
Hydroponic Tomatoes vs Soil-Grown Tomatoes Illustration
Hydroponic tomatoes thrive in nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing precise control over growth conditions, which results in faster maturation and higher yields compared to soil-grown tomatoes. Soil-grown tomatoes benefit from natural microbial interactions enhancing flavor complexity, though they are more susceptible to pests and environmental variability. Choosing between hydroponic and soil-grown tomatoes depends on prioritizing consistent production and resource efficiency or traditional taste and ecosystem integration.
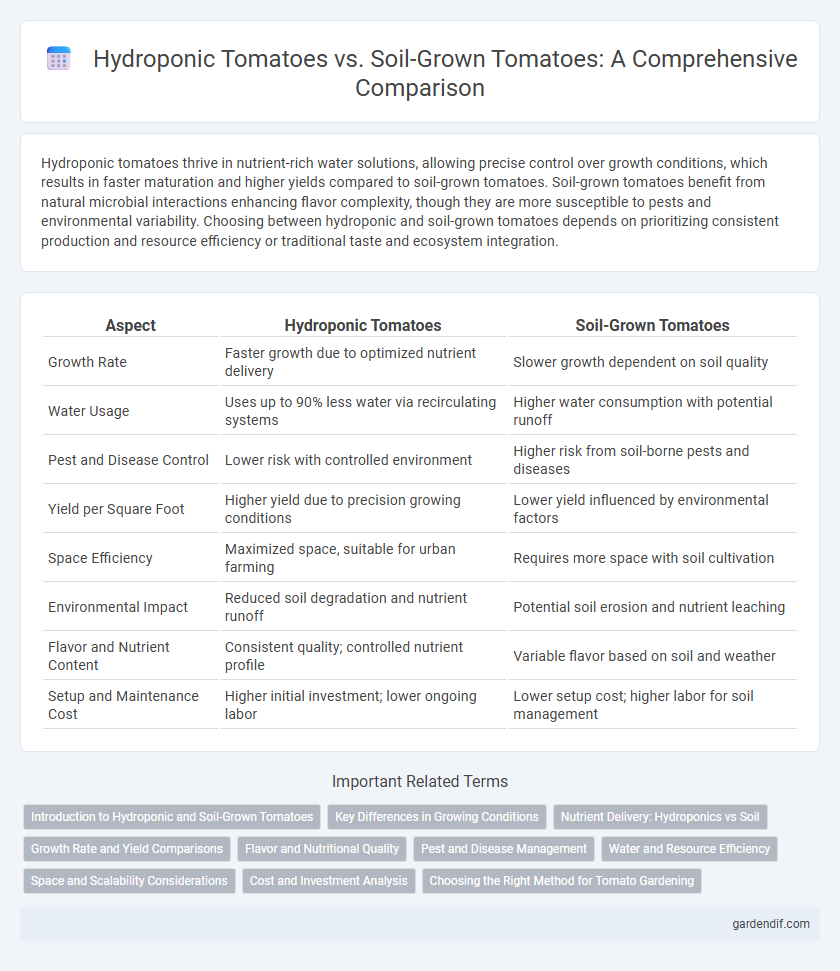
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydroponic Tomatoes | Soil-Grown Tomatoes |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster growth due to optimized nutrient delivery | Slower growth dependent on soil quality |
| Water Usage | Uses up to 90% less water via recirculating systems | Higher water consumption with potential runoff |
| Pest and Disease Control | Lower risk with controlled environment | Higher risk from soil-borne pests and diseases |
| Yield per Square Foot | Higher yield due to precision growing conditions | Lower yield influenced by environmental factors |
| Space Efficiency | Maximized space, suitable for urban farming | Requires more space with soil cultivation |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced soil degradation and nutrient runoff | Potential soil erosion and nutrient leaching |
| Flavor and Nutrient Content | Consistent quality; controlled nutrient profile | Variable flavor based on soil and weather |
| Setup and Maintenance Cost | Higher initial investment; lower ongoing labor | Lower setup cost; higher labor for soil management |
Introduction to Hydroponic and Soil-Grown Tomatoes
Hydroponic tomatoes are cultivated using nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, enabling precise control over growth conditions and faster production cycles. Soil-grown tomatoes rely on natural soil ecosystems, which influence flavor profiles and nutrient uptake but are more susceptible to pests and variable weather. Comparing both methods highlights differences in yield efficiency, resource use, and environmental impact.
Key Differences in Growing Conditions
Hydroponic tomatoes are cultivated in nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing precise control over pH levels, temperature, and nutrient delivery, which promotes faster growth and higher yields compared to soil-grown tomatoes. Soil-grown tomatoes rely on natural soil composition, moisture retention, and microbial activity, making them more susceptible to pests, diseases, and variable environmental conditions. Hydroponic systems also reduce water usage by up to 90% and eliminate soil-borne pathogens, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional tomato farming.
Nutrient Delivery: Hydroponics vs Soil
Hydroponic tomatoes receive nutrients through a precisely controlled water-based solution, allowing for optimal absorption and faster growth compared to traditional soil methods. Soil-grown tomatoes rely on natural mineral content and microbial activity, which can vary widely and affect nutrient availability. This targeted nutrient delivery in hydroponics results in higher yields and more consistent fruit quality.
Growth Rate and Yield Comparisons
Hydroponic tomatoes typically exhibit faster growth rates and higher yields compared to soil-grown tomatoes due to optimized nutrient delivery and controlled environmental conditions. Studies indicate hydroponic systems can increase tomato yield by up to 30-50% while reducing growth cycle duration significantly. Enhanced root oxygenation and precise water management in hydroponics contribute to increased fruit size and overall plant productivity.
Flavor and Nutritional Quality
Hydroponic tomatoes often exhibit a purer, more consistent flavor profile due to controlled nutrient delivery and optimized growing conditions, minimizing environmental stress factors common in soil-grown tomatoes. Nutritional analysis reveals hydroponic tomatoes can have equal or higher levels of key vitamins such as vitamin C and antioxidants like lycopene, attributed to precise nutrient management and reduced exposure to soil-borne pathogens. However, soil-grown tomatoes sometimes offer greater flavor complexity influenced by diverse soil microbiomes that contribute to unique taste attributes.
Pest and Disease Management
Hydroponic tomatoes benefit from a controlled environment that significantly reduces exposure to soil-borne pests and diseases, leading to lower incidences of root rot and nematode infestations compared to soil-grown tomatoes. Precise nutrient delivery and sterile growth media in hydroponic systems limit fungal and bacterial outbreaks, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides. In contrast, soil-grown tomatoes often require integrated pest management strategies due to diverse pathogen presence and fluctuating soil conditions.
Water and Resource Efficiency
Hydroponic tomatoes require up to 90% less water than soil-grown tomatoes by recirculating nutrient solutions in a closed system, minimizing water waste. Soil-grown tomatoes often suffer from inconsistent water distribution and higher evaporation rates, leading to inefficient resource use. Hydroponic systems optimize nutrient absorption and reduce the need for pesticides, enhancing overall resource efficiency and sustainability in tomato cultivation.
Space and Scalability Considerations
Hydroponic tomatoes require significantly less space compared to soil-grown tomatoes, enabling vertical farming and higher plant density per square meter. This space efficiency supports scalable production systems, allowing growers to increase yield without expanding land use. Controlled environment agriculture in hydroponics further enhances scalability by optimizing growth conditions and reducing resource inputs.
Cost and Investment Analysis
Hydroponic tomatoes require a higher initial investment in infrastructure such as nutrient delivery systems and controlled environments, but they offer faster growth cycles and higher yields per square foot compared to soil-grown tomatoes. Operational costs for hydroponics can be lower long-term due to reduced water usage and pesticide needs, yet electricity and system maintenance increase ongoing expenses. Soil-grown tomatoes typically have lower startup costs but face variability in yield and greater risks from pests and climate factors, impacting overall profitability.
Choosing the Right Method for Tomato Gardening
Hydroponic tomatoes offer faster growth rates and higher yields compared to soil-grown tomatoes due to controlled nutrient delivery and reduced pest exposure. Soil-grown tomatoes benefit from natural soil microbes which enhance flavor complexity and resilience against certain diseases. Selecting the right method depends on available resources, space constraints, desired tomato quality, and environmental factors influencing growth conditions.
Hydroponic Tomatoes vs Soil-Grown Tomatoes Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com