
Leaf mulch vs Grass clippings Illustration
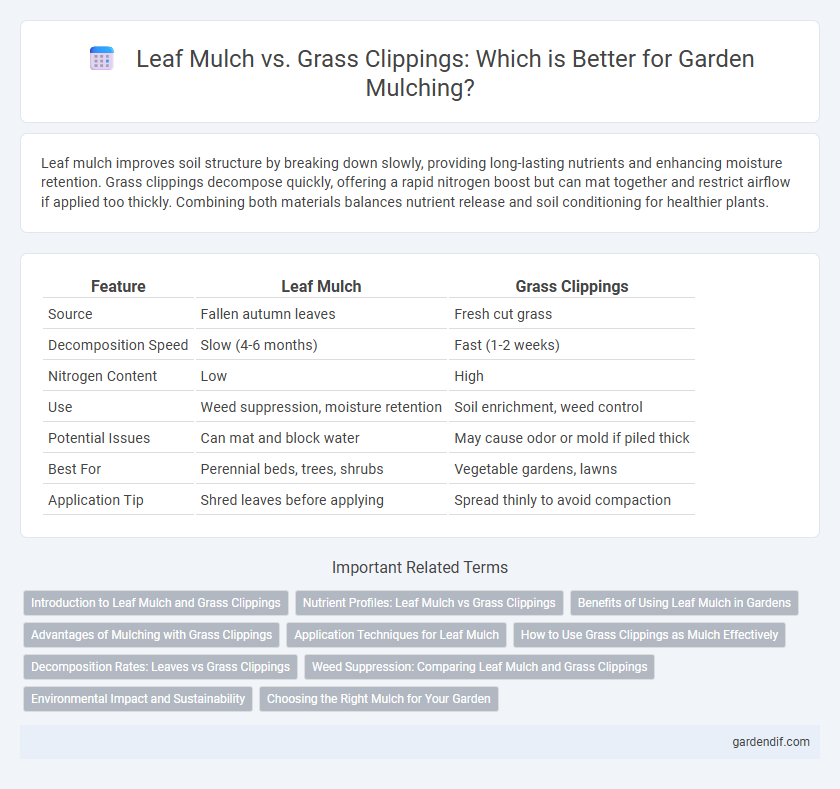
Leaf mulch improves soil structure by breaking down slowly, providing long-lasting nutrients and enhancing moisture retention. Grass clippings decompose quickly, offering a rapid nitrogen boost but can mat together and restrict airflow if applied too thickly. Combining both materials balances nutrient release and soil conditioning for healthier plants.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Leaf Mulch | Grass Clippings |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fallen autumn leaves | Fresh cut grass |
| Decomposition Speed | Slow (4-6 months) | Fast (1-2 weeks) |
| Nitrogen Content | Low | High |
| Use | Weed suppression, moisture retention | Soil enrichment, weed control |
| Potential Issues | Can mat and block water | May cause odor or mold if piled thick |
| Best For | Perennial beds, trees, shrubs | Vegetable gardens, lawns |
| Application Tip | Shred leaves before applying | Spread thinly to avoid compaction |
Introduction to Leaf Mulch and Grass Clippings
Leaf mulch consists of decomposed leaves that enrich soil with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, promoting healthy plant growth and improving soil structure. Grass clippings provide a nitrogen-rich organic layer that breaks down quickly, enhancing soil fertility and moisture retention. Both leaf mulch and grass clippings serve as effective organic mulches, but leaf mulch offers longer-lasting benefits while grass clippings decompose faster, requiring more frequent replacement.
Nutrient Profiles: Leaf Mulch vs Grass Clippings
Leaf mulch offers a rich source of nutrients like carbon, potassium, and micronutrients that slowly release as it decomposes, enhancing soil structure and fertility. Grass clippings provide high nitrogen content, which accelerates decomposition and boosts soil nitrogen levels for faster plant growth. Combining leaf mulch with grass clippings creates a balanced nutrient profile, promoting healthier soil biology and sustained plant nutrition.
Benefits of Using Leaf Mulch in Gardens
Leaf mulch enhances soil fertility by breaking down slowly, releasing essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium over time. It improves soil structure and moisture retention, fostering healthier root development and reducing the need for frequent watering. Using leaf mulch also supports beneficial microbial activity and natural pest control, promoting a balanced garden ecosystem.
Advantages of Mulching with Grass Clippings
Mulching with grass clippings provides essential nutrients such as nitrogen, promoting healthier soil and faster plant growth. Grass clippings decompose quickly, improving soil moisture retention and reducing the need for frequent watering. Using grass clippings as mulch also helps suppress weeds naturally while recycling yard waste effectively.
Application Techniques for Leaf Mulch
Leaf mulch requires shredding leaves before application to enhance decomposition and prevent matting, which improves soil aeration and moisture retention. Applying leaf mulch in a 2 to 3-inch layer around plants helps regulate soil temperature and suppress weeds effectively. It is best to use leaf mulch in garden beds and around trees, avoiding thick layers near plant stems to prevent rot and pest issues.
How to Use Grass Clippings as Mulch Effectively
Grass clippings used as mulch should be applied in thin layers, about half an inch thick, to prevent matting and promote air circulation, which reduces the risk of mold and foul odors. It's essential to dry the grass clippings before mulching to avoid clumping and nitrogen depletion in the soil. Layering fresh grass clippings with other organic materials like leaves or straw enhances decomposition and nutrient release, improving soil fertility and moisture retention.
Decomposition Rates: Leaves vs Grass Clippings
Leaf mulch decomposes more slowly than grass clippings due to its higher carbon content and tougher cell structure, resulting in a longer-lasting protective layer for soil. Grass clippings break down quickly because of their higher nitrogen content and softer texture, providing rapid nutrient release but requiring more frequent replenishment. Choosing between leaf mulch and grass clippings depends on desired decomposition speed and nutrient timing for optimal garden health.
Weed Suppression: Comparing Leaf Mulch and Grass Clippings
Leaf mulch provides superior weed suppression by creating a dense, organic barrier that blocks sunlight, effectively inhibiting weed seed germination. Grass clippings, while rich in nitrogen, tend to mat down and decompose quickly, offering less consistent coverage and allowing more weed growth. Studies show that leaf mulch maintains soil moisture and temperature better, enhancing its ability to prevent weeds compared to the thinner layering of grass clippings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Leaf mulch enhances soil health by decomposing slowly, enriching organic matter, and promoting carbon sequestration, which supports long-term sustainability. Grass clippings decompose quickly, providing a short-term nitrogen boost but can contribute to methane emissions if not managed properly, posing an environmental challenge. Utilizing leaf mulch reduces landfill waste and lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to grass clippings, making it a more eco-friendly option for sustainable gardening.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden
Leaf mulch improves soil structure and nutrient content by decomposing slowly, making it ideal for long-term garden health. Grass clippings break down quickly, releasing nitrogen rapidly and are best suited for immediate nutrient boosts in vegetable beds. Selecting between leaf mulch and grass clippings depends on your garden's specific nutrient needs and desired decomposition speed.
Leaf mulch vs Grass clippings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com