
Mulching with straw vs Mulching with plastic Illustration
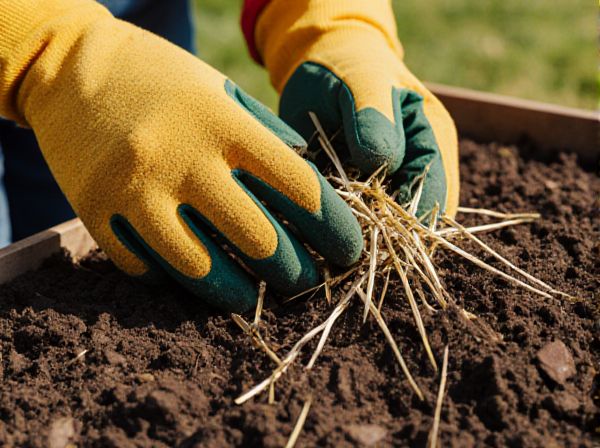
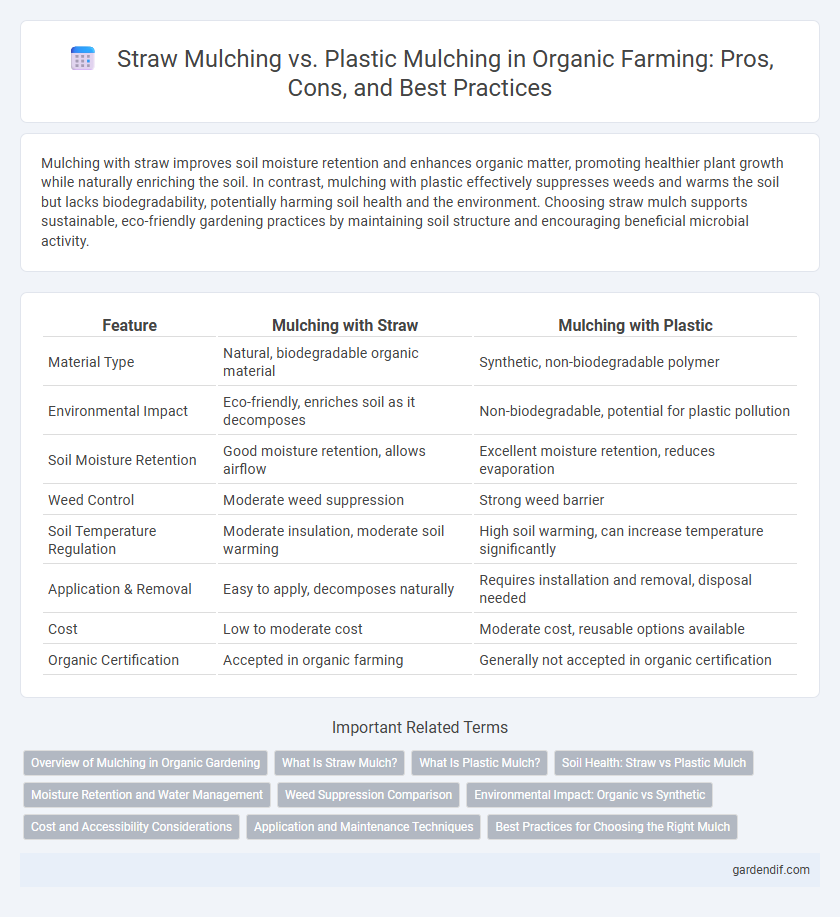
Mulching with straw improves soil moisture retention and enhances organic matter, promoting healthier plant growth while naturally enriching the soil. In contrast, mulching with plastic effectively suppresses weeds and warms the soil but lacks biodegradability, potentially harming soil health and the environment. Choosing straw mulch supports sustainable, eco-friendly gardening practices by maintaining soil structure and encouraging beneficial microbial activity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mulching with Straw | Mulching with Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural, biodegradable organic material | Synthetic, non-biodegradable polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, enriches soil as it decomposes | Non-biodegradable, potential for plastic pollution |
| Soil Moisture Retention | Good moisture retention, allows airflow | Excellent moisture retention, reduces evaporation |
| Weed Control | Moderate weed suppression | Strong weed barrier |
| Soil Temperature Regulation | Moderate insulation, moderate soil warming | High soil warming, can increase temperature significantly |
| Application & Removal | Easy to apply, decomposes naturally | Requires installation and removal, disposal needed |
| Cost | Low to moderate cost | Moderate cost, reusable options available |
| Organic Certification | Accepted in organic farming | Generally not accepted in organic certification |
Overview of Mulching in Organic Gardening
Mulching in organic gardening enhances soil moisture retention, suppresses weeds, and regulates soil temperature, promoting healthier plant growth. Straw mulch, a natural and biodegradable option, improves soil structure and provides habitat for beneficial organisms, while plastic mulch effectively conserves moisture and controls weeds but lacks organic benefits and can contribute to environmental waste. Selecting the appropriate mulch depends on balancing organic soil health goals with practical considerations like moisture management and weed control.
What Is Straw Mulch?
Straw mulch consists of dried stalks of cereal crops such as wheat, barley, or oats, used to cover soil surfaces in organic gardening to retain moisture and suppress weeds naturally. This biodegradable mulch improves soil structure by adding organic matter as it decomposes, enhancing nutrient cycling and promoting beneficial microbial activity. Unlike plastic mulch, straw mulch is eco-friendly, reduces soil temperature fluctuations, and supports sustainable soil health without causing plastic waste.
What Is Plastic Mulch?
Plastic mulch is a synthetic material commonly used in organic farming to cover soil, suppress weeds, and conserve moisture. Unlike straw mulch, plastic mulch creates a barrier that increases soil temperature and reduces evaporation, promoting faster plant growth and higher yields. Its impermeability to water and air requires careful management to prevent negative impacts on soil health and environmental sustainability.
Soil Health: Straw vs Plastic Mulch
Straw mulch enhances soil health by improving moisture retention, promoting microbial activity, and adding organic matter that enriches soil fertility. In contrast, plastic mulch provides effective weed control and temperature regulation but can hinder water infiltration and does not contribute to soil organic content. Over time, straw supports sustainable soil structure and nutrient cycling, while plastic mulch requires careful management to avoid negative impacts on soil ecosystems.
Moisture Retention and Water Management
Mulching with straw enhances moisture retention by allowing better water infiltration and reducing evaporation through an organic, breathable layer that gradually decomposes, enriching soil health. In contrast, plastic mulching creates a non-porous barrier that significantly limits evaporation but may cause water runoff and reduced soil aeration, potentially leading to waterlogging or uneven moisture distribution. Effective water management favors straw mulching in organic systems for promoting sustainable moisture levels while plastic mulching suits high-moisture retention needs but requires careful irrigation control to prevent root stress.
Weed Suppression Comparison
Mulching with straw enhances weed suppression by creating a thick, breathable barrier that blocks sunlight while allowing moisture and air to reach the soil, fostering healthy plant growth. In contrast, plastic mulch forms an impermeable layer that effectively prevents weed emergence by obstructing light but can cause soil overheating and reduced aeration. Studies show straw mulch reduces weed density by up to 60%, while plastic mulching can achieve weed suppression rates exceeding 90%, though environmental impact and soil health considerations often favor organic options.
Environmental Impact: Organic vs Synthetic
Mulching with straw offers a biodegradable option that enriches soil health by adding organic matter and promoting microbial activity, reducing reliance on synthetic inputs. In contrast, plastic mulching contributes to soil pollution and microplastic accumulation, posing long-term environmental hazards despite its effectiveness in moisture retention. Choosing straw mulch supports sustainable farming practices by minimizing waste and enhancing soil biodiversity, aligning with ecological conservation goals.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Mulching with straw offers an affordable and readily accessible option for organic farmers, as straw is biodegradable and often locally sourced, reducing overall costs and environmental impact. Plastic mulching, while more expensive due to material and disposal costs, provides longer durability and better weed control but may require additional investment in removal and recycling. Choosing between straw and plastic mulch depends on budget constraints and the availability of materials within the farming community.
Application and Maintenance Techniques
Mulching with straw involves evenly spreading natural, biodegradable straw around plants, enhancing soil moisture retention and temperature regulation while requiring periodic replenishment as it decomposes. Plastic mulching uses black or clear polyethylene sheets that effectively suppress weeds and retain soil heat, but demand careful installation to avoid tearing and must be removed and disposed of properly after the growing season. Straw mulch promotes organic matter enrichment through decomposition, whereas plastic mulch minimizes water evaporation but necessitates diligent maintenance to prevent root overheating and plastic waste accumulation.
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Mulch
Choosing the right mulch is essential for optimizing soil health and crop yield in organic farming; straw mulch offers excellent moisture retention, temperature regulation, and biodegradability, enhancing soil structure and supporting beneficial microorganisms. Plastic mulch provides superior weed control and soil warmth but can lead to environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential impact on soil microbiota. Best practices recommend selecting straw mulch for long-term soil health and sustainability, while plastic mulch suits short-term, intensive production with proper environmental management and disposal protocols.
Mulching with straw vs Mulching with plastic Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com