
Plastic Mulch vs Organic Mulch Illustration
Plastic mulch offers effective weed control and moisture retention, making it ideal for high-value crops requiring precise growing conditions. Organic mulch improves soil health by adding nutrients and promoting microbial activity as it decomposes, benefiting long-term soil fertility. Choosing between plastic and organic mulch depends on crop needs, environmental impact, and management preferences.
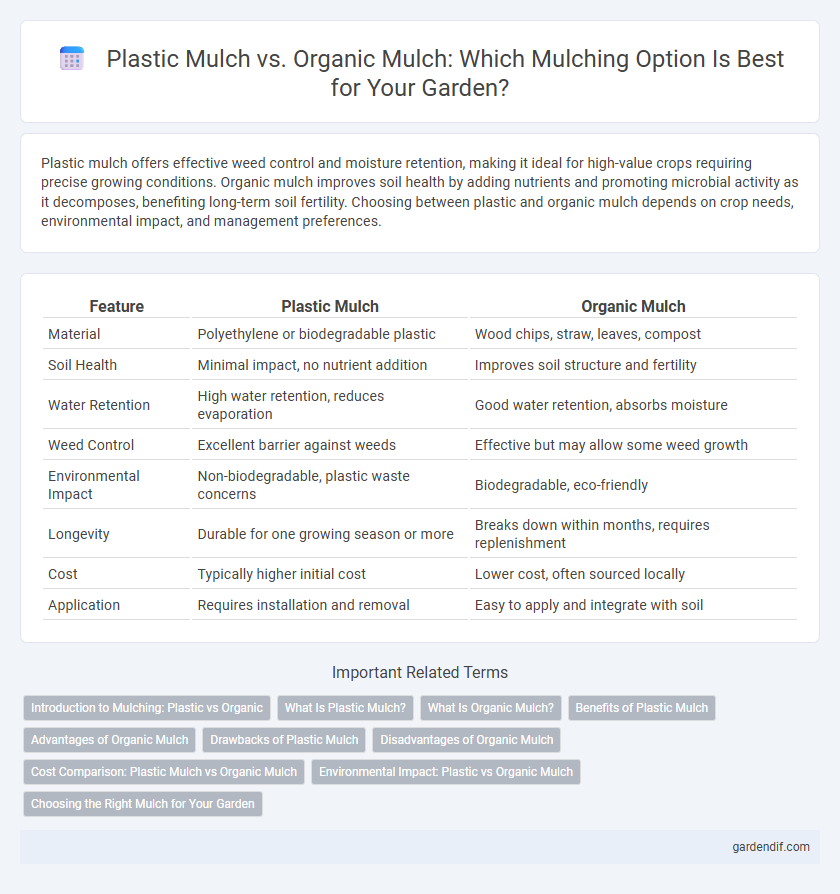
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Mulch | Organic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyethylene or biodegradable plastic | Wood chips, straw, leaves, compost |
| Soil Health | Minimal impact, no nutrient addition | Improves soil structure and fertility |
| Water Retention | High water retention, reduces evaporation | Good water retention, absorbs moisture |
| Weed Control | Excellent barrier against weeds | Effective but may allow some weed growth |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, plastic waste concerns | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Longevity | Durable for one growing season or more | Breaks down within months, requires replenishment |
| Cost | Typically higher initial cost | Lower cost, often sourced locally |
| Application | Requires installation and removal | Easy to apply and integrate with soil |
Introduction to Mulching: Plastic vs Organic
Plastic mulch offers superior weed control, moisture retention, and soil temperature regulation, making it ideal for high-yield vegetable crops and commercial farming. Organic mulch, derived from natural materials like straw, wood chips, and compost, improves soil fertility, enhances microbial activity, and promotes long-term soil health. Choosing between plastic and organic mulch depends on crop type, environmental considerations, and sustainability goals.
What Is Plastic Mulch?
Plastic mulch is a synthetic material typically made from polyethylene designed to cover soil surfaces, improving moisture retention and temperature regulation for crops. It acts as a barrier that suppresses weed growth, reduces soil erosion, and enhances crop yield by maintaining optimal growing conditions. Commonly used in vegetable farming and commercial agriculture, plastic mulch comes in various colors and thicknesses tailored to specific agricultural needs.
What Is Organic Mulch?
Organic mulch consists of natural materials such as wood chips, straw, leaves, and compost that decompose over time, enriching the soil with essential nutrients. It enhances soil structure, moisture retention, and microbial activity, promoting healthier plant growth compared to plastic mulch. Unlike plastic mulch, organic mulch is biodegradable and environmentally sustainable, reducing soil temperature fluctuations without creating waste.
Benefits of Plastic Mulch
Plastic mulch improves soil temperature by retaining heat, promoting faster crop growth and earlier harvests. It significantly reduces weed growth by blocking sunlight, minimizing the need for herbicides and manual weeding. This mulch type also enhances moisture retention, preventing water evaporation and improving irrigation efficiency.
Advantages of Organic Mulch
Organic mulch enhances soil fertility by decomposing and adding essential nutrients, improving soil structure and moisture retention. It supports beneficial microbial activity and earthworm populations, fostering healthier plant growth. Unlike plastic mulch, organic mulch is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, reducing waste and promoting sustainable gardening practices.
Drawbacks of Plastic Mulch
Plastic mulch can lead to environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature, causing soil contamination and waste disposal challenges. It also disrupts soil health by reducing aeration and moisture infiltration, which can negatively impact beneficial microbial activity. Furthermore, plastic mulch increases production costs because of its need for removal and disposal after each growing season.
Disadvantages of Organic Mulch
Organic mulch decomposes over time, requiring frequent replacement that increases labor and material costs. It can attract pests such as termites and rodents, potentially damaging plants and nearby structures. Additionally, excessive moisture retention from organic mulch may promote fungal growth and root rot in some plants.
Cost Comparison: Plastic Mulch vs Organic Mulch
Plastic mulch typically incurs higher upfront costs due to material purchase and installation but offers longer durability and weed suppression benefits, potentially reducing labor expenses over time. Organic mulch requires lower initial investment and provides soil enrichment through decomposition but may necessitate more frequent replacement and increased labor. Analyzing total cost-effectiveness depends on specific crop needs, local climate, and long-term soil health priorities.
Environmental Impact: Plastic vs Organic Mulch
Plastic mulch contributes significantly to environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature, leading to soil contamination and increased plastic waste in landfills. Organic mulch, derived from natural materials like wood chips or straw, enhances soil health by decomposing and enriching nutrient content, while promoting sustainable farming practices. The use of organic mulch reduces carbon footprint and supports biodiversity, contrasting sharply with the ecological harm associated with plastic mulch disposal.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden
Plastic mulch offers superior weed control and moisture retention, making it ideal for vegetable gardens requiring precise climate conditions. Organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, improves soil fertility and promotes beneficial microbial activity while breaking down naturally. Selecting the right mulch depends on your garden's specific needs for soil health, moisture levels, and crop type.
Plastic Mulch vs Organic Mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com