
Rainwater Harvesting vs Irrigation Illustration
Rainwater harvesting captures and stores natural rainfall, reducing dependency on external water sources and promoting sustainable water management in permaculture systems. Irrigation distributes water directly to plants, but often relies on external supplies, which can lead to overconsumption and increased energy use. Integrating rainwater harvesting with efficient irrigation techniques enhances soil moisture retention and supports resilient, low-impact agricultural practices.
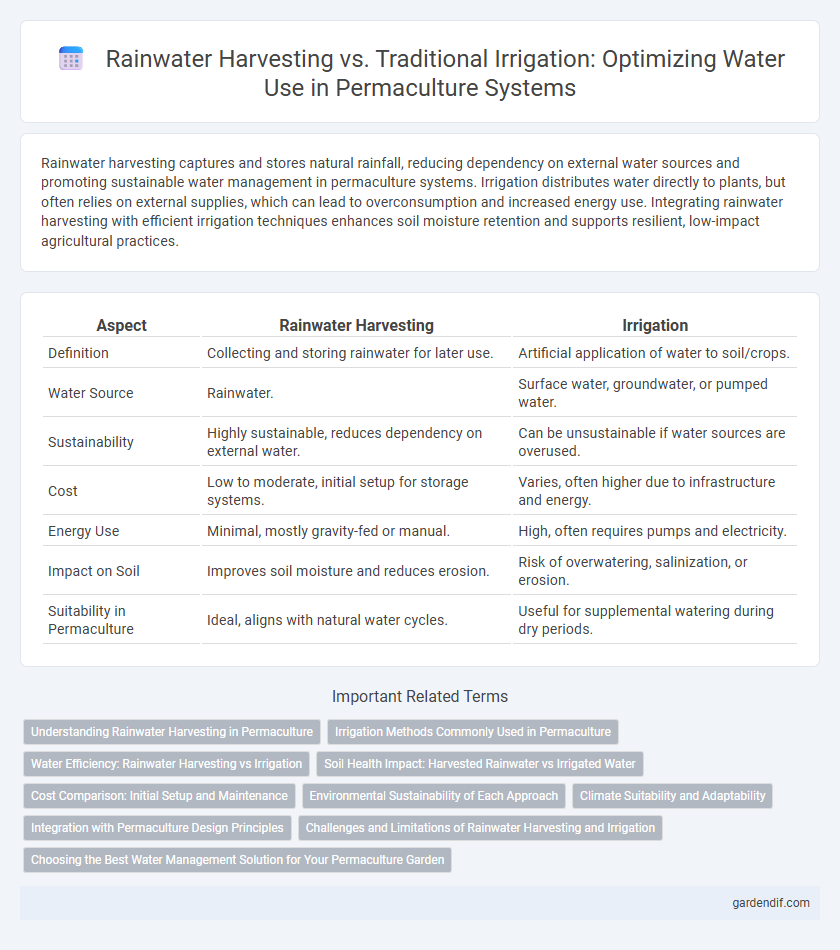
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Rainwater Harvesting | Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collecting and storing rainwater for later use. | Artificial application of water to soil/crops. |
| Water Source | Rainwater. | Surface water, groundwater, or pumped water. |
| Sustainability | Highly sustainable, reduces dependency on external water. | Can be unsustainable if water sources are overused. |
| Cost | Low to moderate, initial setup for storage systems. | Varies, often higher due to infrastructure and energy. |
| Energy Use | Minimal, mostly gravity-fed or manual. | High, often requires pumps and electricity. |
| Impact on Soil | Improves soil moisture and reduces erosion. | Risk of overwatering, salinization, or erosion. |
| Suitability in Permaculture | Ideal, aligns with natural water cycles. | Useful for supplemental watering during dry periods. |
Understanding Rainwater Harvesting in Permaculture
Rainwater harvesting in permaculture captures and stores natural rainfall to reduce dependence on conventional irrigation systems, conserving water and promoting sustainability. By utilizing techniques such as swales, rain gardens, and rain barrels, permaculture designs enhance soil moisture retention and improve plant health while minimizing runoff and erosion. Integrating rainwater harvesting supports ecosystem balance, reduces water bills, and fosters resilient agricultural practices tailored to local climate conditions.
Irrigation Methods Commonly Used in Permaculture
Drip irrigation and soaker hoses are the most efficient methods commonly used in permaculture, delivering water directly to plant roots with minimal evaporation. Swales and contour ditches help manage natural water flow, promoting infiltration and reducing runoff on sloped landscapes. These irrigation techniques optimize water use, support soil health, and enhance the sustainability of permaculture systems.
Water Efficiency: Rainwater Harvesting vs Irrigation
Rainwater harvesting maximizes water efficiency by capturing and storing natural precipitation, reducing reliance on municipal or groundwater sources. Irrigation systems often result in water loss through evaporation and runoff, lowering overall water use efficiency in agricultural practices. Implementing rainwater harvesting in permaculture enhances sustainable water management by providing a renewable, cost-effective supply that directly supports plant growth.
Soil Health Impact: Harvested Rainwater vs Irrigated Water
Harvested rainwater enhances soil health by reducing chemical runoff and maintaining natural microbial activity, promoting nutrient-rich, well-aerated soil structures essential for plant growth. In contrast, conventional irrigation often relies on treated or groundwater sources that may contain salts and chemicals, leading to soil compaction, reduced microbial diversity, and potential nutrient imbalances. Utilizing rainwater harvesting in permaculture systems supports sustainable soil moisture levels and fosters resilient ecosystems with improved long-term fertility.
Cost Comparison: Initial Setup and Maintenance
Rainwater harvesting systems typically require higher initial setup costs due to the need for gutters, storage tanks, and filtration units, but maintenance is relatively low and primarily involves cleaning tanks and filters. Irrigation systems, particularly drip or sprinkler setups, often have lower initial expenses but incur higher ongoing costs from water usage, repairs, and energy consumption. Over time, rainwater harvesting proves more cost-effective by reducing dependence on municipal water and minimizing utility bills, making it a sustainable investment for permaculture projects.
Environmental Sustainability of Each Approach
Rainwater harvesting enhances environmental sustainability by reducing dependency on municipal water sources and minimizing runoff, which helps replenish groundwater and prevents soil erosion. In comparison, traditional irrigation systems often rely on over-extracted groundwater or surface water, leading to depletion of natural water reserves and increased energy consumption for pumping. Implementing rainwater harvesting in permaculture systems optimizes water use efficiency and promotes ecosystem resilience by conserving local hydrological cycles.
Climate Suitability and Adaptability
Rainwater harvesting offers a climate-resilient solution by capturing and storing precipitation, making it ideal for arid and semi-arid regions with irregular rainfall patterns. Irrigation systems provide consistent water supply but require energy and infrastructure, often better suited for climates with predictable water sources and higher water availability. Combining both methods enhances adaptability, allowing permaculture practitioners to optimize water management based on seasonal and climatic variability.
Integration with Permaculture Design Principles
Rainwater harvesting aligns with permaculture design principles by promoting water conservation, reducing runoff, and enhancing soil moisture retention, which supports sustainable plant growth. Unlike conventional irrigation, harvesting rainwater enables decentralized water management, integrating natural cycles and reducing dependency on external water sources. This synergy increases ecosystem resilience and fosters a self-sustaining agricultural system by mimicking natural hydrological patterns.
Challenges and Limitations of Rainwater Harvesting and Irrigation
Rainwater harvesting faces challenges such as limited storage capacity, inconsistent rainfall patterns, and potential contamination risks that can affect water quality. Irrigation systems often contend with issues including high water consumption, soil salinization, and energy-intensive operation costs that reduce sustainability. Both methods require careful management and infrastructure investment to optimize water use efficiency in permaculture systems.
Choosing the Best Water Management Solution for Your Permaculture Garden
Rainwater harvesting captures and stores natural precipitation, reducing dependency on external water sources and promoting sustainability in permaculture gardens. Irrigation systems, while providing controlled water delivery, often require energy inputs and can lead to water wastage if not managed efficiently. Selecting the optimal water management solution depends on local climate, water availability, soil type, and garden design, with rainwater harvesting typically enhancing resilience and resource conservation.
Rainwater Harvesting vs Irrigation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com