
Green manure vs Synthetic soil amendments Illustration
Green manure enriches soil naturally by adding organic matter and improving microbial activity, boosting soil fertility sustainably. Synthetic soil amendments provide targeted nutrient supplementation but may lead to long-term soil degradation and reduced biodiversity. Choosing green manure supports eco-friendly farming practices and enhances soil health over time.
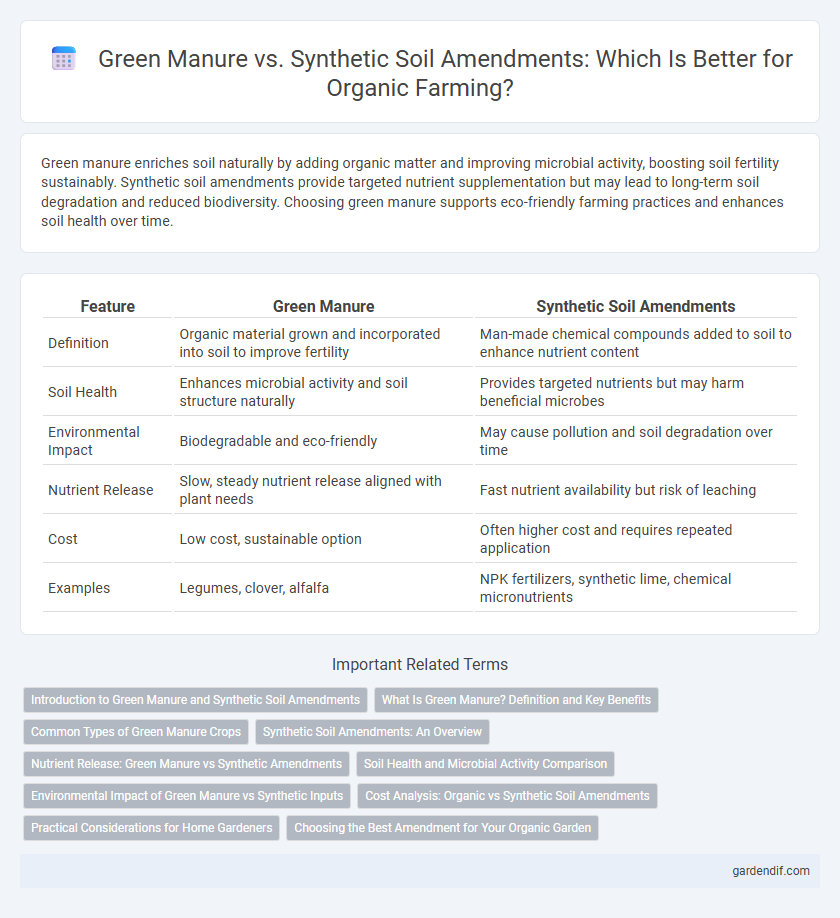
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Manure | Synthetic Soil Amendments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organic material grown and incorporated into soil to improve fertility | Man-made chemical compounds added to soil to enhance nutrient content |
| Soil Health | Enhances microbial activity and soil structure naturally | Provides targeted nutrients but may harm beneficial microbes |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | May cause pollution and soil degradation over time |
| Nutrient Release | Slow, steady nutrient release aligned with plant needs | Fast nutrient availability but risk of leaching |
| Cost | Low cost, sustainable option | Often higher cost and requires repeated application |
| Examples | Legumes, clover, alfalfa | NPK fertilizers, synthetic lime, chemical micronutrients |
Introduction to Green Manure and Synthetic Soil Amendments
Green manure involves growing specific crops like clover or alfalfa to enrich soil with organic matter and essential nutrients, enhancing soil structure and fertility naturally. Synthetic soil amendments consist of chemically formulated substances, such as fertilizers and conditioners, designed to rapidly improve nutrient content and soil properties for immediate plant growth support. Organic farming prioritizes green manure for sustainable nutrient cycling, whereas synthetic amendments offer controlled nutrient delivery in conventional systems.
What Is Green Manure? Definition and Key Benefits
Green manure refers to specific plants grown primarily to be incorporated into the soil to enhance its fertility and organic matter content. This natural soil amendment improves soil structure, boosts microbial activity, and increases nutrient availability, especially nitrogen fixation in legumes. Compared to synthetic soil amendments, green manure promotes sustainable agriculture by reducing chemical inputs and supporting long-term ecosystem health.
Common Types of Green Manure Crops
Common types of green manure crops include legumes like clover, vetch, and alfalfa, which enhance soil nitrogen through natural fixation. Non-leguminous green manures such as rye, buckwheat, and mustard improve soil structure and organic matter content. These crops not only boost soil fertility but also suppress weeds and reduce erosion, offering sustainable benefits compared to synthetic soil amendments.
Synthetic Soil Amendments: An Overview
Synthetic soil amendments consist of chemically formulated products designed to enhance soil fertility and structure by providing essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in precise quantities. These amendments often include compounds like ammonium nitrate, superphosphate, and potassium sulfate, which rapidly improve nutrient availability and promote plant growth. Despite their immediate effectiveness, synthetic amendments may alter soil pH and microbial activity, requiring careful management to prevent long-term soil degradation.
Nutrient Release: Green Manure vs Synthetic Amendments
Green manure releases nutrients gradually through natural decomposition, enriching the soil with organic matter and enhancing microbial activity over time. Synthetic soil amendments provide immediate nutrient availability, delivering precise doses of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for rapid plant uptake. The slow nutrient release from green manure supports long-term soil fertility, while synthetic amendments offer quick correction of nutrient deficiencies.
Soil Health and Microbial Activity Comparison
Green manure improves soil health by enhancing organic matter content and promoting diverse microbial communities, which lead to better nutrient cycling and soil structure. Synthetic soil amendments often provide targeted nutrients but can disrupt microbial balance and reduce long-term soil fertility. Studies show green manure fosters higher microbial biomass and enzymatic activity, supporting sustainable soil ecosystems.
Environmental Impact of Green Manure vs Synthetic Inputs
Green manure significantly enhances soil health by increasing organic matter and promoting microbial diversity, resulting in improved soil structure and water retention. In contrast, synthetic soil amendments often lead to soil degradation and pollution through chemical runoff and reduced biodiversity. The environmental benefits of green manure include carbon sequestration and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, making it a sustainable alternative to synthetic inputs.
Cost Analysis: Organic vs Synthetic Soil Amendments
Green manure offers a cost-effective organic soil amendment by utilizing cover crops to naturally enhance soil fertility and reduce the need for purchased inputs. Synthetic soil amendments often involve higher upfront costs due to manufacturing, transportation, and chemical processing expenses. Over time, organic methods like green manure can lower overall expenses by improving soil health and reducing dependency on synthetic fertilizers.
Practical Considerations for Home Gardeners
Green manure enriches soil naturally by adding organic matter and nutrients, improving soil structure and water retention, while synthetic soil amendments provide targeted nutrient boosts but may disrupt soil ecology over time. Home gardeners should consider the long-term benefits of green manure for sustainable soil health versus the quick nutrient availability from synthetic fertilizers. Balancing these options involves evaluating garden size, plant needs, and commitment to organic practices.
Choosing the Best Amendment for Your Organic Garden
Green manure enriches soil fertility naturally by incorporating cover crops like clover or legumes that fix nitrogen and improve soil structure without chemical residues. Synthetic soil amendments provide targeted nutrient boosts but can disrupt soil biology and are typically avoided in organic gardening. Selecting green manure aligns with organic standards, promoting sustainable soil health and long-term garden productivity.
Green manure vs Synthetic soil amendments Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com