
Green manure vs synthetic mulch Illustration
Green manure enriches soil fertility by decomposing organic matter and promoting beneficial microbial activity, whereas synthetic mulch primarily suppresses weeds and retains soil moisture without contributing nutrients. Unlike synthetic mulch, green manure improves soil structure and long-term health by adding essential nutrients naturally. Choosing green manure supports sustainable agriculture by enhancing biodiversity and reducing reliance on chemical inputs.
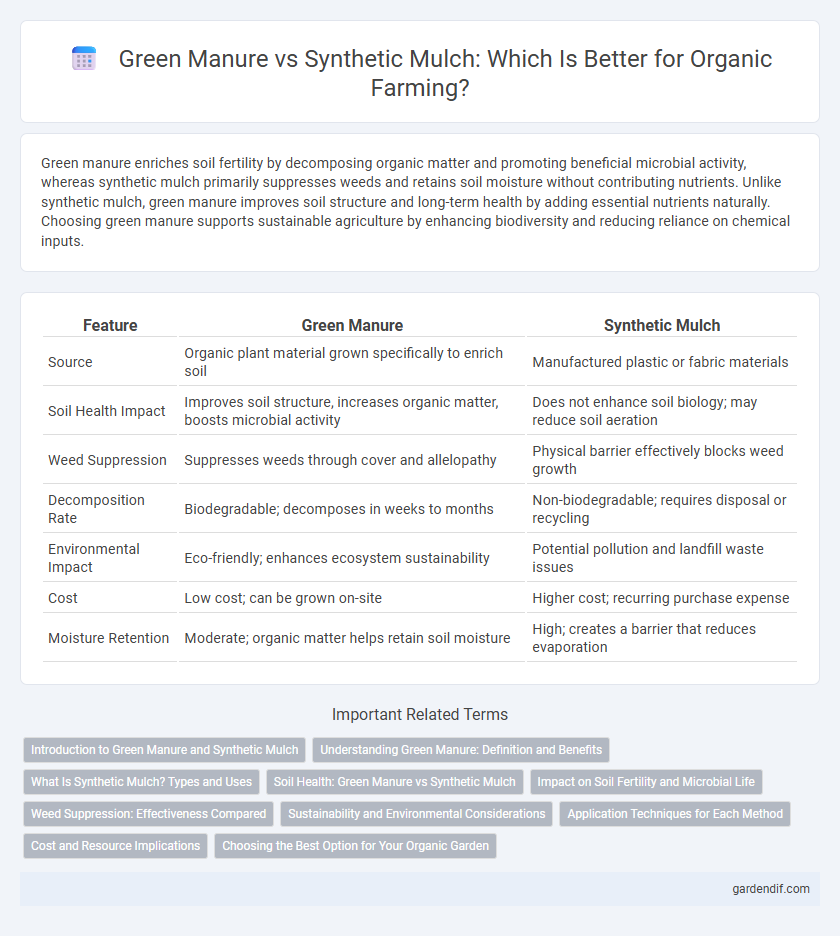
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Manure | Synthetic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Organic plant material grown specifically to enrich soil | Manufactured plastic or fabric materials |
| Soil Health Impact | Improves soil structure, increases organic matter, boosts microbial activity | Does not enhance soil biology; may reduce soil aeration |
| Weed Suppression | Suppresses weeds through cover and allelopathy | Physical barrier effectively blocks weed growth |
| Decomposition Rate | Biodegradable; decomposes in weeks to months | Non-biodegradable; requires disposal or recycling |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; enhances ecosystem sustainability | Potential pollution and landfill waste issues |
| Cost | Low cost; can be grown on-site | Higher cost; recurring purchase expense |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate; organic matter helps retain soil moisture | High; creates a barrier that reduces evaporation |
Introduction to Green Manure and Synthetic Mulch
Green manure consists of cover crops grown specifically to enhance soil fertility by adding organic matter and nitrogen, improving soil structure and moisture retention. Synthetic mulch, made from plastic or other polymers, controls weeds, conserves soil moisture, and regulates soil temperature but lacks the soil-enriching benefits of green manure. Both methods influence crop yields and soil health, with green manure supporting sustainable organic farming practices and synthetic mulch offering immediate physical protection for crops.
Understanding Green Manure: Definition and Benefits
Green manure refers to cover crops grown specifically to improve soil fertility and structure by adding organic matter and nutrients. Its benefits include enhancing soil microbial activity, preventing erosion, and increasing nitrogen content through natural fixation. Unlike synthetic mulch, green manure supports sustainable agriculture by enriching soil health without relying on non-biodegradable materials.
What Is Synthetic Mulch? Types and Uses
Synthetic mulch, made from materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, and landscape fabrics, is designed to suppress weeds, conserve soil moisture, and regulate soil temperature in agricultural and gardening applications. Common types include black plastic mulch, which absorbs heat to promote early plant growth, and woven fabric mulch that provides durability and breathability for long-term weed control. Used extensively in vegetable production and landscaping, synthetic mulch improves crop yield and soil management but lacks the soil-enriching benefits of organic green manure.
Soil Health: Green Manure vs Synthetic Mulch
Green manure enhances soil health by increasing organic matter, improving soil structure, and promoting beneficial microbial activity. Synthetic mulch, while effective at moisture retention and weed suppression, does not contribute nutrients or support microbial ecosystems. Long-term soil fertility benefits more significantly from green manure due to its natural nutrient cycling and carbon input.
Impact on Soil Fertility and Microbial Life
Green manure significantly enhances soil fertility by enriching organic matter and promoting beneficial microbial activity, which improves nutrient cycling and soil structure. Synthetic mulch, while effective in moisture retention and weed suppression, does not contribute nutrients or support microbial diversity, potentially leading to diminished soil health over time. Incorporating green manure into crop rotation fosters a sustainable increase in soil microbial biomass and enzymatic function, critical for long-term soil productivity.
Weed Suppression: Effectiveness Compared
Green manure enhances weed suppression by enriching soil fertility and creating a dense cover that inhibits weed germination naturally. Synthetic mulch provides an immediate and physical barrier to weed growth but lacks the long-term soil health benefits of organic matter. Combining green manure with synthetic mulch can optimize weed control while promoting sustainable soil ecosystems.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Green manure enhances soil fertility and structure by incorporating organic matter directly into the soil, promoting natural nutrient cycling and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Synthetic mulch, while effective at suppressing weeds and conserving moisture, often involves non-biodegradable materials that can contribute to plastic pollution and disrupt soil health over time. Prioritizing green manure supports long-term sustainability by improving biodiversity and minimizing environmental impact compared to synthetic mulch alternatives.
Application Techniques for Each Method
Green manure involves growing cover crops like clover or vetch that are tilled into the soil to enhance organic matter and nutrient content, usually applied before planting the main crop. Synthetic mulch, made from materials such as polyethylene, is laid over the soil surface to suppress weeds and conserve moisture, requiring careful anchoring to prevent displacement. Both methods demand specific timing and soil preparation to maximize benefits, with green manure requiring crop rotation planning and synthetic mulch needing proper installation to avoid soil overheating.
Cost and Resource Implications
Green manure offers a cost-effective solution by enriching soil naturally, reducing the need for purchased fertilizers, and improving long-term soil health through nutrient cycling. Synthetic mulch requires upfront investment in materials and may involve additional costs for disposal or environmental management, while providing immediate weed suppression and moisture retention. Resource-wise, green manure enhances soil biodiversity and carbon sequestration, whereas synthetic mulch relies on non-renewable materials and can contribute to plastic waste.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Organic Garden
Green manure enhances soil fertility naturally by adding organic matter and nitrogen, promoting healthy microbial activity essential for organic gardens. Synthetic mulch, while effective in weed suppression and moisture retention, may introduce non-biodegradable materials that conflict with organic principles. Selecting green manure aligns better with sustainable gardening practices, supporting long-term soil health and organic certification standards.
Green manure vs synthetic mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com