
Neem oil vs Pyrethrin Illustration
Neem oil and pyrethrin are both natural insecticides commonly used in organic gardening, but they work differently to protect plants. Neem oil disrupts the hormonal systems of insects, inhibiting growth and reproduction, while pyrethrin targets the nervous system, causing paralysis and death upon contact. Pyrethrin acts faster but breaks down quickly in sunlight, whereas neem oil offers longer-lasting protection and also has antifungal properties.
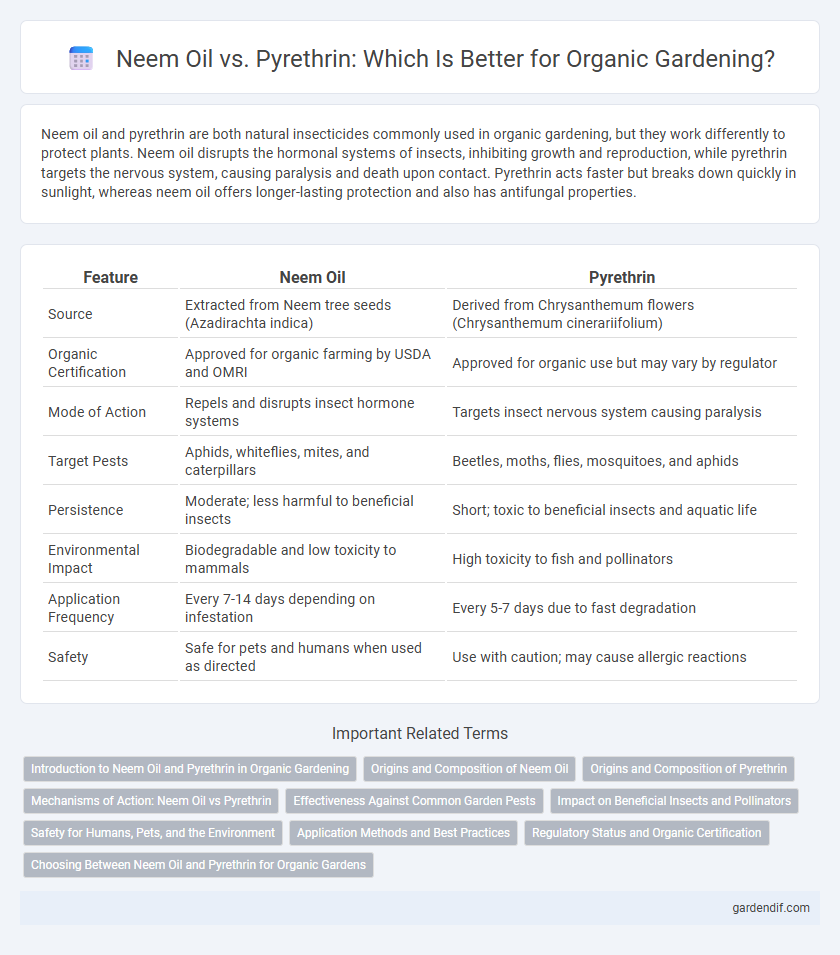
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Neem Oil | Pyrethrin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from Neem tree seeds (Azadirachta indica) | Derived from Chrysanthemum flowers (Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium) |
| Organic Certification | Approved for organic farming by USDA and OMRI | Approved for organic use but may vary by regulator |
| Mode of Action | Repels and disrupts insect hormone systems | Targets insect nervous system causing paralysis |
| Target Pests | Aphids, whiteflies, mites, and caterpillars | Beetles, moths, flies, mosquitoes, and aphids |
| Persistence | Moderate; less harmful to beneficial insects | Short; toxic to beneficial insects and aquatic life |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and low toxicity to mammals | High toxicity to fish and pollinators |
| Application Frequency | Every 7-14 days depending on infestation | Every 5-7 days due to fast degradation |
| Safety | Safe for pets and humans when used as directed | Use with caution; may cause allergic reactions |
Introduction to Neem Oil and Pyrethrin in Organic Gardening
Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree, acts as a natural insect repellent and fungicide in organic gardening, effectively controlling pests without harmful chemicals. Pyrethrin, extracted from chrysanthemum flowers, serves as a fast-acting insecticide targeting a broad spectrum of garden pests, breaking down quickly to minimize environmental impact. Both neem oil and pyrethrin support organic pest management by providing eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic pesticides.
Origins and Composition of Neem Oil
Neem oil is derived from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree, native to the Indian subcontinent, and contains active compounds like azadirachtin, nimbin, and salannin, which contribute to its insecticidal and antifungal properties. Pyrethrin, extracted from the chrysanthemum flower, primarily contains pyrethrins and related esters that affect the nervous systems of insects. The unique triterpenoid structure of neem oil's constituents distinguishes it from pyrethrin's neurotoxic components, influencing their different modes of action and applications in organic pest control.
Origins and Composition of Pyrethrin
Pyrethrin is a natural insecticide derived from the dried flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium and Chrysanthemum coccineum, native to East Africa and Asia. Its composition includes six related ester compounds that target the nervous system of insects, causing paralysis and death. Unlike neem oil, which contains azadirachtin compounds, pyrethrin provides a rapid knockdown effect due to its potent neurotoxic ester components.
Mechanisms of Action: Neem Oil vs Pyrethrin
Neem oil acts as an insect growth regulator by disrupting hormone function, inhibiting larvae development and reducing feeding through azadirachtin compounds. Pyrethrin targets the nervous system of insects by binding to sodium channels, causing paralysis and rapid mortality. The contrasting mechanisms make neem oil a slower, long-term control option, while pyrethrin delivers fast-acting insect knockdown.
Effectiveness Against Common Garden Pests
Neem oil disrupts the life cycle of common garden pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites by acting as an insect growth regulator and repellent. Pyrethrin provides rapid knockdown of a broad spectrum of insects, including beetles and caterpillars, through neurotoxic effects on their nervous systems. Both organic options target different pest types and infestation stages, making them complementary for integrated pest management in organic gardening.
Impact on Beneficial Insects and Pollinators
Neem oil disrupts the life cycle of pests with minimal toxicity to beneficial insects and pollinators such as bees and ladybugs, making it suitable for organic gardening. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, acts quickly but has a broader spectrum toxicity that can harm non-target beneficial insects and pollinators if not carefully applied. Choosing neem oil supports ecological balance by preserving essential insect populations vital for pollination and natural pest control.
Safety for Humans, Pets, and the Environment
Neem oil offers a safer organic pest control option compared to pyrethrin due to its lower toxicity for humans, pets, and beneficial insects. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals and is moderately toxic to cats and aquatic life. Neem oil's biodegradability and minimal environmental impact make it a preferred choice for sustainable pest management in organic gardening.
Application Methods and Best Practices
Neem oil application involves foliar sprays or soil drench techniques to effectively manage pests such as aphids, mites, and whiteflies, emphasizing consistent coverage and timing during early pest development stages. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, is typically applied as a contact insecticide via spraying directly on affected plants, requiring frequent reapplication due to rapid degradation in sunlight. Best practices for neem oil include using warm water emulsions and avoiding application during peak sunlight to prevent phytotoxicity, while pyrethrin use demands careful calibration to minimize impact on beneficial insects and adherence to organic standards.
Regulatory Status and Organic Certification
Neem oil is widely accepted in organic farming due to its natural origin and approval by major certification bodies such as OMRI and USDA Organic, whereas pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, is also certified organic but faces stricter regulatory restrictions in some regions due to its insecticidal potency. Regulatory agencies like the EPA classify neem oil as a minimum risk pesticide with fewer usage limitations, while pyrethrin requires more stringent compliance with residue limits and application controls to ensure environmental and human safety. Choosing between neem oil and pyrethrin for organic practices involves balancing regulatory approval, certification standards, and the specific pest management needs of the crop.
Choosing Between Neem Oil and Pyrethrin for Organic Gardens
Neem oil and pyrethrin are both effective organic pesticides, but neem oil acts as a systemic insect repellent and disrupts insect growth, making it ideal for long-term pest control in organic gardens. Pyrethrin provides rapid knockdown of a broad spectrum of insects but breaks down quickly in sunlight, necessitating frequent applications for sustained protection. Selecting between neem oil and pyrethrin depends on the target pest, desired speed of action, and garden conditions to ensure environmentally safe and effective pest management.
Neem oil vs Pyrethrin Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com