
Hedge Maze vs Knot Garden Illustration
A hedge maze offers a labyrinthine experience with tall, dense hedges that challenge navigation and provide a sense of mystery and adventure. In contrast, a knot garden showcases intricate, geometric patterns formed by low, neatly clipped hedges, emphasizing symmetry and ornamental design. Both styles enhance garden aesthetics but serve different purposes: exploration versus structured beauty.
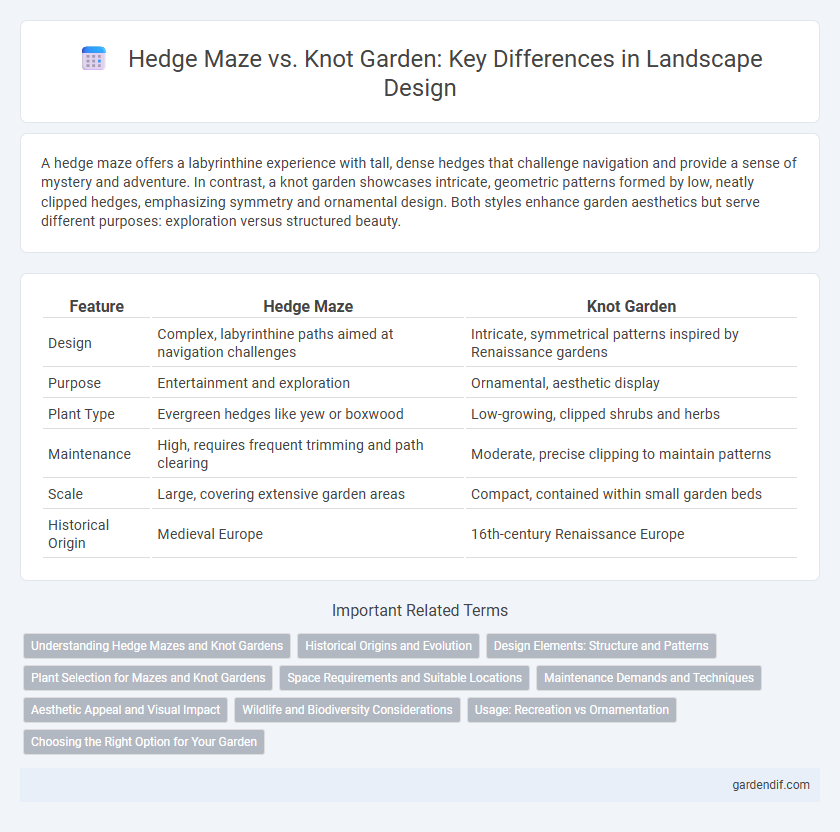
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hedge Maze | Knot Garden |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Complex, labyrinthine paths aimed at navigation challenges | Intricate, symmetrical patterns inspired by Renaissance gardens |
| Purpose | Entertainment and exploration | Ornamental, aesthetic display |
| Plant Type | Evergreen hedges like yew or boxwood | Low-growing, clipped shrubs and herbs |
| Maintenance | High, requires frequent trimming and path clearing | Moderate, precise clipping to maintain patterns |
| Scale | Large, covering extensive garden areas | Compact, contained within small garden beds |
| Historical Origin | Medieval Europe | 16th-century Renaissance Europe |
Understanding Hedge Mazes and Knot Gardens
Hedge mazes are intricate, puzzle-like garden features designed with tall, dense hedges forming winding paths that challenge navigation and offer recreational exploration. Knot gardens consist of meticulously trimmed low hedges arranged in geometric, interlaced patterns resembling intricate knots, emphasizing ornamental design and symmetry rather than maze complexity. Understanding the distinct structure and purpose of hedge mazes versus knot gardens highlights their unique roles in landscape design, where mazes provide adventure and knot gardens enhance visual elegance.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Hedge mazes originated in 16th-century Europe as intricate, labyrinthine garden features symbolizing complexity and mystery, often designed for aristocratic estates. Knot gardens emerged during the Renaissance period, inspired by Tudor horticulture, featuring geometric patterns of clipped hedges that resemble interlacing ribbons or knots. Over time, hedge mazes evolved into elaborate puzzles promoting exploration, while knot gardens maintained their ornamental, formal layout emphasizing symmetry and visual harmony.
Design Elements: Structure and Patterns
Hedge mazes feature intricate, winding paths designed to confuse and challenge navigation, with dense, tall hedges creating a labyrinthine structure. In contrast, knot gardens emphasize geometric precision through low, meticulously clipped hedges arranged in symmetrical, interlaced patterns resembling woven knots. The hedge maze prioritizes complexity and exploration, while the knot garden focuses on ornamental order and visual harmony in landscape design.
Plant Selection for Mazes and Knot Gardens
Hedge mazes typically utilize dense, evergreen shrubs like boxwood (Buxus sempervirens) and yew (Taxus baccata) that maintain year-round structure and allow precise trimming. Knot gardens favor herbs and low-growing plants such as thyme, lavender, and rosemary, chosen for their aromatic qualities and softer textures that emphasize intricate patterns. Both plant selections prioritize growth habits that support maintenance and aesthetic design principles unique to mazes and knot gardens.
Space Requirements and Suitable Locations
Hedge mazes require extensive space due to their intricate pathways and expansive layout, making them ideal for large estates or public parks with ample room for navigation and exploration. Knot gardens demand less space, as their compact, geometric designs fit well into smaller courtyards or formal garden settings where precise patterning enhances visual appeal. Selecting between the two depends on available land size and the desired function, with hedge mazes suited for immersive, large-scale experiences and knot gardens optimal for structured, decorative environments.
Maintenance Demands and Techniques
Hedge mazes require regular pruning and shaping of dense, fast-growing shrubs like yew or boxwood to maintain defined paths and intricate patterns, often demanding skilled gardeners and consistent attention. Knot gardens involve low hedges planted in symmetric geometric designs, relying on precise clipping techniques to preserve their formal appearance but generally requiring less frequent pruning compared to maze hedges. Both landscape features benefit from seasonal maintenance, but hedge mazes typically demand higher labor intensity due to their complexity and growth density.
Aesthetic Appeal and Visual Impact
Hedge mazes create a dynamic aesthetic appeal through intricate pathways that invite exploration and mystery, offering a sense of depth and complexity in garden design. Knot gardens emphasize geometric precision and symmetry, showcasing intricate patterns formed by tightly clipped low hedges, which provide a highly structured and visually striking centerpiece. Both styles enhance landscape appeal, but hedge mazes engage visitors with immersive experience while knot gardens deliver formal elegance and meticulous craftsmanship.
Wildlife and Biodiversity Considerations
Hedge mazes, with their dense evergreen walls, provide shelter and nesting habitats for birds, small mammals, and insects, promoting higher biodiversity compared to the more geometric and open layouts of knot gardens. Knot gardens, typically featuring low, clipped hedges and herbaceous plants, support pollinators like bees and butterflies through flowering species but offer less structural habitat complexity. Selecting hedge maze designs with native, thorny shrubs can enhance wildlife corridors and ecological benefits in landscaped environments.
Usage: Recreation vs Ornamentation
Hedge mazes serve primarily as recreational features designed for exploration and entertainment, often found in large gardens and parks where visitors navigate winding paths. Knot gardens emphasize ornamentation, showcasing intricate, symmetrical patterns made from low hedges to enhance aesthetic appeal and classical garden design. The functional difference lies in hedge mazes providing an interactive experience, while knot gardens act as static, decorative elements in landscape architecture.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Garden
Selecting between a hedge maze and a knot garden depends on spatial constraints and design objectives, where hedge mazes offer dynamic navigation and puzzle-like intrigue, while knot gardens emphasize intricate, formal patterns and symmetry. Hedge mazes require ample space and dense, tall hedging species like hornbeam or yew to create winding pathways, contrasting with knot gardens that utilize low-growing, tightly clipped boxwood or lavender to define geometric shapes. Consider maintenance commitments and the desired visitor experience, as hedge mazes engage through exploration and mystery, whereas knot gardens provide visually striking, restful landscapes perfect for contemplation and traditional aesthetics.
Hedge Maze vs Knot Garden Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com