
Sheet Mulching vs Raised Beds Illustration
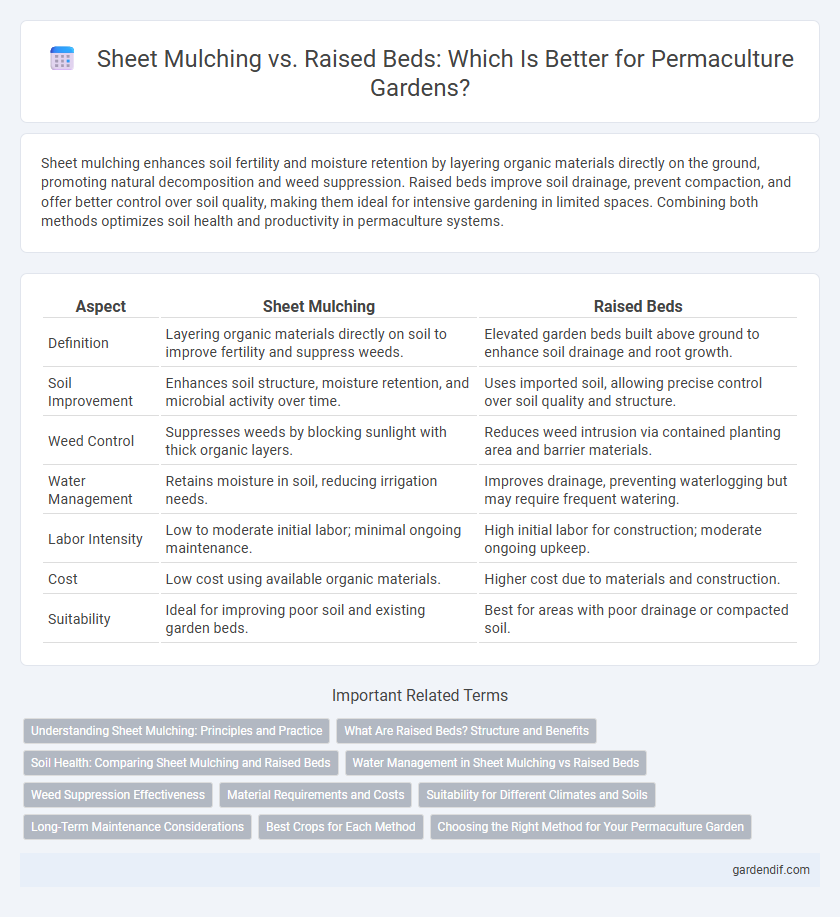
Sheet mulching enhances soil fertility and moisture retention by layering organic materials directly on the ground, promoting natural decomposition and weed suppression. Raised beds improve soil drainage, prevent compaction, and offer better control over soil quality, making them ideal for intensive gardening in limited spaces. Combining both methods optimizes soil health and productivity in permaculture systems.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sheet Mulching | Raised Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layering organic materials directly on soil to improve fertility and suppress weeds. | Elevated garden beds built above ground to enhance soil drainage and root growth. |
| Soil Improvement | Enhances soil structure, moisture retention, and microbial activity over time. | Uses imported soil, allowing precise control over soil quality and structure. |
| Weed Control | Suppresses weeds by blocking sunlight with thick organic layers. | Reduces weed intrusion via contained planting area and barrier materials. |
| Water Management | Retains moisture in soil, reducing irrigation needs. | Improves drainage, preventing waterlogging but may require frequent watering. |
| Labor Intensity | Low to moderate initial labor; minimal ongoing maintenance. | High initial labor for construction; moderate ongoing upkeep. |
| Cost | Low cost using available organic materials. | Higher cost due to materials and construction. |
| Suitability | Ideal for improving poor soil and existing garden beds. | Best for areas with poor drainage or compacted soil. |
Understanding Sheet Mulching: Principles and Practice
Sheet mulching in permaculture involves layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on the soil to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and enrich soil fertility. This method mimics natural forest floor processes, promoting microbial activity and improving soil structure without disturbing existing soil layers. Practicing sheet mulching effectively enhances soil health and plant growth by creating a nutrient-rich, well-aerated environment that supports sustainable gardening.
What Are Raised Beds? Structure and Benefits
Raised beds are elevated garden plots constructed using frames filled with soil and organic matter, designed to improve drainage and soil quality. Their structured form facilitates better root growth, reduces soil compaction, and allows for easier weed and pest control. Raised beds enhance plant health by optimizing nutrient availability, temperature regulation, and water retention, making them a popular choice in permaculture gardening for efficient space use and crop yield.
Soil Health: Comparing Sheet Mulching and Raised Beds
Sheet mulching enhances soil health by promoting microbial activity and organic matter decomposition through layered compost and mulch applications, which improves moisture retention and nutrient availability. Raised beds offer better soil aeration and drainage, reducing compaction and enabling precise soil amendments tailored to plant needs. Both methods improve soil structure but sheet mulching excels in building long-term fertility, while raised beds provide immediate control over soil conditions.
Water Management in Sheet Mulching vs Raised Beds
Sheet mulching enhances water retention by creating a thick, organic mulch layer that absorbs and slowly releases moisture directly to plant roots, reducing runoff and evaporation. Raised beds improve drainage and prevent waterlogging by elevating soil above surrounding ground levels, making them ideal for heavy or compacted soils. Effective water management depends on soil type and climate, with sheet mulching benefiting moisture-hungry plants in drier areas and raised beds optimizing drainage in wetter conditions.
Weed Suppression Effectiveness
Sheet mulching provides excellent weed suppression by creating a thick barrier of organic materials that blocks sunlight and smothers weed seeds, enhancing soil fertility over time. Raised beds offer good weed control by elevating planting areas and minimizing soil disturbance, but they may require regular maintenance to remove persistent weeds along the edges. Comparing both, sheet mulching is often more effective for long-term weed suppression due to continuous organic matter layering and soil health improvement.
Material Requirements and Costs
Sheet mulching requires primarily organic materials such as cardboard, newspaper, compost, and mulch, often sourced from recycled or local waste products, keeping costs low and environmentally friendly. Raised beds demand more substantial inputs including quality soil, wood for framing, and hardware, leading to higher initial investment but improved soil depth and drainage. Both methods benefit permaculture systems by enhancing soil health, but sheet mulching excels in minimal material expense while raised beds offer better structural control.
Suitability for Different Climates and Soils
Sheet mulching adapts well to diverse climates by improving soil structure and moisture retention, making it ideal for both arid and temperate regions. Raised beds excel in areas with poor drainage or compacted soils, providing enhanced aeration and root development. Selecting between these methods depends on soil texture, drainage capacity, and local climate conditions to optimize plant health and yield in permaculture systems.
Long-Term Maintenance Considerations
Sheet mulching reduces long-term maintenance by suppressing weeds, enhancing soil structure, and retaining moisture, which decreases the need for watering and weeding. Raised beds offer improved drainage, easier access for planting and harvesting, and better control over soil composition, but they may require occasional soil replenishment and structural repairs. Both methods promote sustainable soil health, but sheet mulching demands less ongoing physical upkeep compared to the periodic maintenance needed for raised beds.
Best Crops for Each Method
Sheet mulching best supports shade-tolerant, moisture-loving crops such as leafy greens, herbs, and root vegetables like carrots and beets due to its excellent weed suppression and moisture retention. Raised beds favor crops requiring well-drained soil and deeper root systems, including tomatoes, peppers, and beans, as they offer improved aeration and soil warming. Both methods enhance soil health but selecting crops based on moisture and root depth needs optimizes growth and yield in permaculture systems.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Permaculture Garden
Sheet mulching enhances soil health by layering organic materials that suppress weeds and improve moisture retention, ideal for establishing new garden areas with minimal soil disturbance. Raised beds offer superior drainage, increased soil warmth, and ease of access, making them suitable for intensive planting and areas with poor native soil. Selecting between sheet mulching and raised beds depends on factors like soil quality, garden goals, and resource availability to maximize productivity and sustainability.
Sheet Mulching vs Raised Beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com