
Bone meal vs Artificial phosphate Illustration
Bone meal provides a natural source of phosphorus and calcium, promoting healthier soil and plant growth by slowly releasing nutrients over time. Artificial phosphate fertilizers offer a quicker nutrient boost but may lead to soil degradation and increased environmental runoff. Choosing bone meal supports sustainable gardening practices and long-term soil fertility, making it preferable for organic farming.
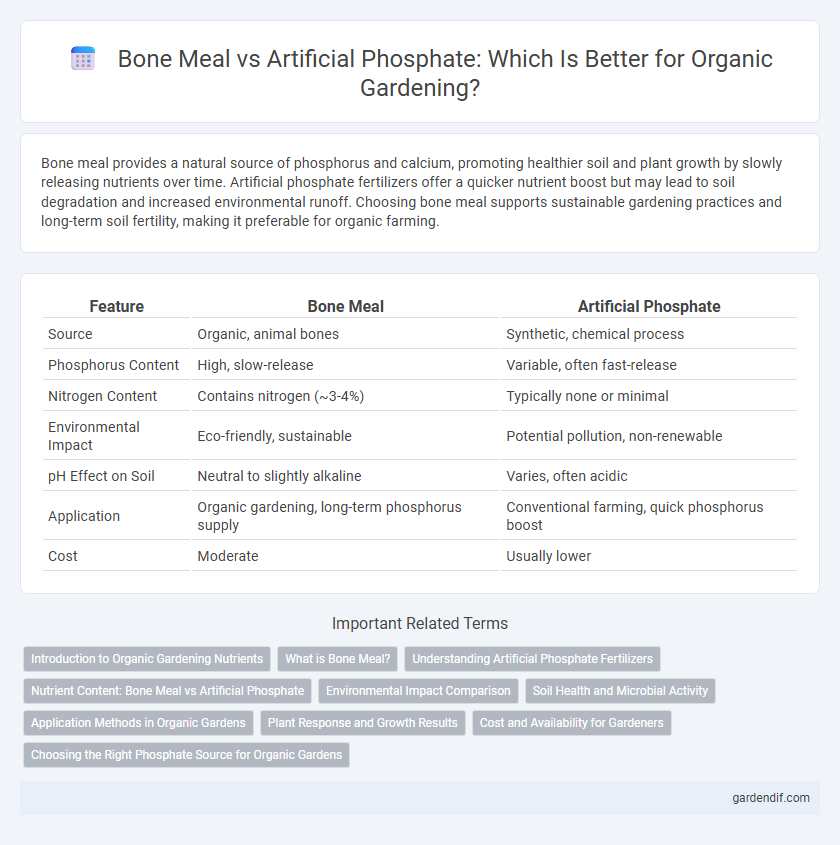
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone Meal | Artificial Phosphate |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Organic, animal bones | Synthetic, chemical process |
| Phosphorus Content | High, slow-release | Variable, often fast-release |
| Nitrogen Content | Contains nitrogen (~3-4%) | Typically none or minimal |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable | Potential pollution, non-renewable |
| pH Effect on Soil | Neutral to slightly alkaline | Varies, often acidic |
| Application | Organic gardening, long-term phosphorus supply | Conventional farming, quick phosphorus boost |
| Cost | Moderate | Usually lower |
Introduction to Organic Gardening Nutrients
Bone meal, a natural source of phosphorus and calcium, enhances soil fertility by gradually releasing nutrients essential for root development and flowering in organic gardening. Artificial phosphate fertilizers provide a rapid phosphorus boost but may cause nutrient imbalances and soil degradation over time. Organic gardeners prefer bone meal for its sustainable nutrient supply and soil health benefits, aligning with eco-friendly cultivation practices.
What is Bone Meal?
Bone meal is a natural fertilizer made from finely ground animal bones, rich in phosphorus and calcium essential for plant development. It releases nutrients slowly, promoting strong root systems and improved flowering in organic gardening. Unlike artificial phosphate fertilizers, bone meal provides a steady nutrient supply without harmful chemicals or synthetic additives.
Understanding Artificial Phosphate Fertilizers
Artificial phosphate fertilizers are synthetic compounds primarily derived from phosphate rock treated with sulfuric acid to produce water-soluble phosphates, which enhance plant growth by improving root development and energy transfer. Unlike bone meal, a natural organic source rich in calcium and phosphorus that releases nutrients slowly, artificial phosphate fertilizers offer quick nutrient availability, making them suitable for immediate soil enrichment. Careful management is essential to prevent phosphorus runoff, which can cause environmental issues such as water eutrophication.
Nutrient Content: Bone Meal vs Artificial Phosphate
Bone meal provides a natural source of phosphorus and calcium, essential for plant root development and overall soil health, with slow-release properties that improve nutrient availability over time. Artificial phosphate fertilizers contain higher concentrations of readily available phosphorus, promoting rapid nutrient uptake but potentially leading to soil imbalances and environmental runoff. Organic gardening often favors bone meal for its sustained nutrient release and soil enrichment benefits compared to synthetic phosphate alternatives.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bone meal, derived from animal bones, offers a sustainable and biodegradable source of phosphorus, promoting soil health without contributing to pollution. Artificial phosphate, often produced through energy-intensive mining and chemical processing, leads to habitat destruction and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Organic systems benefit from bone meal's slower nutrient release, reducing runoff and minimizing eutrophication risks compared to synthetic phosphate fertilizers.
Soil Health and Microbial Activity
Bone meal enhances soil health by providing a slow-release source of phosphorus, promoting sustained microbial activity essential for nutrient cycling. Artificial phosphate fertilizers deliver phosphorus rapidly but can disrupt soil microbial communities and reduce biodiversity over time. Maintaining balanced microbial activity with bone meal supports long-term soil fertility and ecosystem resilience in organic farming systems.
Application Methods in Organic Gardens
Bone meal enhances soil phosphorus through slow-release nutrients ideal for organic gardens, promoting robust root development and flower growth. It is typically applied by mixing directly into the soil during planting or as a top dressing around established plants, ensuring gradual nutrient availability without chemical residues. Artificial phosphate fertilizers, often water-soluble, deliver quick phosphorus spikes but are less favored in organic gardening due to synthetic origins and potential soil imbalance.
Plant Response and Growth Results
Bone meal, a natural source of phosphorus, supports steady nutrient release that enhances root development and overall plant vigor, while artificial phosphate delivers phosphorus quickly but risks nutrient imbalances and potential toxicity. Studies show plants grown with bone meal exhibit improved long-term growth and stronger root systems due to its slow-release properties, compared to rapid but sometimes short-lived effects from synthetic phosphates. Organic bone meal also enriches soil microbial activity, promoting healthier plant responses and sustainable growth outcomes.
Cost and Availability for Gardeners
Bone meal is a natural source of phosphorus that is generally more expensive and less readily available than artificial phosphate fertilizers, which are mass-produced and widely distributed. Gardeners seeking cost-effective options often find artificial phosphate more affordable and accessible in large quantities, while bone meal appeals for organic or sustainable gardening despite its higher price and limited supply. Availability varies regionally, with bone meal often stocked in specialty organic stores, contrasting with the broader availability of synthetic phosphate fertilizers in general garden centers.
Choosing the Right Phosphate Source for Organic Gardens
Bone meal provides a natural, slow-release source of phosphorus and calcium essential for root development in organic gardens, promoting healthy plant growth without synthetic chemicals. Artificial phosphate fertilizers offer immediate nutrient availability but often contain additives that may not comply with organic standards or disrupt soil microbiomes. Selecting bone meal supports sustainable soil health and aligns with organic certification requirements, making it the preferred phosphate source for organic gardeners.
Bone meal vs Artificial phosphate Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com