
Straw mulch vs hay mulch Illustration
Straw mulch consists of dried stalks left after grain harvesting and provides excellent weed suppression and moisture retention without introducing many weed seeds. Hay mulch includes grassy or legume plants and tends to contain more weed seeds, which can lead to unwanted plant growth in garden beds. Both mulches improve soil health, but straw mulch is often preferred for cleaner gardens and reduced weed pressure.
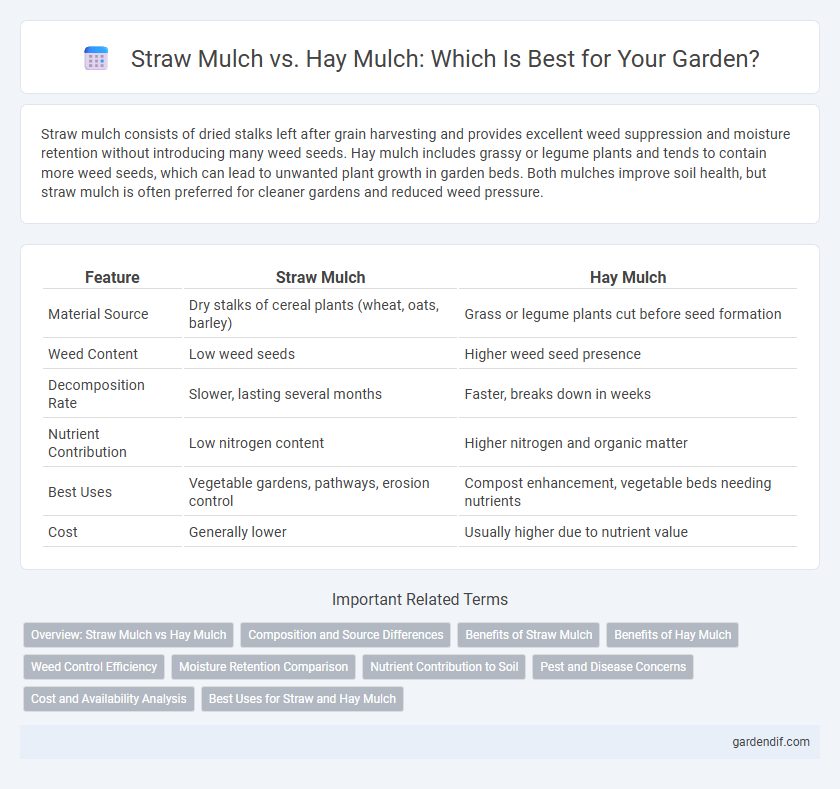
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Straw Mulch | Hay Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Dry stalks of cereal plants (wheat, oats, barley) | Grass or legume plants cut before seed formation |
| Weed Content | Low weed seeds | Higher weed seed presence |
| Decomposition Rate | Slower, lasting several months | Faster, breaks down in weeks |
| Nutrient Contribution | Low nitrogen content | Higher nitrogen and organic matter |
| Best Uses | Vegetable gardens, pathways, erosion control | Compost enhancement, vegetable beds needing nutrients |
| Cost | Generally lower | Usually higher due to nutrient value |
Overview: Straw Mulch vs Hay Mulch
Straw mulch consists mainly of stalks from cereal crops like wheat, offering low weed seed content and excellent moisture retention, whereas hay mulch includes a mix of grass and legumes with a higher potential for weed seeds and nutrient addition. Straw mulch is preferred for vegetable gardens due to its cleaner composition and less weed growth risk, while hay mulch provides more organic matter and nitrogen but requires careful management to prevent unwanted weed proliferation. Both mulches enhance soil health and moisture conservation, but selection depends on garden goals and weed control priorities.
Composition and Source Differences
Straw mulch primarily consists of the dried stalks of cereal grains like wheat, barley, or rye, offering a clean, low-seed composition that minimizes weed growth. Hay mulch contains a mix of grasses and legumes, often including seeds that can introduce weeds if not properly processed. The source of straw mulch is cereal crop residues, whereas hay mulch originates from harvested forage plants, impacting their nutrient content and decomposition rates in garden or agricultural settings.
Benefits of Straw Mulch
Straw mulch offers superior weed suppression and soil moisture retention compared to hay mulch, reducing the need for frequent watering and chemical herbicides. Its lower seed content minimizes weed growth, creating a cleaner garden environment. Straw mulch also decomposes more slowly, enhancing long-term soil fertility and structure.
Benefits of Hay Mulch
Hay mulch enriches soil fertility by adding organic matter and nutrients, promoting healthier plant growth. Its dense texture helps retain soil moisture effectively, reducing the need for frequent watering. Furthermore, hay mulch suppresses weed growth better than straw due to its coarse composition, contributing to improved garden maintenance.
Weed Control Efficiency
Straw mulch offers superior weed control efficiency compared to hay mulch due to its lower seed content and denser coverage, effectively suppressing weed germination and growth. Hay mulch often contains weed seeds that can introduce new weeds into garden environments, reducing its weed control reliability. Choosing straw mulch enhances garden health by minimizing weed competition and supporting moisture retention.
Moisture Retention Comparison
Straw mulch provides superior moisture retention compared to hay mulch due to its coarser texture and lower density, which allows better airflow and reduces water evaporation. Hay mulch, containing more fine particles and seeds, tends to compact and can restrict water infiltration, leading to less effective moisture conservation. Gardeners aiming for optimal soil hydration often prefer straw mulch to maintain consistent soil moisture levels.
Nutrient Contribution to Soil
Straw mulch contributes minimal nutrients to the soil as it is primarily composed of stalks with low nitrogen content, making it a slow decomposing material that mainly improves soil moisture retention and weed control. Hay mulch contains more nutrient-rich plant parts, including seeds and leaves, resulting in higher nitrogen content and faster decomposition that enriches the soil with organic matter and essential nutrients. Choosing between straw and hay mulch impacts soil fertility, with hay mulch providing greater nutrient contribution for improved soil health and plant growth.
Pest and Disease Concerns
Straw mulch is less likely to harbor pests and diseases compared to hay mulch, as hay often contains weed seeds and can introduce fungal pathogens. Straw mulch typically decomposes slower, reducing conditions favorable for pests like slugs and rodents. Using weed-free straw minimizes the risk of pest infestations and disease transmission in garden beds.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Straw mulch is generally more affordable and widely available due to its abundance as a byproduct of cereal grain harvesting, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. Hay mulch tends to be pricier and less accessible because it is primarily used as livestock feed, limiting surplus quantities suitable for mulching. The cost difference impacts budget planning for landscaping and agricultural projects, with straw offering a more economical and readily sourced option.
Best Uses for Straw and Hay Mulch
Straw mulch is best used for vegetable gardens and flower beds due to its lightweight texture that allows air and water to penetrate easily, promoting healthy root growth. Hay mulch, richer in seeds and nutrients, is ideal for soil improvement and erosion control in larger garden areas but may require more maintenance to manage weed growth. Both mulches retain soil moisture effectively and regulate temperature, but straw is preferred for seed starting beds while hay excels in adding organic matter.
Straw mulch vs hay mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com