
Straw Mulch vs Grass Clipping Mulch Illustration
Straw mulch provides excellent insulation and moisture retention, making it ideal for garden beds and vegetable patches. Grass clipping mulch decomposes faster, enriching the soil with nitrogen but requires careful application to avoid matting and odor issues. Choosing between straw and grass clippings depends on the specific needs of your garden and soil health goals.
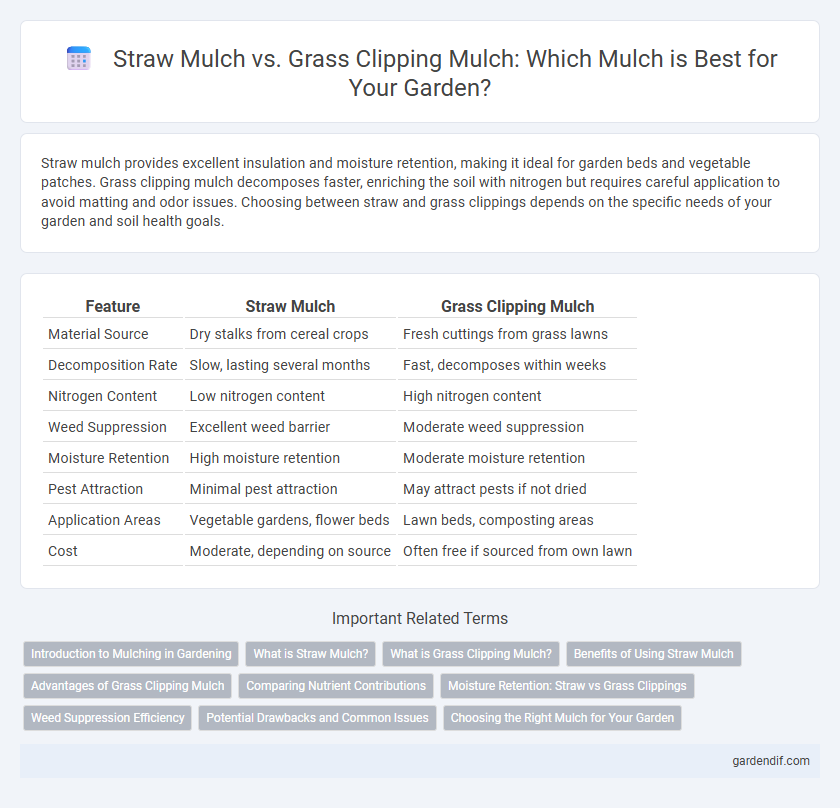
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Straw Mulch | Grass Clipping Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Dry stalks from cereal crops | Fresh cuttings from grass lawns |
| Decomposition Rate | Slow, lasting several months | Fast, decomposes within weeks |
| Nitrogen Content | Low nitrogen content | High nitrogen content |
| Weed Suppression | Excellent weed barrier | Moderate weed suppression |
| Moisture Retention | High moisture retention | Moderate moisture retention |
| Pest Attraction | Minimal pest attraction | May attract pests if not dried |
| Application Areas | Vegetable gardens, flower beds | Lawn beds, composting areas |
| Cost | Moderate, depending on source | Often free if sourced from own lawn |
Introduction to Mulching in Gardening
Mulching is a vital gardening practice that conserves soil moisture, regulates temperature, and suppresses weeds. Straw mulch, made from dried cereal crop stalks, offers excellent insulation and improves soil structure as it decomposes, while grass clipping mulch, derived from freshly cut lawns, provides high nitrogen content that accelerates organic matter breakdown and enriches soil fertility. Selecting the appropriate mulch type depends on garden needs, plant species, and desired soil nutrient balance for optimal plant growth.
What is Straw Mulch?
Straw mulch consists of dried stalks from cereal crops such as wheat, oats, or barley, providing excellent moisture retention and weed suppression in gardens. It is lightweight, easy to spread, and decomposes slowly, enriching the soil with organic matter over time. Straw mulch is particularly favored for vegetable beds and around fruit trees due to its ability to protect root zones and reduce soil temperature fluctuations.
What is Grass Clipping Mulch?
Grass clipping mulch consists of finely chopped grass blades collected from regular lawn mowing, serving as an organic ground cover that enriches soil fertility and moisture retention. Rich in nitrogen, grass clipping mulch decomposes rapidly, supplying essential nutrients that boost soil health and promote plant growth. It is an eco-friendly option that recycles yard waste while suppressing weeds and reducing soil erosion.
Benefits of Using Straw Mulch
Straw mulch improves soil moisture retention and reduces erosion, promoting healthier plant growth by maintaining consistent soil temperature. It also decomposes slowly, enriching the soil with organic matter and nutrients over time, which supports sustainable gardening practices. Its lightweight nature allows for easy application and prevents compaction compared to grass clippings, enhancing soil aeration.
Advantages of Grass Clipping Mulch
Grass clipping mulch offers superior nitrogen content compared to straw mulch, enriching soil fertility and promoting robust plant growth. Its quicker decomposition rate enhances microbial activity and accelerates nutrient cycling, benefiting garden ecosystems. Utilizing grass clippings reduces yard waste and provides an eco-friendly, cost-effective mulching option for gardeners.
Comparing Nutrient Contributions
Straw mulch provides a balanced release of nutrients, particularly rich in carbon, which improves soil structure and supports microbial activity over time. Grass clippings mulch offers a higher nitrogen content, promoting rapid nutrient availability that accelerates plant growth but may require careful management to prevent nitrogen overloading. Both mulches enhance soil fertility, yet straw is preferred for long-term soil health, while grass clippings are ideal for quick nutrient boosts.
Moisture Retention: Straw vs Grass Clippings
Straw mulch offers superior moisture retention due to its thick, loosely packed structure that reduces evaporation and insulates soil effectively. Grass clippings decompose faster and can form a dense mat, which sometimes limits water infiltration and air circulation. For long-term moisture management, straw mulch is generally preferred over grass clippings in gardening and landscaping.
Weed Suppression Efficiency
Straw mulch offers superior weed suppression due to its thicker, denser coverage that blocks sunlight more effectively, reducing weed germination. Grass clipping mulch breaks down faster, providing nutrients but allowing more light penetration, which can result in higher weed growth. For optimal weed control, straw mulch is preferred in long-term garden beds where persistent weed suppression is critical.
Potential Drawbacks and Common Issues
Straw mulch tends to decompose slowly, which can delay nutrient release and harbor pests like rodents or slugs, potentially damaging plants. Grass clipping mulch may compact quickly, restricting water and air flow to the soil, and can introduce weed seeds if not properly dried. Both types can cause nitrogen depletion in soil during decomposition if not managed with supplemental fertilization.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden
Straw mulch improves soil aeration and moisture retention, making it ideal for vegetable gardens prone to soil compaction. Grass clipping mulch decomposes rapidly, enriching soil with nitrogen but requires regular application to prevent matting and odor. Selecting mulch depends on garden type, desired nutrient input, and maintenance capacity.
Straw Mulch vs Grass Clipping Mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com