
Oxygenation vs Circulation Illustration
Oxygenation in hydroponic systems is essential for promoting healthy root development by ensuring adequate oxygen supply to plant roots. Circulation helps distribute water and nutrients evenly throughout the system, preventing stagnation and maintaining consistent nutrient availability. Efficient hydroponic setups balance both oxygenation and circulation to optimize plant growth and prevent root diseases.
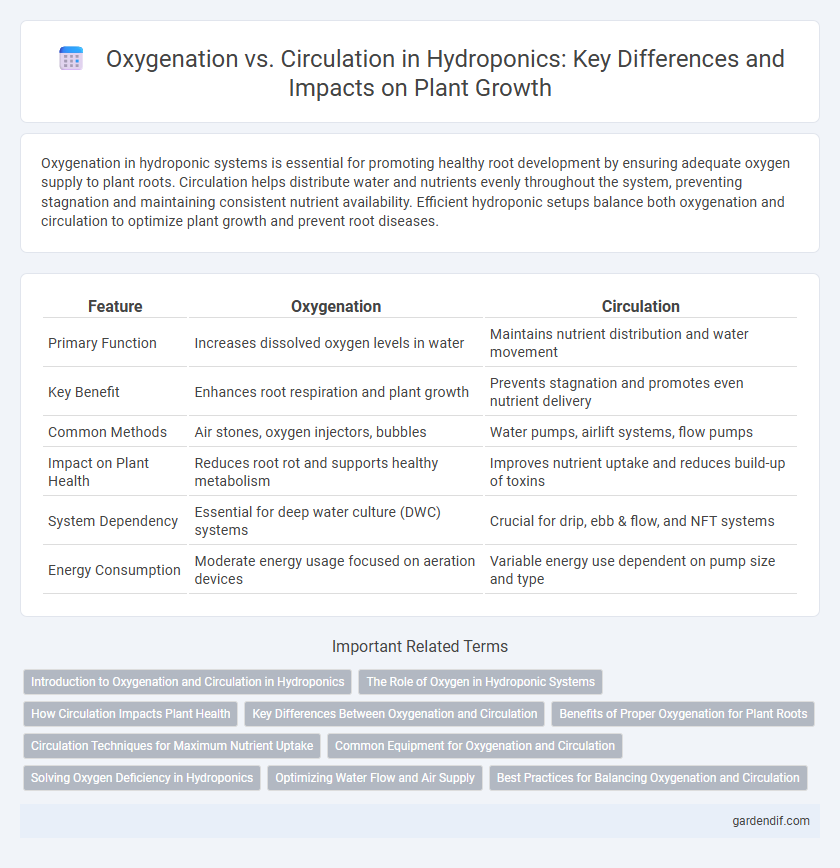
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oxygenation | Circulation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Increases dissolved oxygen levels in water | Maintains nutrient distribution and water movement |
| Key Benefit | Enhances root respiration and plant growth | Prevents stagnation and promotes even nutrient delivery |
| Common Methods | Air stones, oxygen injectors, bubbles | Water pumps, airlift systems, flow pumps |
| Impact on Plant Health | Reduces root rot and supports healthy metabolism | Improves nutrient uptake and reduces build-up of toxins |
| System Dependency | Essential for deep water culture (DWC) systems | Crucial for drip, ebb & flow, and NFT systems |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate energy usage focused on aeration devices | Variable energy use dependent on pump size and type |
Introduction to Oxygenation and Circulation in Hydroponics
Oxygenation in hydroponics involves the infusion of oxygen into the nutrient solution, enhancing root respiration and nutrient uptake essential for plant growth. Circulation refers to the continuous movement of the nutrient solution, which distributes oxygen, nutrients, and removes waste products from the root zone. Effective management of both oxygenation and circulation optimizes root health, nutrient absorption, and overall hydroponic system efficiency.
The Role of Oxygen in Hydroponic Systems
Oxygenation in hydroponic systems is crucial for root respiration, enabling nutrient uptake and promoting healthy plant growth. Effective oxygen supply prevents root rot by maintaining aerobic conditions in the nutrient solution, while poor oxygen circulation can lead to hypoxia and plant stress. Maintaining optimal dissolved oxygen levels, typically between 5-8 mg/L, enhances nutrient absorption and overall system efficiency.
How Circulation Impacts Plant Health
Efficient water circulation in hydroponic systems ensures even distribution of nutrients and oxygen, preventing stagnation that can lead to root rot and nutrient deficiencies. Improved circulation enhances root respiration and supports beneficial microbial activity, which collectively boost plant growth and health. Consistent movement of the nutrient solution also helps maintain optimal pH and temperature levels, crucial for maximizing plant vitality.
Key Differences Between Oxygenation and Circulation
Oxygenation in hydroponics involves increasing the dissolved oxygen levels in the nutrient solution to promote root health and nutrient uptake, while circulation ensures uniform distribution of nutrients and prevents stagnation in the system. Key differences highlight that oxygenation targets gas exchange efficiency using air stones or oxygen pumps, whereas circulation relies on water pumps to maintain flow and consistent nutrient delivery. Both processes are essential for optimal plant growth, but oxygenation primarily enhances root respiration and microbial activity, while circulation maintains solution homogeneity and prevents root suffocation.
Benefits of Proper Oxygenation for Plant Roots
Proper oxygenation in hydroponic systems enhances root respiration, leading to increased nutrient uptake and faster growth rates. Efficient oxygen delivery prevents root diseases such as root rot by inhibiting anaerobic conditions. High dissolved oxygen levels promote healthy root development, resulting in stronger, more resilient plants and higher overall yields.
Circulation Techniques for Maximum Nutrient Uptake
Effective circulation techniques in hydroponic systems, such as using submersible pumps, air stones, or water wicks, ensure optimal nutrient distribution and prevent stagnation. Maintaining continuous water movement enhances root exposure to oxygen and nutrients, boosting overall plant growth and health. Techniques like drip circulation and nutrient film technique (NFT) maximize nutrient uptake by creating a consistent flow of nutrient-rich water across the root zone.
Common Equipment for Oxygenation and Circulation
Hydroponic systems rely on specific equipment to ensure optimal oxygenation and circulation for plant health. Air pumps and air stones are common oxygenation tools that increase dissolved oxygen levels in nutrient solutions, promoting root respiration and preventing stagnation. Water pumps and recirculating systems maintain nutrient solution circulation, distributing oxygen and nutrients evenly to roots while preventing anaerobic conditions.
Solving Oxygen Deficiency in Hydroponics
Effective oxygenation in hydroponics involves introducing dissolved oxygen directly into the nutrient solution to combat oxygen deficiency, which is critical for root respiration and nutrient uptake. Circulation supports oxygenation by continuously moving the solution, preventing stagnation, and ensuring uniform oxygen distribution around the root zone. Combining targeted oxygenation methods like air stones or oxygen injectors with consistent circulation optimizes root health and plant growth in hydroponic systems.
Optimizing Water Flow and Air Supply
Optimizing water flow and air supply in hydroponic systems enhances root oxygenation and nutrient uptake, crucial for plant health and growth. Effective oxygenation involves introducing sufficient dissolved oxygen through air stones or oxygen diffusers, while circulation ensures uniform distribution of nutrients and prevents stagnation. Balancing oxygenation and circulation maximizes root zone oxygen levels and maintains consistent nutrient availability, promoting robust and high-yield hydroponic crops.
Best Practices for Balancing Oxygenation and Circulation
Balancing oxygenation and circulation in hydroponic systems requires maintaining dissolved oxygen levels above 6 mg/L while ensuring consistent nutrient flow to prevent root zone stagnation. Utilizing air stones or diffusers enhances oxygen diffusion, whereas adjustable pumps optimize water movement without creating high shear stress on delicate roots. Regular monitoring of oxygen concentration and flow rates maximizes plant health and nutrient uptake efficiency.
Oxygenation vs Circulation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com