
Mixed Border vs Monoculture Bed Illustration
A mixed border enhances garden biodiversity by combining various plant species, creating a dynamic and visually appealing landscape that supports pollinators and reduces pest outbreaks. In contrast, a monoculture bed focuses on a single plant variety, simplifying maintenance but often increasing vulnerability to diseases and pests. Choosing a mixed border promotes ecological balance and year-round interest, while monoculture beds suit minimalist designs requiring uniformity and easier upkeep.
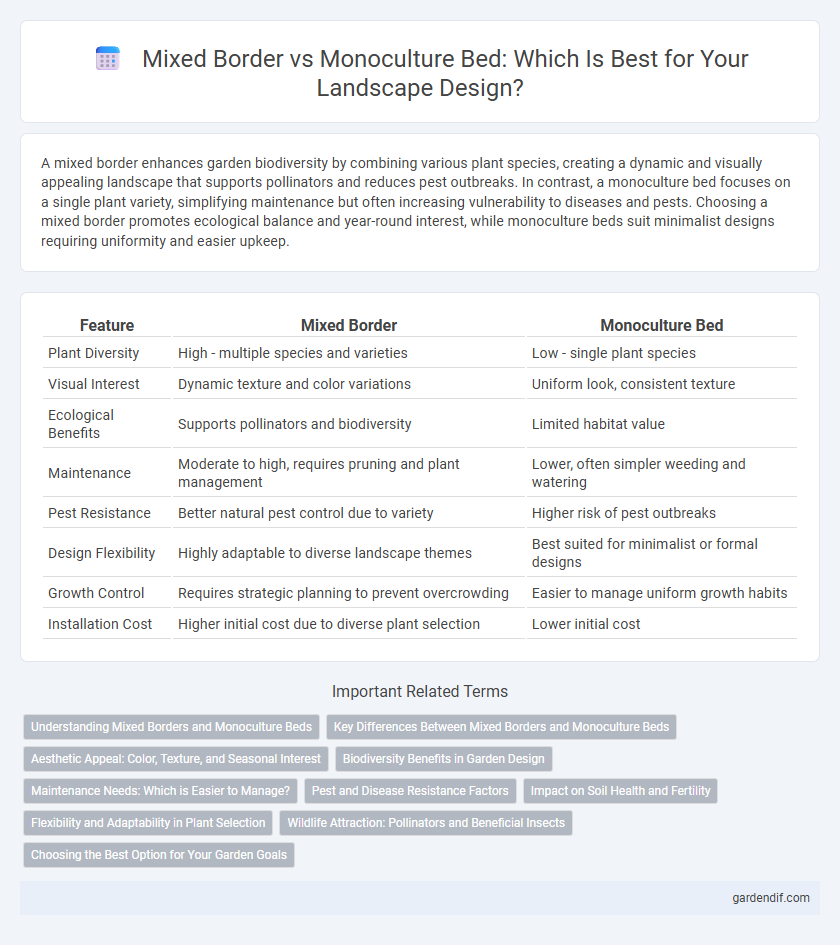
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mixed Border | Monoculture Bed |
|---|---|---|
| Plant Diversity | High - multiple species and varieties | Low - single plant species |
| Visual Interest | Dynamic texture and color variations | Uniform look, consistent texture |
| Ecological Benefits | Supports pollinators and biodiversity | Limited habitat value |
| Maintenance | Moderate to high, requires pruning and plant management | Lower, often simpler weeding and watering |
| Pest Resistance | Better natural pest control due to variety | Higher risk of pest outbreaks |
| Design Flexibility | Highly adaptable to diverse landscape themes | Best suited for minimalist or formal designs |
| Growth Control | Requires strategic planning to prevent overcrowding | Easier to manage uniform growth habits |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost due to diverse plant selection | Lower initial cost |
Understanding Mixed Borders and Monoculture Beds
Mixed borders combine diverse plant species to enhance biodiversity, improve pest resistance, and create visually dynamic landscapes with varying textures and colors. Monoculture beds consist of a single plant type, simplifying maintenance and ensuring uniform bloom timing but increasing vulnerability to pests and diseases. Understanding these differences helps landscapers choose between ecological benefits and easier management based on design goals.
Key Differences Between Mixed Borders and Monoculture Beds
Mixed borders feature diverse plant species arranged to provide continuous seasonal interest and enhanced biodiversity, while monoculture beds consist of a single plant type emphasizing uniformity and ease of maintenance. Mixed borders improve pest resistance and soil health through plant variety, whereas monoculture beds may be more susceptible to disease and require more intensive care. Garden design goals and maintenance preferences often determine the choice between these planting strategies.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color, Texture, and Seasonal Interest
Mixed borders enhance landscape aesthetics by combining diverse plant species that offer varied colors, textures, and seasonal interest, creating dynamic and visually engaging garden spaces. Monoculture beds, while uniform and simple in appearance, tend to provide limited textural contrast and less seasonal variation, often resulting in a static and less captivating visual effect. Incorporating a mix of perennials, shrubs, and annuals in borders boosts the overall appeal through a richer palette and evolving scenery across different seasons.
Biodiversity Benefits in Garden Design
Mixed borders in garden design enhance biodiversity by incorporating a variety of plant species that attract diverse pollinators, beneficial insects, and wildlife, creating a balanced ecosystem. In contrast, monoculture beds limit habitat variety and reduce resilience against pests and diseases due to the uniform plant selection. Emphasizing mixed borders supports ecological health and promotes sustainable garden ecosystems through increased species interactions and nutrient cycling.
Maintenance Needs: Which is Easier to Manage?
Mixed borders require diverse plant care routines due to varying water, pruning, and pest control needs, making maintenance more complex but promoting ecosystem health. Monoculture beds simplify management with uniform care practices, reducing time and resources needed for upkeep but increasing vulnerability to pests and diseases. Gardeners seeking lower maintenance often prefer monoculture beds, while those valuing biodiversity and resilience choose mixed borders despite higher effort.
Pest and Disease Resistance Factors
Mixed borders promote pest and disease resistance by increasing plant diversity, which disrupts pest habitats and reduces the spread of pathogens. Monoculture beds, with uniform plant species, are more vulnerable to pests and diseases due to the lack of natural barriers and genetic variation. Incorporating a variety of species in mixed borders enhances ecological balance and resilience against infestations.
Impact on Soil Health and Fertility
Mixed borders enhance soil health and fertility by promoting biodiversity, which improves nutrient cycling and microbial activity compared to monoculture beds. Diverse root systems in mixed borders reduce soil erosion and increase organic matter, fostering a more resilient soil structure. Monoculture beds often deplete specific nutrients quickly and reduce microbial diversity, leading to poorer soil quality and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Plant Selection
Mixed borders offer superior flexibility and adaptability in plant selection by combining diverse species with varying growth habits, bloom times, and environmental preferences. This diversity enhances resilience against pests, diseases, and changing climate conditions, allowing for dynamic seasonal interest and continuous garden evolution. In contrast, monoculture beds restrict adaptability due to uniform plant selection, making them more vulnerable to environmental stresses and limiting creative planting options.
Wildlife Attraction: Pollinators and Beneficial Insects
Mixed borders with diverse plant species create a rich habitat that attracts a variety of pollinators and beneficial insects, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health. In contrast, monoculture beds often lack the floral diversity needed to support a wide range of wildlife, limiting pollinator activity and beneficial insect populations. Incorporating native wildflowers, grasses, and shrubs in mixed borders promotes natural pest control and improves pollination efficiency in the landscape.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Garden Goals
Mixed borders offer diverse plant species that enhance visual interest and support biodiversity, making them ideal for gardens emphasizing ecological balance and year-round appeal. Monoculture beds concentrate on a single plant type, simplifying maintenance and fostering uniform growth, perfect for showcasing specific colors or textures. Selecting between mixed borders and monoculture beds depends on whether garden goals prioritize ecological variety or streamlined design.
Mixed Border vs Monoculture Bed Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com