
Rainwater harvesting vs Tap irrigation Illustration
Rainwater harvesting conserves natural resources by collecting and storing rainwater for irrigation, reducing dependency on municipal water supplies. Tap irrigation relies on treated water from centralized systems, which can increase water bills and strain local water sources. Employing rainwater harvesting promotes sustainable gardening by minimizing water waste and supporting eco-friendly practices.
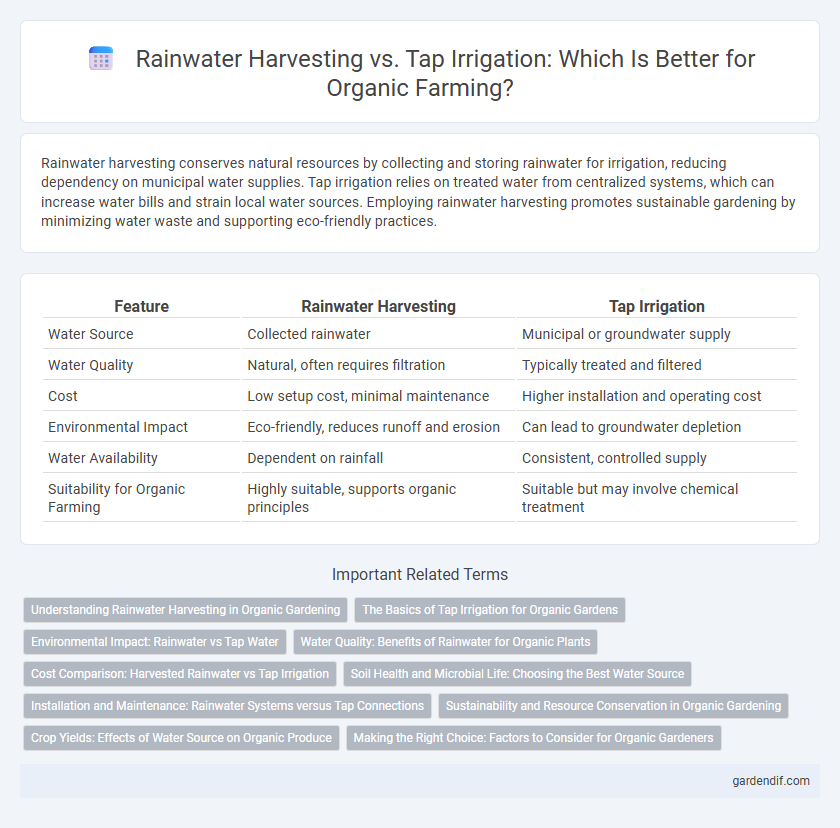
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rainwater Harvesting | Tap Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Source | Collected rainwater | Municipal or groundwater supply |
| Water Quality | Natural, often requires filtration | Typically treated and filtered |
| Cost | Low setup cost, minimal maintenance | Higher installation and operating cost |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces runoff and erosion | Can lead to groundwater depletion |
| Water Availability | Dependent on rainfall | Consistent, controlled supply |
| Suitability for Organic Farming | Highly suitable, supports organic principles | Suitable but may involve chemical treatment |
Understanding Rainwater Harvesting in Organic Gardening
Rainwater harvesting in organic gardening captures and stores natural precipitation, reducing dependence on tap irrigation and lowering environmental impact by conserving municipal water resources. This method provides plants with chemical-free, nutrient-rich water, enhancing soil health and promoting sustainable growth without synthetic inputs. Implementing rainwater harvesting systems improves water efficiency, supports plant resilience during droughts, and aligns with eco-friendly gardening practices.
The Basics of Tap Irrigation for Organic Gardens
Tap irrigation for organic gardens involves delivering water directly to the plant roots through a network of pipes, valves, and emitters, ensuring efficient water use and minimizing runoff. This method supports organic practices by reducing soil erosion and preventing excess moisture that can cause root diseases. Compared to rainwater harvesting, tap irrigation provides consistent water supply regardless of weather, promoting steady plant growth in organic systems.
Environmental Impact: Rainwater vs Tap Water
Rainwater harvesting reduces reliance on municipal tap water, conserving groundwater reserves and minimizing energy consumption associated with water treatment and distribution. Tap irrigation depends heavily on treated water, often involving high carbon emissions due to pumping and chemical processes. Utilizing rainwater promotes sustainable agriculture by lowering water wastage and decreasing soil erosion linked to excessive tap water use.
Water Quality: Benefits of Rainwater for Organic Plants
Rainwater harvesting provides high-quality water free from chemicals and salts commonly found in tap water, promoting healthier organic plant growth. This natural water source contains fewer contaminants, reducing the risk of soil degradation and nutrient imbalance in organic farming. Rainwater's soft nature enhances nutrient absorption and supports sustainable irrigation practices essential for organic crop vitality.
Cost Comparison: Harvested Rainwater vs Tap Irrigation
Harvested rainwater systems require initial investment in catchment, storage tanks, and filtration but significantly reduce recurring costs by minimizing dependency on municipal water bills. Tap irrigation involves continuous expenditure for water consumption based on local utility rates, which can be high in areas with water scarcity or aging infrastructure. Over time, rainwater harvesting proves more cost-effective with lower operational expenses and potential government incentives supporting sustainable water management practices.
Soil Health and Microbial Life: Choosing the Best Water Source
Rainwater harvesting enhances soil health by providing naturally soft, chlorine-free water that supports diverse microbial life and improves soil structure. Tap irrigation often contains chemicals and salts that can disrupt microbial ecosystems and lead to soil degradation over time. Opting for rainwater harvesting fosters a balanced soil microbiome, promoting nutrient cycling and long-term agricultural sustainability.
Installation and Maintenance: Rainwater Systems versus Tap Connections
Rainwater harvesting systems require installation of collection surfaces, gutters, storage tanks, and filtration units, demanding periodic maintenance to prevent clogging and contamination. Tap irrigation setups involve straightforward pipe connections to municipal water supply with simpler installation but require regular monitoring for leaks and pressure regulation. Both systems benefit from routine maintenance, but rainwater harvesting demands more frequent cleaning to ensure water quality and system efficiency.
Sustainability and Resource Conservation in Organic Gardening
Rainwater harvesting significantly enhances sustainability in organic gardening by reducing dependence on municipal water supplies and conserving freshwater resources. Tap irrigation often relies on treated water, which has a higher environmental footprint compared to sustainably collected rainwater that naturally nourishes plants without added chemicals. Integrating rainwater harvesting with organic gardening practices promotes resource conservation, reduces runoff pollution, and supports resilient ecosystems.
Crop Yields: Effects of Water Source on Organic Produce
Rainwater harvesting enhances crop yields by providing naturally soft water rich in nutrients, which improves soil health and boosts organic produce growth compared to tap irrigation. Tap water often contains chlorine and other chemicals that can negatively impact microbial activity in the soil, reducing nutrient availability for crops. Studies show that fields irrigated with rainwater harvesting systems yield higher quality organic fruits and vegetables with increased nutrient density and better taste profiles.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider for Organic Gardeners
Rainwater harvesting offers organic gardeners a sustainable and chemical-free water source that enhances soil health by reducing exposure to chlorine and fluoride found in tap water. Tap irrigation provides consistent water supply, crucial during dry spells, but may introduce contaminants that affect beneficial microbial activity in organic soils. Evaluating water quality, availability, and environmental impact ensures the right irrigation method supports organic gardening goals effectively.
Rainwater harvesting vs Tap irrigation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com