varieties that can be saved for future planting. Hybrid seeds provide higher yields and disease resistance, making them suitable for small farms aiming for consistent production but typically require purchase each season as saved seeds may not retain desired traits. Home gardeners seeking sustainability and unique varieties often prefer heirloom seeds, while small farms focused on productivity and market demands might opt for hybrids.
Environmental Impact of Seed Choices
Heirloom seeds support biodiversity by preserving genetic variety vital for ecosystem resilience, while hybrid seeds often prioritize uniformity and high yield at the expense of genetic diversity. The cultivation of heirloom varieties typically demands fewer chemical inputs, reducing soil degradation and promoting healthier pollinator populations compared to hybrids that may require intensive pesticide and fertilizer use. Choosing heirloom seeds contributes to sustainable agriculture by enhancing environmental stability and mitigating negative impacts associated with industrial seed production.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Your Gardening Goals
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and offer unique flavors and adaptability, ideal for gardeners seeking traditional, open-pollinated plants that can be saved year after year. Hybrid seeds provide higher yields, disease resistance, and uniform growth, making them suitable for those prioritizing productivity and consistent crop performance. Selecting the right seeds requires evaluating your garden's climate, soil conditions, and whether you value heritage traits or enhanced vigor.
Heirloom seeds vs Hybrid seeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com