
Green mulch vs brown mulch Illustration
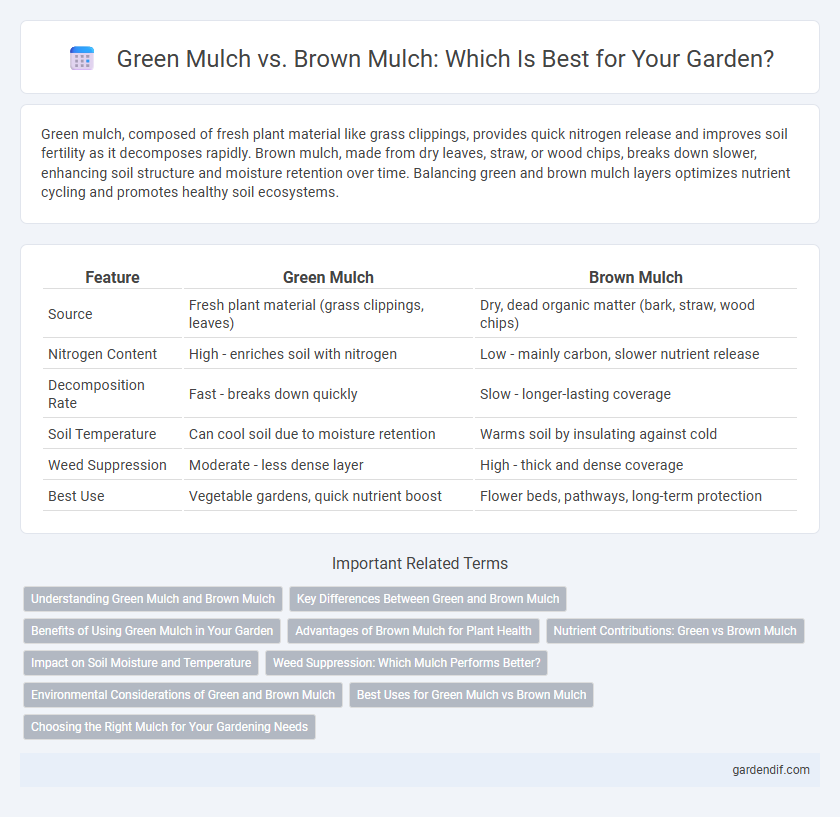
Green mulch, composed of fresh plant material like grass clippings, provides quick nitrogen release and improves soil fertility as it decomposes rapidly. Brown mulch, made from dry leaves, straw, or wood chips, breaks down slower, enhancing soil structure and moisture retention over time. Balancing green and brown mulch layers optimizes nutrient cycling and promotes healthy soil ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Mulch | Brown Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fresh plant material (grass clippings, leaves) | Dry, dead organic matter (bark, straw, wood chips) |
| Nitrogen Content | High - enriches soil with nitrogen | Low - mainly carbon, slower nutrient release |
| Decomposition Rate | Fast - breaks down quickly | Slow - longer-lasting coverage |
| Soil Temperature | Can cool soil due to moisture retention | Warms soil by insulating against cold |
| Weed Suppression | Moderate - less dense layer | High - thick and dense coverage |
| Best Use | Vegetable gardens, quick nutrient boost | Flower beds, pathways, long-term protection |
Understanding Green Mulch and Brown Mulch
Green mulch consists of fresh, nitrogen-rich organic materials such as grass clippings and green leaves that decompose quickly, enriching the soil with essential nutrients. Brown mulch is made from carbon-rich, dry materials like straw, wood chips, or dried leaves, which break down slowly and improve soil structure and moisture retention. Combining green and brown mulch balances nitrogen and carbon levels, fostering healthier soil ecosystems and promoting sustainable plant growth.
Key Differences Between Green and Brown Mulch
Green mulch consists mainly of fresh, nitrogen-rich organic materials like grass clippings and vegetable scraps, which break down quickly to enrich soil fertility. Brown mulch is composed of carbon-rich, dry materials such as leaves, straw, and wood chips, providing effective moisture retention and weed suppression. The primary difference lies in their nutrient content and decomposition rate, with green mulch accelerating nutrient cycling while brown mulch offers longer-lasting soil coverage.
Benefits of Using Green Mulch in Your Garden
Green mulch enriches soil fertility by decomposing organic matter and releasing essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which promote healthy plant growth. This type of mulch retains moisture effectively, reducing watering frequency and enhancing soil structure while suppressing weed growth. Unlike brown mulch, green mulch accelerates microbial activity in the soil, improving nutrient cycling and fostering a vibrant, resilient garden ecosystem.
Advantages of Brown Mulch for Plant Health
Brown mulch, rich in organic matter, improves soil fertility and moisture retention, promoting stronger root development and healthier plants. Its slow decomposition releases essential nutrients, enhancing soil structure and reducing erosion. Brown mulch also suppresses weeds effectively, minimizing competition for water and nutrients critical for plant health.
Nutrient Contributions: Green vs Brown Mulch
Green mulch, composed of fresh plant materials like grass clippings and kitchen scraps, decomposes rapidly, releasing high nitrogen levels that enrich soil fertility and promote vigorous plant growth. Brown mulch, made from dry leaves, straw, or wood chips, breaks down slower and provides carbon-rich organic matter essential for soil structure and microbial activity. Balancing green and brown mulch creates an optimal nutrient cycle, enhancing soil health by supplying both nitrogen and carbon for sustainable plant development.
Impact on Soil Moisture and Temperature
Green mulch, rich in nitrogen, breaks down faster and helps retain higher soil moisture levels by improving organic matter content, leading to cooler soil temperatures during hot weather. Brown mulch, composed mainly of carbon-rich materials like dried leaves or straw, decomposes more slowly, providing longer-lasting insulation that stabilizes soil temperature and conserves moisture over extended periods. Both mulches play crucial roles in enhancing soil health, but green mulch is more effective for immediate moisture retention, while brown mulch excels in temperature regulation and long-term moisture conservation.
Weed Suppression: Which Mulch Performs Better?
Green mulch, often composed of fresh grass clippings or living plants, provides moderate weed suppression by creating a dense ground cover that limits sunlight exposure to weed seeds. Brown mulch, including materials like shredded bark, straw, or wood chips, excels in weed suppression due to its thicker, long-lasting layer that blocks light and physically prevents weed growth more effectively. Studies show brown mulch reduces weed emergence by up to 90% compared to green mulch's approximately 60%, making brown mulch the superior choice for prolonged weed control in garden beds.
Environmental Considerations of Green and Brown Mulch
Green mulch, composed of fresh organic materials like grass clippings and kitchen scraps, enhances soil moisture retention and promotes microbial activity that supports plant health. Brown mulch, made from dried leaves, straw, or wood chips, provides longer-lasting weed suppression and helps regulate soil temperature by insulating roots during seasonal changes. Both mulches contribute to reducing soil erosion and improving carbon sequestration, but green mulch decomposes faster, offering quicker nutrient release with a lower carbon footprint compared to the more durable, slowly decomposing brown mulch.
Best Uses for Green Mulch vs Brown Mulch
Green mulch, consisting of fresh plant material like grass clippings and vegetable scraps, is ideal for enriching soil nutrients and promoting microbial activity in garden beds and vegetable patches. Brown mulch, made from dry leaves, straw, or wood chips, excels in moisture retention and weed suppression, making it perfect for pathways, flower beds, and around trees. Using green mulch in nutrient-demanding areas and brown mulch for moisture conservation maximizes garden health and soil quality.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Gardening Needs
Green mulch, composed of fresh plant materials like grass clippings and kitchen scraps, provides high nitrogen content that accelerates decomposition and enriches soil fertility. Brown mulch, made from dried leaves, straw, or wood chips, offers carbon-rich organic matter that improves soil structure and moisture retention. Selecting the appropriate mulch depends on your garden's nutrient requirements and moisture management goals, balancing nitrogen and carbon inputs for optimal plant growth.
Green mulch vs brown mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com