
Swale Building vs Terracing Illustration
Swale building captures and directs water on contour lines to enhance soil moisture and prevent erosion, making it ideal for landscapes with gentle slopes. Terracing transforms steep slopes into flat, productive areas by creating a series of stepped levels that slow water runoff and maximize arable land. Both techniques improve water management in permaculture, but swales are more suitable for conservation in rolling terrain, while terracing is effective for intensive cultivation on steeper land.
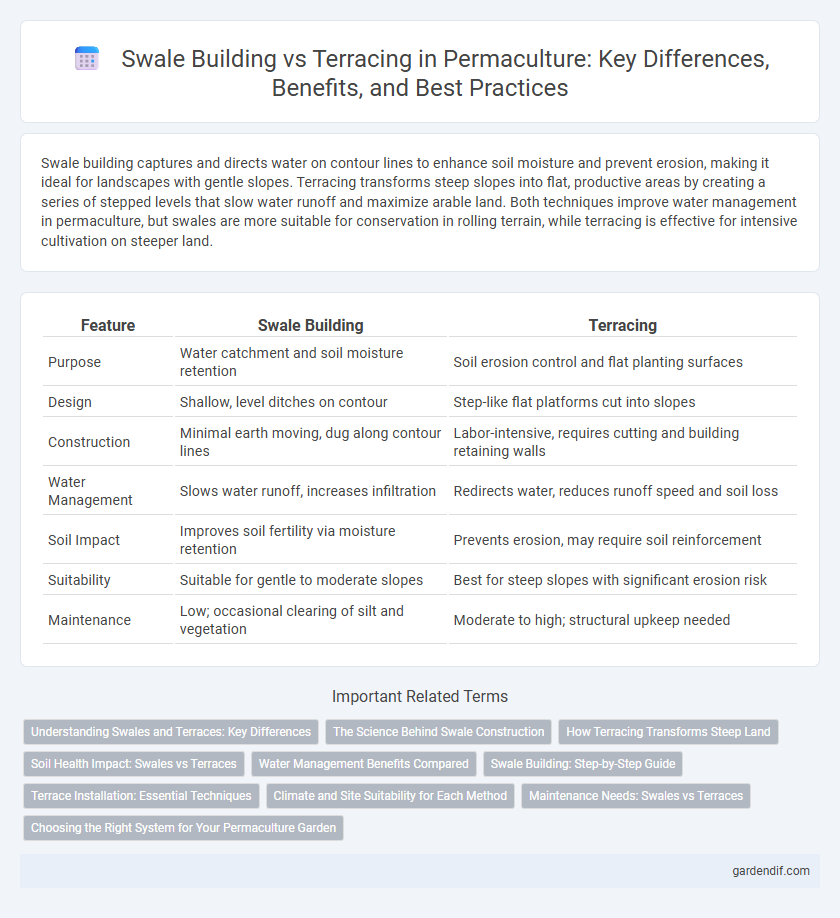
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Swale Building | Terracing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Water catchment and soil moisture retention | Soil erosion control and flat planting surfaces |
| Design | Shallow, level ditches on contour | Step-like flat platforms cut into slopes |
| Construction | Minimal earth moving, dug along contour lines | Labor-intensive, requires cutting and building retaining walls |
| Water Management | Slows water runoff, increases infiltration | Redirects water, reduces runoff speed and soil loss |
| Soil Impact | Improves soil fertility via moisture retention | Prevents erosion, may require soil reinforcement |
| Suitability | Suitable for gentle to moderate slopes | Best for steep slopes with significant erosion risk |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional clearing of silt and vegetation | Moderate to high; structural upkeep needed |
Understanding Swales and Terraces: Key Differences
Swales are shallow, water-absorbing ditches designed on contour to capture and infiltrate rainwater, promoting soil hydration and reducing erosion in permaculture landscapes. Terracing involves constructing stepped levels on slopes to minimize runoff and create flat planting areas, which enhances soil retention and cultivates diverse crops. Understanding these key differences helps in selecting appropriate techniques for water management and sustainable land use in different topographies.
The Science Behind Swale Construction
Swale construction leverages key principles of hydrology and soil science to maximize water retention and infiltration on sloped land, reducing erosion and promoting groundwater recharge. By precisely contouring swales along natural land gradients, they capture runoff efficiently, allowing slow percolation and minimizing nutrient loss compared to traditional terracing. This sustainable water management technique enhances soil health and vegetation growth, aligning with permaculture goals of ecosystem restoration and resource conservation.
How Terracing Transforms Steep Land
Terracing transforms steep land by creating leveled steps that reduce soil erosion and improve water retention, making otherwise unusable slopes productive for agriculture. Unlike swale building, which captures water along contour lines, terracing physically reshapes the land to prevent runoff and increase surface area for planting. This method enhances soil stability and nutrient distribution, allowing for diverse crop cultivation on hilly terrains in permaculture systems.
Soil Health Impact: Swales vs Terraces
Swale building enhances soil health by capturing and infiltrating water directly into the ground, promoting deep root growth and reducing erosion through natural water diffusion. Terracing controls erosion by creating flat planting areas on slopes, but can sometimes disturb soil structure and limit natural water infiltration. Swales tend to preserve soil microbial life and organic matter better than terraces, fostering long-term soil fertility and resilience in permaculture systems.
Water Management Benefits Compared
Swale building enhances water retention by capturing runoff and allowing gradual infiltration into the soil, promoting groundwater recharge and reducing erosion. Terracing controls water flow on steep slopes by creating level steps, minimizing surface runoff and preventing soil loss while directing water more efficiently to plants. Both techniques improve water management, but swales are more effective for passive water harvesting in gently sloped areas, whereas terracing is optimal for steep terrains needing structural support.
Swale Building: Step-by-Step Guide
Swale building involves digging contour-aligned trenches to capture and infiltrate rainwater, reducing erosion and improving soil moisture for permaculture systems. Begin by mapping the land's contour lines using an A-frame or water level, then dig swales along these lines with appropriate dimensions based on slope and rainfall patterns. Fill swales with organic matter or mulch to enhance water retention, and plant native, deep-rooted vegetation along the edges to stabilize soil and promote biodiversity.
Terrace Installation: Essential Techniques
Terrace installation involves creating level steps on sloped land to reduce soil erosion and increase water retention, typically using earth-moving equipment to shape precise flat surfaces. Essential techniques include constructing sturdy bench terraces with proper drainage channels and compacted soil layers to prevent collapse and ensure stability. Incorporating contour lines matching the natural slope optimizes water infiltration and supports sustainable permaculture design.
Climate and Site Suitability for Each Method
Swale building excels in arid and semi-arid climates by efficiently capturing and infiltrating rainwater along contour lines, making it ideal for gentle to moderate slopes with low erosion risk. Terracing suits steep slopes in regions with high rainfall, preventing soil erosion and retaining moisture through step-like structures that stabilize the land. Site suitability depends on slope gradient, rainfall intensity, and erosion potential, with swales favored in drier, flatter areas and terracing preferred in wetter, steep terrains.
Maintenance Needs: Swales vs Terraces
Swale building requires moderate maintenance, primarily involving regular inspection for erosion, sediment buildup, and vegetation management to ensure water infiltration and flow control. Terracing demands higher maintenance due to the need for continuous reinforcement of terrace walls, erosion control measures, and repair after heavy rainfall or landslides. Swales typically offer a more sustainable, low-maintenance solution for water retention compared to the labor-intensive upkeep of terraces.
Choosing the Right System for Your Permaculture Garden
Selecting between swale building and terracing for your permaculture garden depends on your land slope, soil type, and water management goals. Swales are ideal for gently sloping terrain to capture and infiltrate rainwater, enhancing soil moisture and reducing erosion naturally. Terracing suits steeper slopes by creating level planting areas that prevent runoff and improve crop yield through structured soil retention.
Swale Building vs Terracing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com