
Composted mulch vs Fresh mulch Illustration
Composted mulch offers nutrient-rich organic matter that improves soil structure and promotes healthy plant growth, while fresh mulch primarily provides moisture retention and weed suppression. Unlike fresh mulch, composted mulch breaks down more slowly, releasing nutrients steadily and reducing the risk of nitrogen depletion in the soil. Choosing composted mulch enhances long-term soil fertility and supports sustainable gardening practices.
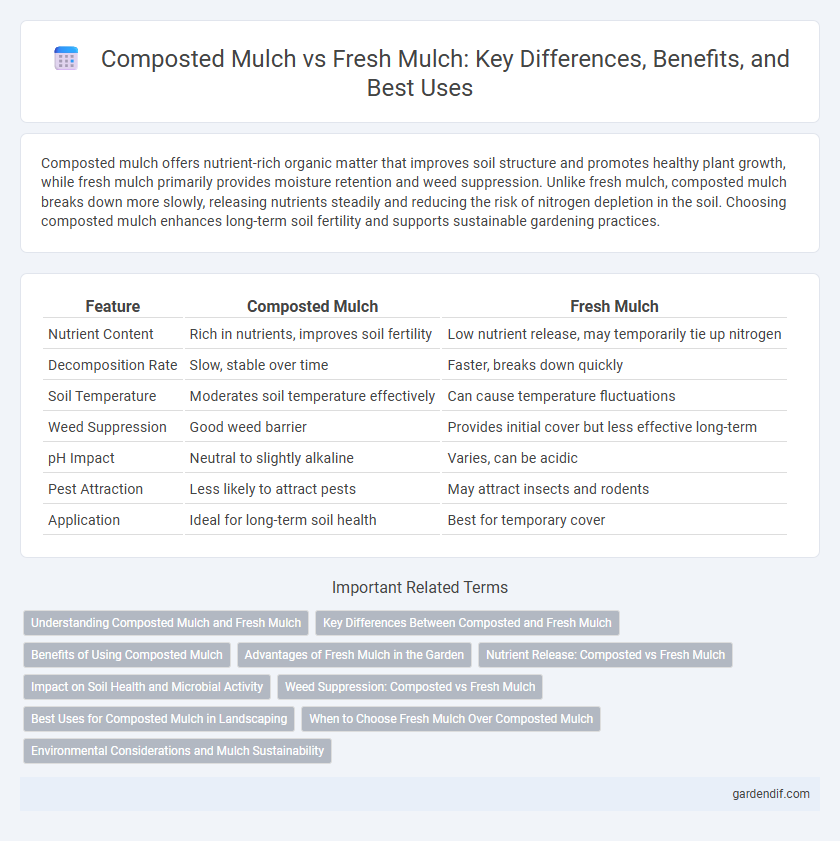
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Composted Mulch | Fresh Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Content | Rich in nutrients, improves soil fertility | Low nutrient release, may temporarily tie up nitrogen |
| Decomposition Rate | Slow, stable over time | Faster, breaks down quickly |
| Soil Temperature | Moderates soil temperature effectively | Can cause temperature fluctuations |
| Weed Suppression | Good weed barrier | Provides initial cover but less effective long-term |
| pH Impact | Neutral to slightly alkaline | Varies, can be acidic |
| Pest Attraction | Less likely to attract pests | May attract insects and rodents |
| Application | Ideal for long-term soil health | Best for temporary cover |
Understanding Composted Mulch and Fresh Mulch
Composted mulch is organic material that has undergone decomposition, resulting in a nutrient-rich, stable product that improves soil structure and fertility. Fresh mulch consists of raw plant materials like wood chips or leaves that provide immediate weed suppression and moisture retention but may temporarily tie up soil nitrogen during decomposition. Understanding the differences between composted and fresh mulch helps optimize garden health by balancing nutrient availability and maintaining soil moisture effectively.
Key Differences Between Composted and Fresh Mulch
Composted mulch is aged and broken down, providing improved nutrient content, better soil structure, and reduced risk of weed growth compared to fresh mulch. Fresh mulch retains more moisture initially but can deplete soil nitrogen as it decomposes, potentially hindering plant growth. The choice between composted and fresh mulch depends on garden goals, with composted mulch enhancing long-term soil health and fresh mulch offering immediate moisture retention.
Benefits of Using Composted Mulch
Composted mulch enhances soil structure by increasing microbial activity and nutrient availability, promoting healthier plant growth compared to fresh mulch. It reduces the risk of nitrogen depletion commonly caused by fresh mulch as it breaks down, ensuring a balanced nutrient supply for plants. This type of mulch also offers improved weed suppression and moisture retention, extending the benefits throughout the growing season.
Advantages of Fresh Mulch in the Garden
Fresh mulch offers superior moisture retention and temperature regulation for garden soil, promoting healthier plant roots and reducing weed growth effectively. Its rapid decomposition releases essential nutrients like nitrogen, enhancing soil fertility and stimulating microbial activity. Compared to composted mulch, fresh mulch provides a thicker protective layer that minimizes erosion and supports robust plant development.
Nutrient Release: Composted vs Fresh Mulch
Composted mulch releases nutrients gradually as it breaks down, providing a steady supply of essential minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium that enhance soil fertility over time. Fresh mulch, such as fresh wood chips or leaves, temporarily immobilizes nitrogen in the soil due to microbial activity, which can limit nutrient availability for plants initially. Choosing composted mulch supports long-term soil health, while fresh mulch may require supplemental fertilization to meet immediate nutrient demands.
Impact on Soil Health and Microbial Activity
Composted mulch enhances soil health by providing stabilized nutrients and promoting beneficial microbial activity that improves soil structure and nutrient cycling. Fresh mulch, while rich in organic material, can temporarily deplete soil nitrogen as microbes break down carbon-rich, undecomposed matter. Using composted mulch supports long-term soil fertility and active microbial populations, essential for sustainable plant growth.
Weed Suppression: Composted vs Fresh Mulch
Composted mulch offers superior weed suppression compared to fresh mulch due to its dense, decomposed structure that forms a thicker barrier against weed germination. Fresh mulch, while effective initially, tends to break down faster and may allow weed seeds to penetrate and sprout more easily. Studies show composted mulch reduces weed growth by up to 70%, enhancing soil health while minimizing maintenance.
Best Uses for Composted Mulch in Landscaping
Composted mulch enhances soil structure and nutrient content, making it ideal for flower beds, vegetable gardens, and around established shrubs where improved fertility is essential. Unlike fresh mulch, composted mulch breaks down slower, providing long-term moisture retention and weed suppression in landscaping applications. Its stabilized organic matter supports beneficial microbial activity, promoting healthier plant growth and reducing the need for frequent replenishment.
When to Choose Fresh Mulch Over Composted Mulch
Fresh mulch is ideal for insulating plants in colder months and suppressing weeds immediately after application due to its higher moisture retention and slower decomposition rate. Choose fresh mulch when rapid soil temperature regulation and quick ground coverage are priorities for garden beds or new plantings. Avoid fresh mulch close to stems or trunks to prevent potential fungal issues, favoring it instead in open areas where its protective benefits are maximized.
Environmental Considerations and Mulch Sustainability
Composted mulch enhances soil health by recycling organic waste, reducing landfill impact, and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions compared to fresh mulch, which may deplete soil nutrients and require more frequent replacement. Utilizing composted mulch supports sustainable landscaping by improving soil microbial activity and moisture retention, thereby reducing water consumption and the need for chemical fertilizers. Environmental considerations favor composted mulch for its role in carbon sequestration and lowering the overall ecological footprint of garden maintenance.
Composted mulch vs Fresh mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com