
Natural pest control vs systemic pesticides Illustration
Natural pest control relies on biological methods and organic substances to manage pests, promoting ecosystem balance and reducing chemical residues in crops. Systemic pesticides, absorbed by plants and distributed throughout their tissues, can offer broad-spectrum pest protection but may negatively impact beneficial insects and soil health. Choosing natural pest control supports sustainable agriculture by minimizing environmental risks and preserving biodiversity.
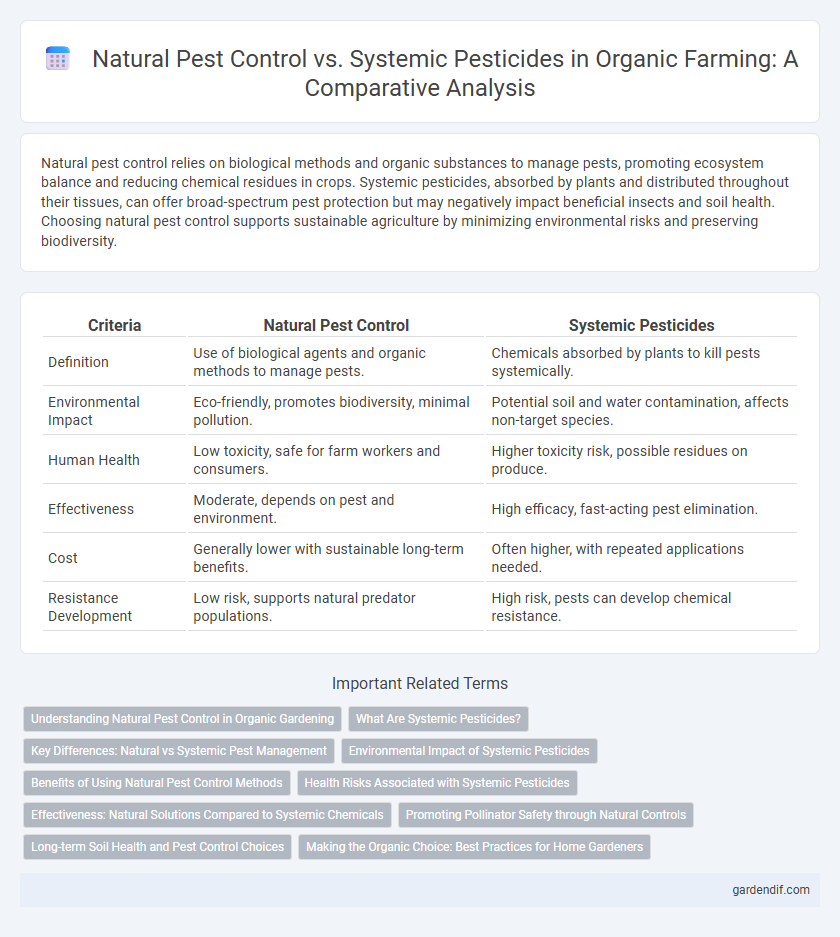
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Natural Pest Control | Systemic Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of biological agents and organic methods to manage pests. | Chemicals absorbed by plants to kill pests systemically. |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, promotes biodiversity, minimal pollution. | Potential soil and water contamination, affects non-target species. |
| Human Health | Low toxicity, safe for farm workers and consumers. | Higher toxicity risk, possible residues on produce. |
| Effectiveness | Moderate, depends on pest and environment. | High efficacy, fast-acting pest elimination. |
| Cost | Generally lower with sustainable long-term benefits. | Often higher, with repeated applications needed. |
| Resistance Development | Low risk, supports natural predator populations. | High risk, pests can develop chemical resistance. |
Understanding Natural Pest Control in Organic Gardening
Natural pest control in organic gardening utilizes beneficial insects, crop rotation, and companion planting to manage pests without harmful chemicals. This approach maintains soil health and biodiversity by avoiding systemic pesticides, which can accumulate in plant tissues and disrupt ecosystems. Emphasizing ecological balance, natural pest control supports sustainable agriculture and reduces environmental contamination.
What Are Systemic Pesticides?
Systemic pesticides are chemicals absorbed by plants, distributing toxins throughout their tissues to protect against pests from within. Unlike natural pest control methods that rely on biological agents or organic substances, systemic pesticides target pests at a molecular level but may pose risks to beneficial insects and environmental health. These pesticides are commonly used in conventional agriculture for long-lasting pest resistance but raise concerns about soil and water contamination.
Key Differences: Natural vs Systemic Pest Management
Natural pest control employs biological agents like beneficial insects and organic repellents to target pests while preserving ecosystem balance, whereas systemic pesticides involve chemical substances absorbed by plants to provide internal protection against pests. Natural methods prioritize environmental sustainability and minimize chemical residues, contrasting with systemic pesticides that can impact non-target organisms and accumulate in the food chain. The effectiveness of natural pest control depends on fostering biodiversity, while systemic pesticides offer immediate and widespread pest suppression.
Environmental Impact of Systemic Pesticides
Systemic pesticides penetrate plants and persist in soil, leading to contamination of water sources and harm to beneficial insects such as pollinators. These chemicals can accumulate in the food chain, causing long-term ecological damage and reducing biodiversity. Natural pest control methods minimize environmental risks by enhancing ecosystem balance and avoiding toxic residues.
Benefits of Using Natural Pest Control Methods
Natural pest control methods reduce environmental harm by targeting specific pests without disrupting beneficial insect populations, unlike systemic pesticides that can contaminate soil and water. These techniques promote biodiversity and enhance soil health by maintaining the natural balance of ecosystems, supporting sustainable agricultural practices. Organic farmers benefit from natural pest control through reduced chemical residues on crops, safeguarding consumer health and meeting organic certification standards.
Health Risks Associated with Systemic Pesticides
Systemic pesticides pose significant health risks due to their ability to infiltrate plant tissues, making residues persistent in fruits and vegetables consumed by humans. Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to hormonal disruptions, neurological impairments, and increased risk of chronic illnesses. Natural pest control methods reduce these risks by utilizing non-toxic substances and biological agents that target pests without contaminating the food supply.
Effectiveness: Natural Solutions Compared to Systemic Chemicals
Natural pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects and using neem oil, offer targeted effectiveness by promoting ecological balance without residual toxicity. Systemic pesticides provide rapid and broad-spectrum pest elimination but can lead to resistance build-up and negatively impact non-target organisms. Research indicates that integrated pest management combining natural solutions with selective systemic applications enhances long-term crop protection and sustainability.
Promoting Pollinator Safety through Natural Controls
Natural pest control methods prioritize the use of biological agents and plant-based solutions to minimize harm to pollinators like bees and butterflies, essential for ecosystem balance. Unlike systemic pesticides, which can contaminate nectar and pollen, natural controls reduce chemical residues in the environment, preserving pollinator health and promoting biodiversity. Implementing integrated pest management strategies with natural predators supports sustainable agriculture while safeguarding pollinator populations critical for crop pollination.
Long-term Soil Health and Pest Control Choices
Natural pest control methods enhance long-term soil health by preserving beneficial microorganisms and maintaining ecological balance, unlike systemic pesticides that can disrupt soil biodiversity. Systemic pesticides often accumulate in the soil, leading to decreased fertility and increased pest resistance over time. Choosing natural pest control supports sustainable farming practices by promoting resilient soil ecosystems and reducing chemical dependency.
Making the Organic Choice: Best Practices for Home Gardeners
Natural pest control employs beneficial insects, companion planting, and organic sprays to manage pests without harmful chemicals, preserving soil health and biodiversity. Systemic pesticides infiltrate the plant's vascular system, offering prolonged protection but posing risks to pollinators and beneficial insects. Home gardeners choosing organic methods should prioritize integrated pest management, soil enrichment with compost, and selecting resistant plant varieties to ensure sustainable, chemical-free gardening.
Natural pest control vs systemic pesticides Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com