
Plastic mulch vs Landscape fabric Illustration
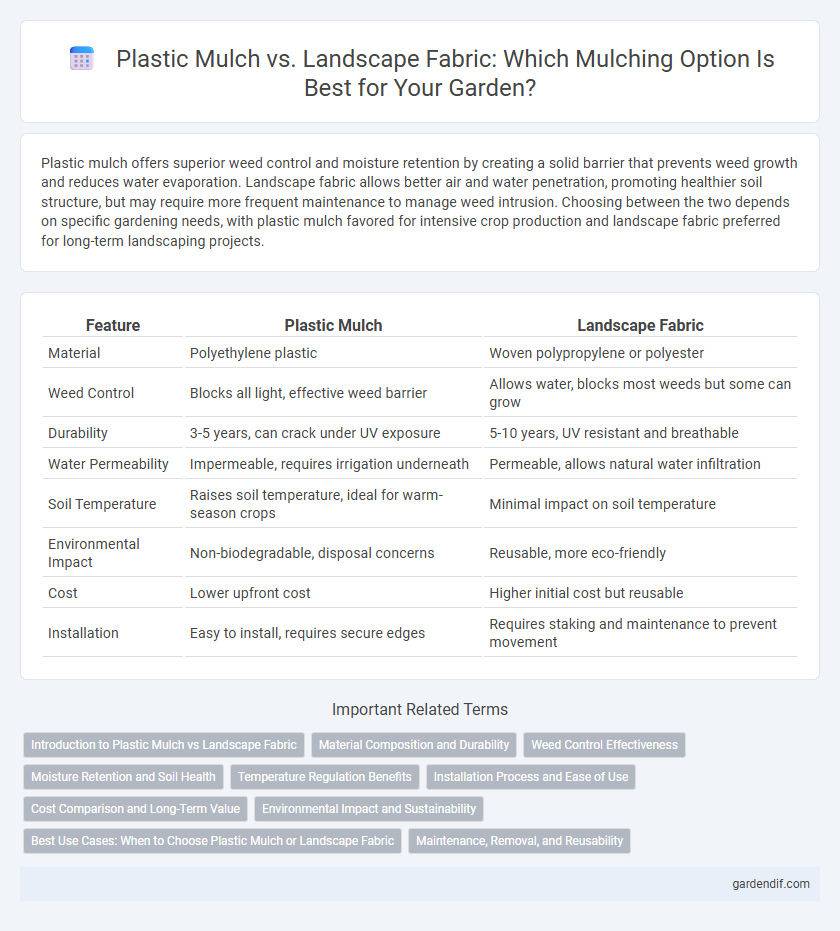
Plastic mulch offers superior weed control and moisture retention by creating a solid barrier that prevents weed growth and reduces water evaporation. Landscape fabric allows better air and water penetration, promoting healthier soil structure, but may require more frequent maintenance to manage weed intrusion. Choosing between the two depends on specific gardening needs, with plastic mulch favored for intensive crop production and landscape fabric preferred for long-term landscaping projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Mulch | Landscape Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyethylene plastic | Woven polypropylene or polyester |
| Weed Control | Blocks all light, effective weed barrier | Allows water, blocks most weeds but some can grow |
| Durability | 3-5 years, can crack under UV exposure | 5-10 years, UV resistant and breathable |
| Water Permeability | Impermeable, requires irrigation underneath | Permeable, allows natural water infiltration |
| Soil Temperature | Raises soil temperature, ideal for warm-season crops | Minimal impact on soil temperature |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, disposal concerns | Reusable, more eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost but reusable |
| Installation | Easy to install, requires secure edges | Requires staking and maintenance to prevent movement |
Introduction to Plastic Mulch vs Landscape Fabric
Plastic mulch and landscape fabric serve distinct roles in garden and agricultural weed control. Plastic mulch is a synthetic sheet that blocks sunlight to suppress weeds, conserves soil moisture, and increases soil temperature for faster plant growth. Landscape fabric, made from woven polypropylene or polyester, allows water and air penetration while reducing weed growth, providing a breathable yet protective ground cover.
Material Composition and Durability
Plastic mulch is typically made from polyethylene, offering a waterproof barrier that effectively conserves soil moisture and suppresses weeds, while landscape fabric consists of woven or non-woven polypropylene designed to allow water and air penetration. Polyethylene plastic mulch generally lasts one growing season but can degrade under UV exposure, whereas high-quality landscape fabric provides multi-season durability with resistance to tearing and decomposition. Choosing between plastic mulch and landscape fabric depends on the specific garden needs for moisture retention versus long-term soil health and aeration.
Weed Control Effectiveness
Plastic mulch provides a superior weed control effectiveness by forming a durable, impermeable barrier that blocks sunlight and prevents weed seed germination. Landscape fabric allows for water and air permeability but is less effective in suppressing deep-rooted or persistent weeds due to its porous nature. Studies show plastic mulch reduces weed growth by up to 95%, while landscape fabric typically offers 60-75% weed suppression.
Moisture Retention and Soil Health
Plastic mulch offers superior moisture retention by creating a barrier that reduces evaporation, ideal for water conservation in dry climates. However, landscape fabric enhances soil health by allowing air and water permeability, promoting microbial activity and preventing soil compaction. Choosing between plastic mulch and landscape fabric depends on balancing the need for moisture conservation with long-term soil fertility and ecosystem sustainability.
Temperature Regulation Benefits
Plastic mulch offers superior temperature regulation benefits by trapping soil heat more effectively, promoting earlier seed germination and faster crop growth compared to landscape fabric. Its impermeable surface retains warmth consistently, which can extend the growing season in cooler climates. Landscape fabric provides moderate temperature control but allows more soil exposure to air fluctuations, making it less effective for heat retention.
Installation Process and Ease of Use
Plastic mulch typically requires careful soil preparation and precise cutting for installation, making it more labor-intensive but effective at moisture retention and weed control. Landscape fabric offers simpler installation by laying it directly over the soil and securing with staples, providing better breathability and easier repositioning. Both materials enhance garden aesthetics and weed suppression, but landscape fabric is favored for quicker setup and user-friendly maintenance.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Value
Plastic mulch typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to landscape fabric, making it attractive for short-term gardening projects. However, landscape fabric provides greater durability and reusability, translating into better long-term value by reducing replacement expenses. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, consider plastic mulch's limited lifespan alongside landscape fabric's enhanced weed control and soil moisture retention benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plastic mulch contributes significantly to plastic waste accumulation due to its non-biodegradable nature, often ending up in landfills or causing soil contamination. Landscape fabric offers a more sustainable alternative as it is typically made from woven polypropylene that allows water and air permeability while reducing soil erosion and weed growth. However, long-term environmental benefits depend on proper disposal and the use of biodegradable or reusable materials to minimize ecological footprints.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Plastic Mulch or Landscape Fabric
Plastic mulch excels in vegetable gardens and high-value crop production by enhancing soil temperature, moisture retention, and weed control. Landscape fabric is ideal for perennial beds, pathways, and ornamental gardens, offering long-term weed suppression while allowing air and water penetration. Choosing between them depends on crop type, durability needs, and desired soil health benefits.
Maintenance, Removal, and Reusability
Plastic mulch offers low maintenance by effectively suppressing weeds and retaining soil moisture but can be challenging to remove due to its durability and tendency to break into pieces. Landscape fabric allows easier removal and is reusable for multiple seasons, though it may require more frequent weeding and maintenance to prevent soil buildup on top. Both materials have trade-offs: plastic mulch is less labor-intensive during use but less environmentally friendly upon disposal, while landscape fabric supports sustainable gardening practices through reusability and easier cleanup.
Plastic mulch vs Landscape fabric Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com