
Polyculture vs Polycropping Illustration
Polyculture involves growing multiple complementary plant species together in the same space to mimic natural ecosystems, enhancing biodiversity and soil health. Polycropping, on the other hand, refers to growing different crops simultaneously but in distinct rows or patches, optimizing land use and reducing pest outbreaks. Both approaches promote sustainable agriculture by improving resilience and resource efficiency within permaculture systems.
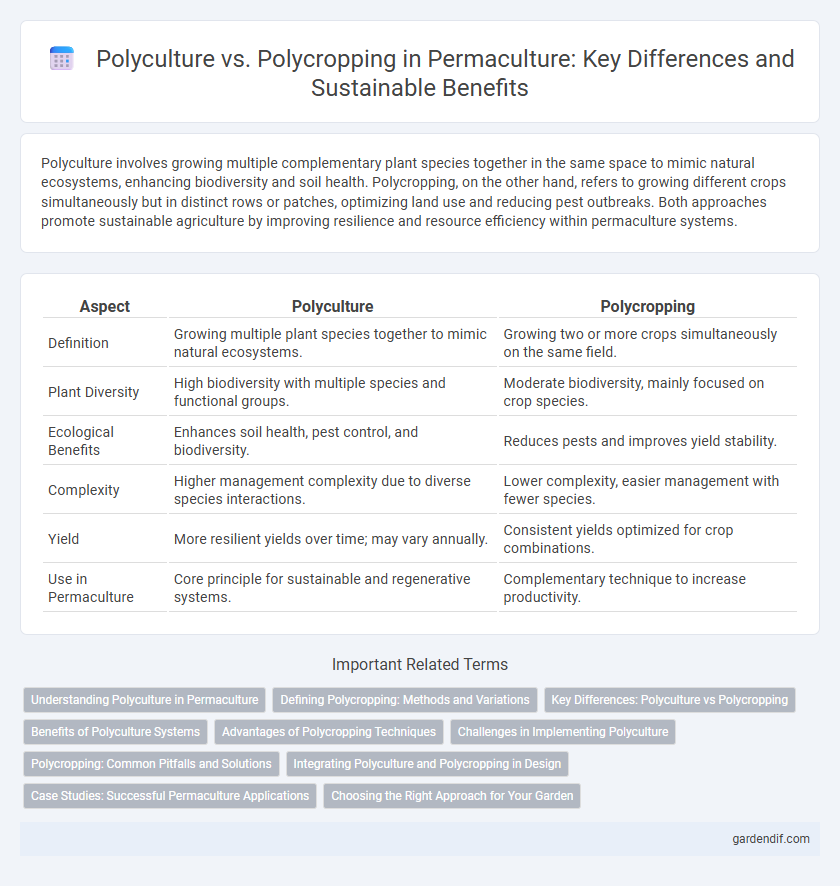
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Polyculture | Polycropping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing multiple plant species together to mimic natural ecosystems. | Growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field. |
| Plant Diversity | High biodiversity with multiple species and functional groups. | Moderate biodiversity, mainly focused on crop species. |
| Ecological Benefits | Enhances soil health, pest control, and biodiversity. | Reduces pests and improves yield stability. |
| Complexity | Higher management complexity due to diverse species interactions. | Lower complexity, easier management with fewer species. |
| Yield | More resilient yields over time; may vary annually. | Consistent yields optimized for crop combinations. |
| Use in Permaculture | Core principle for sustainable and regenerative systems. | Complementary technique to increase productivity. |
Understanding Polyculture in Permaculture
Polyculture in permaculture involves cultivating multiple complementary plant species together to enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and create resilient ecosystems. This practice contrasts with polycropping by emphasizing ecological relationships and long-term sustainability rather than just multiple crops grown simultaneously. Understanding polyculture helps optimize resource use, reduce pests naturally, and increase overall productivity in permaculture systems.
Defining Polycropping: Methods and Variations
Polycropping involves cultivating multiple crop species simultaneously within the same space to maximize biodiversity and resource use efficiency. Common methods include intercropping, strip cropping, and relay cropping, each varying in planting arrangement and timing to optimize growth conditions and pest management. This approach contrasts with monoculture by promoting ecological balance and enhancing soil fertility through diverse root structures and nutrient cycles.
Key Differences: Polyculture vs Polycropping
Polyculture involves cultivating multiple crop species in the same area to mimic natural ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and resilience, while polycropping refers specifically to growing two or more crops in the same field simultaneously for maximizing yield and efficient space use. Key differences include polyculture's emphasis on ecological balance and long-term sustainability, whereas polycropping focuses more on optimizing agricultural productivity and resource utilization. Both practices support soil health and pest management but vary in complexity and ecological intentionality.
Benefits of Polyculture Systems
Polyculture systems enhance biodiversity by integrating multiple plant species in the same area, improving pest control and soil health compared to monocultures. These systems increase resilience against climate variability and reduce the need for chemical inputs by promoting natural ecological processes. Research shows polyculture farms yield higher overall productivity and support sustainable land management practices essential for long-term permaculture success.
Advantages of Polycropping Techniques
Polycropping techniques enhance biodiversity by cultivating multiple crops simultaneously, improving pest control and reducing the risk of crop failure compared to monoculture. This method increases soil fertility through natural nutrient cycling and optimizes land use efficiency by maximizing yield per area. Integrating complementary plant species in polycropping systems supports sustainable agriculture and promotes ecosystem resilience.
Challenges in Implementing Polyculture
Implementing polyculture faces significant challenges such as complex plant species interactions that require advanced knowledge of ecological relationships and careful planning to avoid competition for resources. Maintaining biodiversity demands ongoing monitoring and adaptive management to ensure all species thrive without one dominating. Economic constraints and labor-intensive practices also limit scalability compared to monoculture or simpler polycropping systems.
Polycropping: Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Polycropping involves growing multiple crop species simultaneously in the same space to maximize yield and biodiversity but can encounter common pitfalls such as competition for nutrients, water, and light among plants. To overcome these challenges, strategic plant selection based on complementary root depths, nutrient needs, and growth rates is essential, along with proper spatial arrangement and timely interventions like mulching and targeted irrigation. Employing crop rotation and companion planting further enhances soil health and reduces pest pressure, ensuring a more resilient and productive polycropping system.
Integrating Polyculture and Polycropping in Design
Integrating polyculture and polycropping in permaculture design enhances biodiversity and soil health by combining multiple plant species within the same area and across sequential planting cycles. This approach maximizes resource use efficiency, pest control, and resilience, creating synergistic interactions that support sustainable food production. Effective design leverages spatial and temporal diversity to optimize ecosystem functions and improve overall productivity.
Case Studies: Successful Permaculture Applications
Case studies in permaculture demonstrate the benefits of polyculture systems where diverse plant species coexist to enhance ecosystem resilience and soil health, such as the multi-layered food forests in Australia that mimic natural forests for sustainable yields. Polycropping techniques used in traditional Asian rice paddies combine compatible crops like legumes and vegetables, increasing biodiversity and reducing pest outbreaks while improving overall productivity. Evidence from these successful permaculture applications highlights the critical role of species diversity and complementary plant interactions in creating sustainable agricultural landscapes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Garden
Polyculture integrates diverse plant species in one area to promote ecological balance, pest resistance, and soil health, making it ideal for sustainable permaculture systems. Polycropping involves growing multiple crops simultaneously but often in distinct rows or sections, optimizing space and crop yield for specific garden goals. Choosing the right approach depends on garden size, soil conditions, and crop diversity preferences, ensuring resilient and productive growth tailored to your permaculture design.
Polyculture vs Polycropping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com