
Leaf litter vs compost mulch Illustration
Leaf litter mulch provides a natural, lightweight covering that retains moisture and slowly breaks down to enrich soil with organic matter. Compost mulch offers a nutrient-rich, dense layer that improves soil fertility and supports microbial activity more rapidly. Choosing between leaf litter and compost mulch depends on your garden's specific nutrient needs and desired rate of soil enrichment.
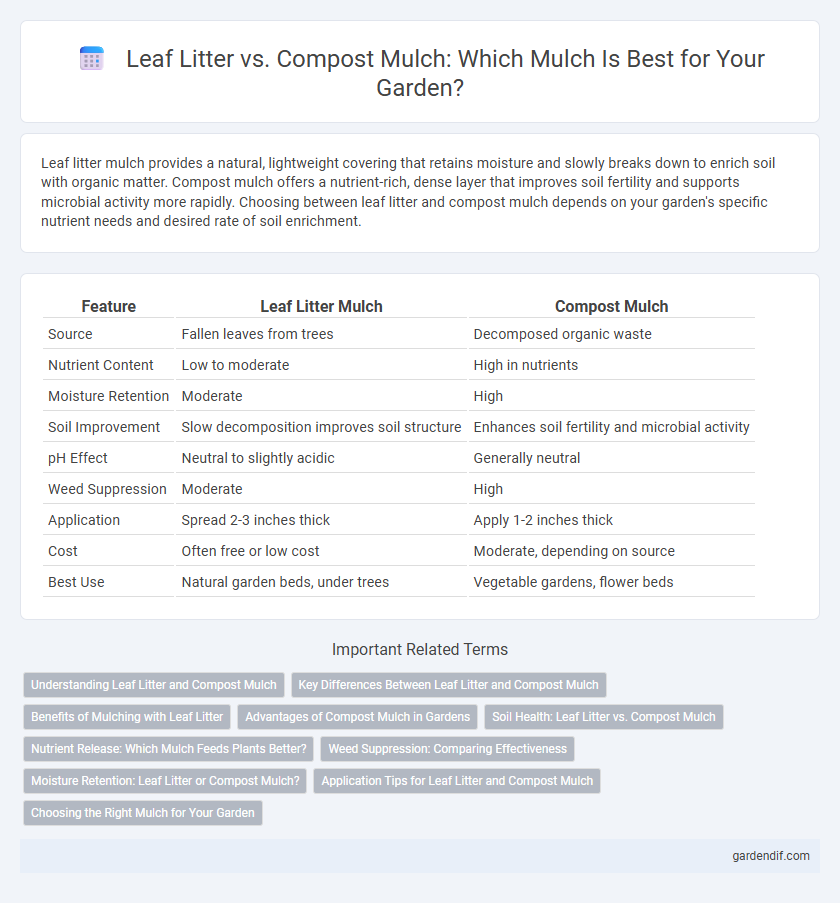
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Leaf Litter Mulch | Compost Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fallen leaves from trees | Decomposed organic waste |
| Nutrient Content | Low to moderate | High in nutrients |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate | High |
| Soil Improvement | Slow decomposition improves soil structure | Enhances soil fertility and microbial activity |
| pH Effect | Neutral to slightly acidic | Generally neutral |
| Weed Suppression | Moderate | High |
| Application | Spread 2-3 inches thick | Apply 1-2 inches thick |
| Cost | Often free or low cost | Moderate, depending on source |
| Best Use | Natural garden beds, under trees | Vegetable gardens, flower beds |
Understanding Leaf Litter and Compost Mulch
Leaf litter mulch consists of naturally fallen leaves that decompose slowly, providing a gradual release of nutrients and improving soil structure over time. Compost mulch, made from fully decomposed organic matter, offers immediate nutrient availability and enhances microbial activity for rapid soil enrichment. Both mulches contribute to weed suppression and moisture retention but differ in nutrient release speed and effects on soil health.
Key Differences Between Leaf Litter and Compost Mulch
Leaf litter mulch consists of natural fallen leaves that provide a protective layer, improve soil aeration, and slowly decompose, enriching the soil with organic matter. Compost mulch, made from decomposed organic waste, offers a nutrient-rich amendment that accelerates soil fertility and enhances microbial activity. Key differences include leaf litter's slower nutrient release and physical insulation qualities versus compost mulch's immediate nutrient availability and improved soil structure.
Benefits of Mulching with Leaf Litter
Mulching with leaf litter enhances soil fertility by gradually decomposing and releasing essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, improving plant growth and health. It conserves soil moisture effectively, reduces erosion, and promotes beneficial microbial activity, enhancing overall soil structure and aeration. Leaf litter also suppresses weed growth naturally, minimizing the need for chemical herbicides and supporting sustainable gardening practices.
Advantages of Compost Mulch in Gardens
Compost mulch enriches garden soil by providing essential nutrients that promote healthy plant growth and improve soil structure. Unlike leaf litter, compost mulch helps retain moisture more effectively while suppressing weeds, reducing the need for frequent watering and herbicide use. Its ability to enhance microbial activity accelerates organic matter decomposition, fostering a fertile environment for roots and beneficial organisms.
Soil Health: Leaf Litter vs. Compost Mulch
Leaf litter mulch enhances soil health by providing a natural, slow-releasing source of organic matter that supports diverse microbial life and improves soil structure. Compost mulch delivers concentrated nutrients and beneficial microorganisms, accelerating nutrient cycling and boosting soil fertility. Both mulches contribute to moisture retention and erosion control, but leaf litter decomposes more gradually, promoting long-term soil ecosystem stability.
Nutrient Release: Which Mulch Feeds Plants Better?
Leaf litter mulch decomposes slowly, offering a gradual release of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which supports long-term soil fertility. Compost mulch breaks down more rapidly, providing an immediate and rich supply of essential nutrients that boost plant growth quickly. Choosing between leaf litter and compost mulch depends on whether plants need sustained feeding or a fast nutrient boost for optimal development.
Weed Suppression: Comparing Effectiveness
Leaf litter mulch provides moderate weed suppression by creating a natural barrier that limits sunlight to weed seeds, though its uneven texture may allow some weeds to emerge. Compost mulch offers superior weed control due to its denser, finer composition that smothers weeds more effectively and inhibits seed germination. Studies show compost mulch can reduce weed growth by up to 70%, outperforming leaf litter, which typically achieves around 40-50% suppression in garden environments.
Moisture Retention: Leaf Litter or Compost Mulch?
Leaf litter mulch excels in moisture retention by creating a natural, porous layer that reduces evaporation and allows water to penetrate the soil evenly. Compost mulch also retains moisture effectively due to its dense organic matter, which holds water and releases it gradually to plant roots. Choosing between leaf litter and compost mulch depends on the specific moisture needs of your garden plants and soil type.
Application Tips for Leaf Litter and Compost Mulch
Leaf litter mulch should be applied in a thin, even layer around plants to prevent matting and ensure proper water penetration, typically 2-3 inches thick. Compost mulch requires careful application to avoid nutrient runoff; spread 1-2 inches around the base of plants, keeping mulch a few inches away from stems to prevent rot. Both mulches benefit from periodic turning to enhance aeration and maintain soil health.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden
Leaf litter mulch enriches soil with natural nutrients as it decomposes, promoting microbial activity and improving soil structure. Compost mulch provides concentrated organic matter and essential nutrients, accelerating plant growth and enhancing moisture retention. Selecting the right mulch depends on garden needs: leaf litter is ideal for native plant beds, while compost mulch suits vegetable gardens requiring nutrient-rich soil.
Leaf litter vs compost mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com