
Inline Air Pump vs Submersible Pump Illustration
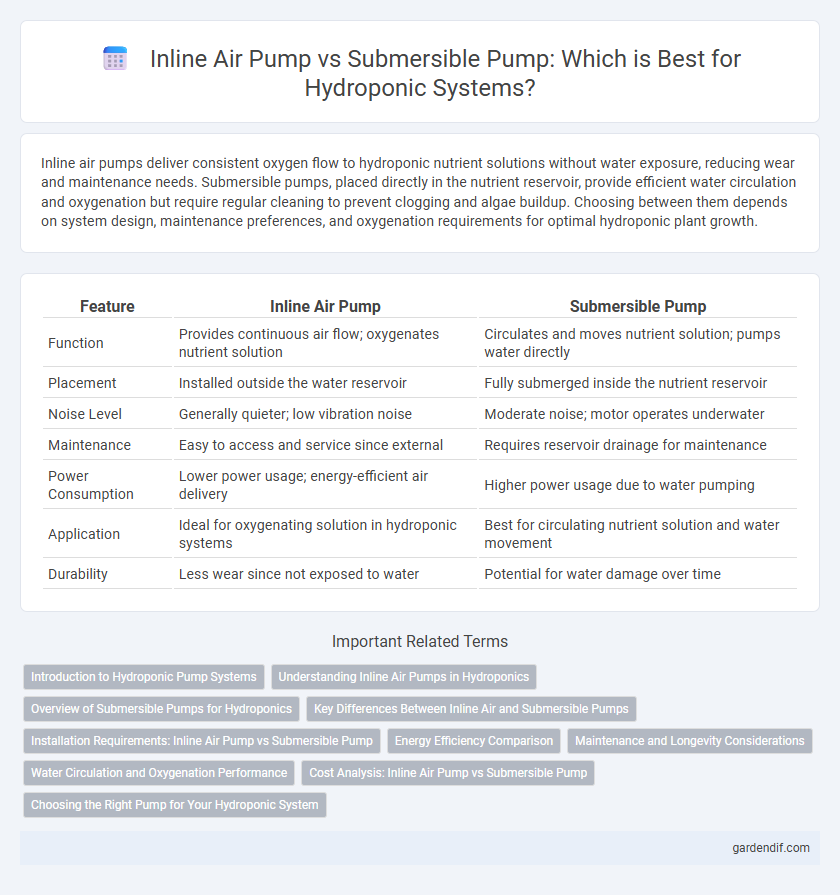
Inline air pumps deliver consistent oxygen flow to hydroponic nutrient solutions without water exposure, reducing wear and maintenance needs. Submersible pumps, placed directly in the nutrient reservoir, provide efficient water circulation and oxygenation but require regular cleaning to prevent clogging and algae buildup. Choosing between them depends on system design, maintenance preferences, and oxygenation requirements for optimal hydroponic plant growth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inline Air Pump | Submersible Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides continuous air flow; oxygenates nutrient solution | Circulates and moves nutrient solution; pumps water directly |
| Placement | Installed outside the water reservoir | Fully submerged inside the nutrient reservoir |
| Noise Level | Generally quieter; low vibration noise | Moderate noise; motor operates underwater |
| Maintenance | Easy to access and service since external | Requires reservoir drainage for maintenance |
| Power Consumption | Lower power usage; energy-efficient air delivery | Higher power usage due to water pumping |
| Application | Ideal for oxygenating solution in hydroponic systems | Best for circulating nutrient solution and water movement |
| Durability | Less wear since not exposed to water | Potential for water damage over time |
Introduction to Hydroponic Pump Systems
Hydroponic pump systems play a crucial role in delivering nutrient-rich water to plant roots in soil-less cultivation. Inline air pumps, positioned outside the reservoir, provide continuous oxygenation by pushing air through tubing directly into the system, enhancing root respiration without water contact. Submersible pumps, submerged within the nutrient solution, efficiently circulate water and nutrients, promoting uniform distribution and reducing the risk of anaerobic conditions in hydroponic setups.
Understanding Inline Air Pumps in Hydroponics
Inline air pumps in hydroponics provide continuous and reliable oxygenation by delivering air directly into the nutrient solution through tubing, enhancing root respiration and nutrient uptake. These pumps are typically compact, energy-efficient, and positioned outside the water reservoir, reducing water contamination risks and simplifying maintenance. Compared to submersible pumps, inline air pumps offer quieter operation and greater control over airflow rates, making them ideal for precise oxygen delivery in hydroponic systems.
Overview of Submersible Pumps for Hydroponics
Submersible pumps for hydroponics are designed to be fully immersed in nutrient solutions, providing efficient water circulation and oxygenation directly within the reservoir. These pumps typically feature durable, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or high-grade plastics to withstand constant exposure to moisture and nutrients. Their quiet operation, compact size, and ability to handle continuous use make submersible pumps ideal for maintaining optimal plant growth environments in hydroponic systems.
Key Differences Between Inline Air and Submersible Pumps
Inline air pumps deliver oxygen directly into hydroponic nutrient solutions through external tubing, promoting root respiration without water immersion. Submersible pumps operate submerged within the nutrient reservoir, circulating water and nutrients efficiently while also providing aeration. Key differences include placement, with inline pumps external and submersible pumps internal, and their primary functions, where inline pumps focus on oxygenation and submersible pumps on water movement.
Installation Requirements: Inline Air Pump vs Submersible Pump
Inline air pumps require external placement, ensuring proper ventilation and easy access for maintenance, whereas submersible pumps must be fully submerged in water, demanding waterproof connections and careful positioning within the hydroponic reservoir. Inline pumps typically involve simpler installation with fewer risks of water damage but may require longer tubing to reach the target area. Submersible pumps offer compact, submerged operation but necessitate watertight seals and secure mounting to prevent movement and ensure consistent water flow.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Inline air pumps generally consume less energy compared to submersible pumps due to their external placement and streamlined motor design, which reduces heat dissipation and mechanical resistance. Submersible pumps often require more power to overcome water pressure and maintain continuous operation within the reservoir. Energy-efficient hydroponic setups favor inline air pumps for sustained aeration with lower electricity costs, improving overall system sustainability.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Inline air pumps generally require less frequent maintenance due to their external placement, reducing exposure to water and potential debris. Submersible pumps often need regular cleaning to prevent clogging from nutrient buildup and algae growth, impacting their operational lifespan. Choosing an inline air pump can enhance longevity by minimizing wear from water exposure, while submersible pumps benefit from careful water quality management to extend service life.
Water Circulation and Oxygenation Performance
Inline air pumps excel in consistent water circulation by delivering steady airflow without submersion, enhancing root oxygenation in hydroponic systems. Submersible pumps provide robust water movement directly within the nutrient solution, promoting efficient oxygen distribution but may produce more heat affecting plant roots. Optimal hydroponic oxygenation depends on balancing the pulsation of inline air pumps with the powerful flow of submersible pumps to maintain nutrient-rich, well-aerated water.
Cost Analysis: Inline Air Pump vs Submersible Pump
Inline air pumps generally incur higher upfront costs compared to submersible pumps due to more complex design and additional external components required for installation. Submersible pumps offer a cost-effective solution with lower initial investment and reduced maintenance expenses, as their compact, integrated design minimizes wear and energy consumption. Evaluating lifecycle costs and energy efficiency is crucial for budget-conscious hydroponic growers aiming to optimize long-term operational expenses.
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Hydroponic System
Selecting the right pump for your hydroponic system depends on factors like system size, water flow requirements, and noise tolerance. Inline air pumps provide consistent air pressure and are ideal for larger setups needing steady oxygen flow, while submersible pumps offer efficient water circulation directly within the nutrient reservoir. Evaluating pump capacity, energy efficiency, and maintenance needs ensures optimal plant growth and system performance.
Inline Air Pump vs Submersible Pump Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com