
Interplanting vs Block Planting Illustration
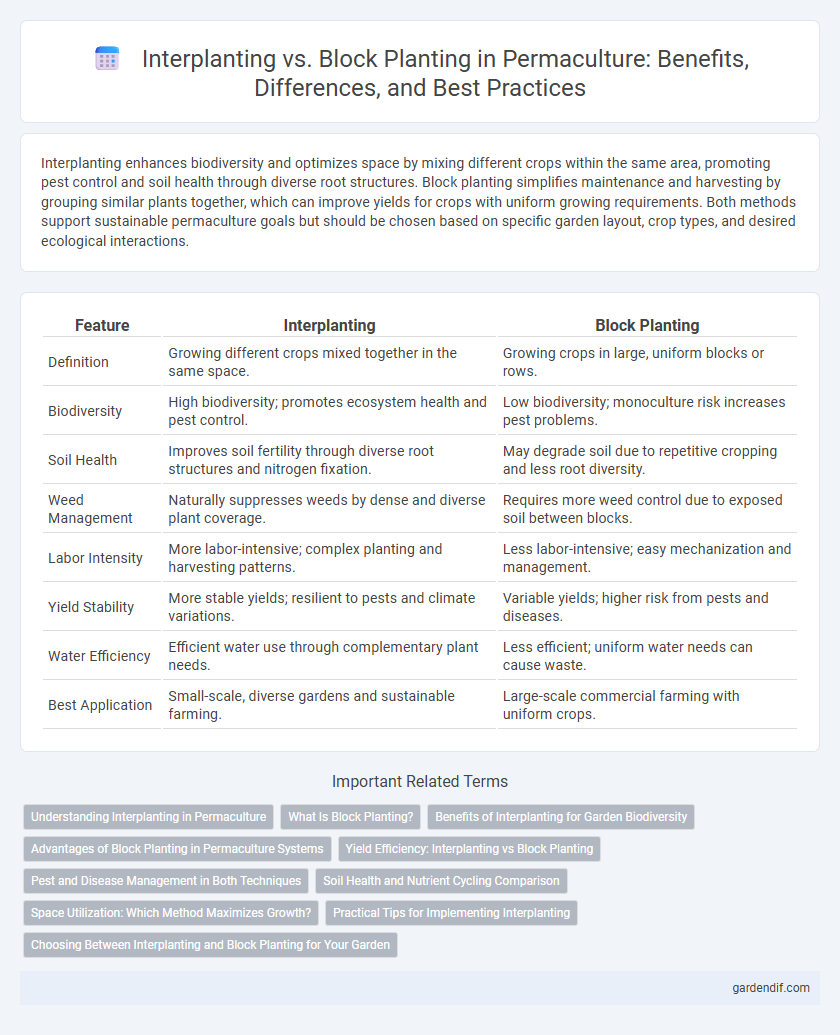
Interplanting enhances biodiversity and optimizes space by mixing different crops within the same area, promoting pest control and soil health through diverse root structures. Block planting simplifies maintenance and harvesting by grouping similar plants together, which can improve yields for crops with uniform growing requirements. Both methods support sustainable permaculture goals but should be chosen based on specific garden layout, crop types, and desired ecological interactions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Interplanting | Block Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing different crops mixed together in the same space. | Growing crops in large, uniform blocks or rows. |
| Biodiversity | High biodiversity; promotes ecosystem health and pest control. | Low biodiversity; monoculture risk increases pest problems. |
| Soil Health | Improves soil fertility through diverse root structures and nitrogen fixation. | May degrade soil due to repetitive cropping and less root diversity. |
| Weed Management | Naturally suppresses weeds by dense and diverse plant coverage. | Requires more weed control due to exposed soil between blocks. |
| Labor Intensity | More labor-intensive; complex planting and harvesting patterns. | Less labor-intensive; easy mechanization and management. |
| Yield Stability | More stable yields; resilient to pests and climate variations. | Variable yields; higher risk from pests and diseases. |
| Water Efficiency | Efficient water use through complementary plant needs. | Less efficient; uniform water needs can cause waste. |
| Best Application | Small-scale, diverse gardens and sustainable farming. | Large-scale commercial farming with uniform crops. |
Understanding Interplanting in Permaculture
Interplanting in permaculture involves growing diverse crops simultaneously in the same area to mimic natural ecosystems, enhancing soil health and pest control. This technique promotes efficient use of space by combining plants with complementary growth habits, nutrient requirements, and pest-repellent properties. Understanding interplanting helps optimize biodiversity, improve yields, and create resilient, sustainable garden ecosystems compared to traditional block planting methods.
What Is Block Planting?
Block planting is a gardening technique where a group of the same plant species is cultivated together in a dense, compact area to maximize yield and ease of maintenance. This method enhances microclimate conditions such as moisture retention and pest control by creating a unified plant community. Block planting contrasts with interplanting by focusing on monoculture clusters rather than diverse, mixed-species arrangements typical in permaculture designs.
Benefits of Interplanting for Garden Biodiversity
Interplanting enhances garden biodiversity by cultivating multiple plant species simultaneously in close proximity, creating diverse habitats that attract beneficial insects and pollinators. This method promotes natural pest control and improves soil health through complementary root systems and nutrient cycling. Increased plant variety also supports ecosystem resilience, reducing the risk of disease outbreaks and crop failure compared to monoculture block planting.
Advantages of Block Planting in Permaculture Systems
Block planting in permaculture systems maximizes space efficiency and creates microclimates that enhance water retention and soil fertility. This method supports stronger pest control by concentrating beneficial insects and facilitating easier crop management. Enhanced root zone development and improved nutrient cycling further optimize plant health and yield in diverse ecosystems.
Yield Efficiency: Interplanting vs Block Planting
Interplanting maximizes yield efficiency by utilizing space vertically and horizontally, enabling multiple crops to grow simultaneously and reducing competition for resources. Block planting simplifies management but often results in lower overall yield per square foot due to single-crop monocultures that underutilize available space. Studies in permaculture systems show interplanting can increase total productivity by up to 30% compared to traditional block planting methods.
Pest and Disease Management in Both Techniques
Interplanting in permaculture enhances pest and disease management by promoting biodiversity, which attracts beneficial insects and disrupts pest cycles, reducing the likelihood of widespread infestations. Block planting, while easier to manage, can create monoculture patches that may increase vulnerability to pests and diseases due to the uniformity of host plants. Integrating diverse species through interplanting supports natural pest control mechanisms and improves overall ecosystem resilience in sustainable gardening systems.
Soil Health and Nutrient Cycling Comparison
Interplanting enhances soil health by promoting diverse root structures that improve soil aeration and microbial activity, leading to more efficient nutrient cycling compared to block planting. Diverse plant interactions in interplanted systems facilitate nitrogen fixation and organic matter contribution, boosting soil fertility and reducing the need for synthetic inputs. Block planting, while simpler to manage, often results in nutrient depletion and reduced microbial diversity due to monoculture practices.
Space Utilization: Which Method Maximizes Growth?
Interplanting optimizes space utilization by combining complementary plants in the same area, promoting biodiversity and efficient nutrient use, which maximizes overall growth. Block planting concentrates a single crop in a designated section, simplifying management but often leaving soil underutilized and reducing potential yield per square foot. Studies in permaculture emphasize interplanting's superior ability to enhance productivity through layered growth and effective space sharing.
Practical Tips for Implementing Interplanting
Interplanting maximizes space by growing complementary plants together, enhancing biodiversity and pest control in permaculture gardens. Practical tips include selecting plants with compatible root depths, growth habits, and nutrient needs to reduce competition and improve overall yield. Regular monitoring and adjusting planting patterns ensure optimal light exposure and soil health, promoting sustainable productivity.
Choosing Between Interplanting and Block Planting for Your Garden
Selecting between interplanting and block planting depends on your garden's goals and spatial dynamics. Interplanting enhances biodiversity and maximizes space by mixing compatible crops, which can improve pest control and soil health. Block planting simplifies management and irrigation, making it ideal for larger gardens focused on single crop yields or clearer harvesting schedules.
Interplanting vs Block Planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com